在过去的几年里,深度学习网络获得了巨大的普及。注意力机制 "与深度学习网络整合,以提高其性能。在网络中添加注意力组件,在机器翻译、图像识别、文本总结和类似应用等任务中显示出明显的改善。
本教程展示了如何向使用递归神经网络构建的网络添加一个自定义的注意力层。我们将使用一个非常简单的数据集来说明时间序列预测的端到端应用。本教程是为那些希望对如何向深度学习网络添加用户定义层有基本了解的人设计的,并使用这个简单的例子来构建更复杂的应用。
完成本教程后,你将知道。
- 在Keras中创建一个自定义注意力层需要哪些方法
- 如何在用SimpleRNN构建的网络中加入新层
让我们开始吧。
教程概述
本教程分为三个部分,它们是:。
- 准备一个用于时间序列预测的简单数据集
- 如何使用通过SimpleRNN构建的网络进行时间序列预测
- 在SimpleRNN网络中添加一个自定义的注意力层
前提条件
假设你已经熟悉了以下主题。你可以点击下面的链接来了解一下。
数据集
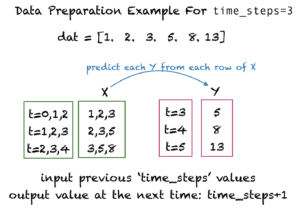
本文的重点是对如何为深度学习网络建立一个自定义的注意力层有一个基本的了解。为此,我们将使用一个非常简单的斐波那契数列的例子,其中一个数字是由之前的两个数字构建的。该序列的前10个数字如下所示。
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, ...
当给定前面的't'个数字时,我们能否让机器准确地重建下一个数字?这将意味着摒弃所有之前的输入,除了最后两个,并对最后两个数字进行正确的操作。
在本教程中,我们将从t 时间步骤中构建训练实例,并将t+1 的值作为目标。例如,如果t=3 ,那么训练实例和相应的目标值将如下所示。
SimpleRNN网络
在本节中,我们将编写基本代码来生成数据集并使用SimpleRNN网络来预测斐波那契数列的下一个数字。
导入部分
让我们先写一下导入部分。
from pandas import read_csv
import numpy as np
from keras import Model
from keras.layers import Layer
import keras.backend as K
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, SimpleRNN
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.metrics import mean_squared_error
准备数据集
下面的函数生成了一个由n个斐波那契数字组成的序列(不包括开始的两个值)。如果scale_data ,那么它也会使用scikit-learn的MinMaxScaler ,将0和1之间的值进行缩放。让我们看看它对n=10 的输出。
def get_fib_seq(n, scale_data=True):
# Get the Fibonacci sequence
seq = np.zeros(n)
fib_n1 = 0.0
fib_n = 1.0
for i in range(n):
seq[i] = fib_n1 + fib_n
fib_n1 = fib_n
fib_n = seq[i]
scaler = []
if scale_data:
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
seq = np.reshape(seq, (n, 1))
seq = scaler.fit_transform(seq).flatten()
return seq, scaler
fib_seq = get_fib_seq(10, False)[0]
print(fib_seq)
[ 1. 2. 3. 5. 8. 13. 21. 34. 55. 89.]
接下来,我们需要一个函数get_fib_XY() ,将序列重新格式化为训练实例和目标值,供Keras输入层使用。当给定time_steps 作为参数时,get_fib_XY() 用time_steps 的列数构建数据集的每一行。这个函数不仅从斐波那契数列中构建训练集和测试集,而且还对训练实例进行洗牌,并将其重塑为所需的TensorFlow格式,即total_samples x time_steps x features 。同时,如果scale_data 被设置为True ,该函数返回缩放值的scaler 对象。
让我们生成一个小的训练集,看看它是什么样子的。我们设置了time_steps=3 ,total_fib_numbers=12 ,大约70%的例子走向测试点。请注意,训练和测试的例子已经被permutation() 函数洗过了。
def get_fib_XY(total_fib_numbers, time_steps, train_percent, scale_data=True):
dat, scaler = get_fib_seq(total_fib_numbers, scale_data)
Y_ind = np.arange(time_steps, len(dat), 1)
Y = dat[Y_ind]
rows_x = len(Y)
X = dat[0:rows_x]
for i in range(time_steps-1):
temp = dat[i+1:rows_x+i+1]
X = np.column_stack((X, temp))
# random permutation with fixed seed
rand = np.random.RandomState(seed=13)
idx = rand.permutation(rows_x)
split = int(train_percent*rows_x)
train_ind = idx[0:split]
test_ind = idx[split:]
trainX = X[train_ind]
trainY = Y[train_ind]
testX = X[test_ind]
testY = Y[test_ind]
trainX = np.reshape(trainX, (len(trainX), time_steps, 1))
testX = np.reshape(testX, (len(testX), time_steps, 1))
return trainX, trainY, testX, testY, scaler
trainX, trainY, testX, testY, scaler = get_fib_XY(12, 3, 0.7, False)
print('trainX = ', trainX)
print('trainY = ', trainY)
trainX = [[[ 8.]
[13.]
[21.]]
[[ 5.]
[ 8.]
[13.]]
[[ 2.]
[ 3.]
[ 5.]]
[[13.]
[21.]
[34.]]
[[21.]
[34.]
[55.]]
[[34.]
[55.]
[89.]]]
trainY = [ 34. 21. 8. 55. 89. 144.]
设置网络
现在让我们来设置一个有两层的小网络。第一个是SimpleRNN 层,第二个是Dense 层。下面是该模型的摘要。
# Set up parameters
time_steps = 20
hidden_units = 2
epochs = 30
# Create a traditional RNN network
def create_RNN(hidden_units, dense_units, input_shape, activation):
model = Sequential()
model.add(SimpleRNN(hidden_units, input_shape=input_shape, activation=activation[0]))
model.add(Dense(units=dense_units, activation=activation[1]))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
return model
model_RNN = create_RNN(hidden_units=hidden_units, dense_units=1, input_shape=(time_steps,1),
activation=['tanh', 'tanh'])
model_RNN.summary()
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
simple_rnn_3 (SimpleRNN) (None, 2) 8
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 3
=================================================================
Total params: 11
Trainable params: 11
Non-trainable params: 0
训练网络并进行评估
下一步是添加代码,生成一个数据集,训练网络,并对其进行评估。这一次,我们将在0和1之间扩展数据。我们不需要传递scale_data 参数,因为它的默认值是True 。
# Generate the dataset
trainX, trainY, testX, testY, scaler = get_fib_XY(1200, time_steps, 0.7)
model_RNN.fit(trainX, trainY, epochs=epochs, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# Evalute model
train_mse = model_RNN.evaluate(trainX, trainY)
test_mse = model_RNN.evaluate(testX, testY)
# Print error
print("Train set MSE = ", train_mse)
print("Test set MSE = ", test_mse)
作为输出,你会看到训练的进展和以下的均方误差值。
Train set MSE = 5.631405292660929e-05
Test set MSE = 2.623497312015388e-05
在网络中添加一个自定义注意力层
在Keras中,通过子类化Layer ,很容易创建一个实现注意力的自定义层。Keras指南列出了通过子类创建一个新层的清晰步骤。我们将在这里使用这些指南。所有对应于单个层的权重和偏置都被这个类封装起来了。我们需要编写__init__ 方法,以及覆盖以下方法。
build():Keras指南建议,一旦知道输入的大小,就在这个方法中添加权重。这个方法 "懒散地 "创建权重。内建函数add_weight(),可以用来添加权重和注意力层的偏差。call():call()方法实现了输入到输出的映射。它应该在训练中实现前向传递。
注意层的调用方法
注意层的调用方法必须计算对齐分数、权重和背景。你可以在Stefania的优秀文章《从零开始的注意力机制》中了解这些参数的细节。我们将在我们的call() 方法中实现Bahdanau注意力。
从KerasLayer 类中继承一个层并通过add_weights() 方法添加权重的好处是,权重会自动调整。Keras相当于对call() 方法的操作/计算进行了 "逆向工程",并在训练期间计算梯度。在添加权重时,指定trainable=True 是很重要的。如果需要的话,你也可以给你的自定义层添加一个train_step() 方法,并指定你自己的方法进行权重训练。
下面的代码实现了我们的自定义注意力层。
# Add attention layer to the deep learning network
class attention(Layer):
def __init__(self,**kwargs):
super(attention,self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self,input_shape):
self.W=self.add_weight(name='attention_weight', shape=(input_shape[-1],1),
initializer='random_normal', trainable=True)
self.b=self.add_weight(name='attention_bias', shape=(input_shape[1],1),
initializer='zeros', trainable=True)
super(attention, self).build(input_shape)
def call(self,x):
# Alignment scores. Pass them through tanh function
e = K.tanh(K.dot(x,self.W)+self.b)
# Remove dimension of size 1
e = K.squeeze(e, axis=-1)
# Compute the weights
alpha = K.softmax(e)
# Reshape to tensorFlow format
alpha = K.expand_dims(alpha, axis=-1)
# Compute the context vector
context = x * alpha
context = K.sum(context, axis=1)
return context
带有注意力层的RNN网络
现在让我们为我们先前创建的RNN网络添加一个注意力层。函数create_RNN_with_attention() 现在指定网络中的RNN层、注意力层和密集层。请确保在指定SimpleRNN时设置return_sequences=True 。这将返回之前所有时间步骤的隐藏单元的输出。
让我们来看看我们的模型在注意力方面的总结。
def create_RNN_with_attention(hidden_units, dense_units, input_shape, activation):
x=Input(shape=input_shape)
RNN_layer = SimpleRNN(hidden_units, return_sequences=True, activation=activation)(x)
attention_layer = attention()(RNN_layer)
outputs=Dense(dense_units, trainable=True, activation=activation)(attention_layer)
model=Model(x,outputs)
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
return model
model_attention = create_RNN_with_attention(hidden_units=hidden_units, dense_units=1,
input_shape=(time_steps,1), activation='tanh')
model_attention.summary()
Model: "model_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_2 (InputLayer) [(None, 20, 1)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
simple_rnn_2 (SimpleRNN) (None, 20, 2) 8
_________________________________________________________________
attention_1 (attention) (None, 2) 22
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 3
=================================================================
Total params: 33
Trainable params: 33
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
训练和评估带有注意力的深度学习网络
现在是时候训练和测试我们的模型了,看看它在预测一个序列的下一个斐波那契数字方面的表现。
model_attention.fit(trainX, trainY, epochs=epochs, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# Evalute model
train_mse_attn = model_attention.evaluate(trainX, trainY)
test_mse_attn = model_attention.evaluate(testX, testY)
# Print error
print("Train set MSE with attention = ", train_mse_attn)
print("Test set MSE with attention = ", test_mse_attn)
你会看到训练进度的输出和以下内容。
Train set MSE with attention = 5.3511179430643097e-05
Test set MSE with attention = 9.053358553501312e-06
我们可以看到,即使是这个简单的例子,使用注意力层后,测试集上的均方误差也比较低。你可以通过超参数调整和模型选择取得更好的结果。请在更复杂的问题上进行尝试,并在网络中加入更多的层。你也可以使用scaler 对象将数字缩回到它们的原始值。
你可以通过使用LSTM而不是SimpleRNN使这个例子更进一步,或者你可以通过卷积和池化层建立一个网络。如果你愿意,你也可以把它改成一个编码器解码器网络。
整合后的代码
如果你想尝试,本教程的全部代码粘贴在下面。请注意,由于该算法的随机性,你的输出会与本教程中给出的不同。
# Prepare data
def get_fib_seq(n, scale_data=True):
# Get the Fibonacci sequence
seq = np.zeros(n)
fib_n1 = 0.0
fib_n = 1.0
for i in range(n):
seq[i] = fib_n1 + fib_n
fib_n1 = fib_n
fib_n = seq[i]
scaler = []
if scale_data:
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
seq = np.reshape(seq, (n, 1))
seq = scaler.fit_transform(seq).flatten()
return seq, scaler
def get_fib_XY(total_fib_numbers, time_steps, train_percent, scale_data=True):
dat, scaler = get_fib_seq(total_fib_numbers, scale_data)
Y_ind = np.arange(time_steps, len(dat), 1)
Y = dat[Y_ind]
rows_x = len(Y)
X = dat[0:rows_x]
for i in range(time_steps-1):
temp = dat[i+1:rows_x+i+1]
X = np.column_stack((X, temp))
# random permutation with fixed seed
rand = np.random.RandomState(seed=13)
idx = rand.permutation(rows_x)
split = int(train_percent*rows_x)
train_ind = idx[0:split]
test_ind = idx[split:]
trainX = X[train_ind]
trainY = Y[train_ind]
testX = X[test_ind]
testY = Y[test_ind]
trainX = np.reshape(trainX, (len(trainX), time_steps, 1))
testX = np.reshape(testX, (len(testX), time_steps, 1))
return trainX, trainY, testX, testY, scaler
# Set up parameters
time_steps = 20
hidden_units = 2
epochs = 30
# Create a traditional RNN network
def create_RNN(hidden_units, dense_units, input_shape, activation):
model = Sequential()
model.add(SimpleRNN(hidden_units, input_shape=input_shape, activation=activation[0]))
model.add(Dense(units=dense_units, activation=activation[1]))
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
return model
model_RNN = create_RNN(hidden_units=hidden_units, dense_units=1, input_shape=(time_steps,1),
activation=['tanh', 'tanh'])
# Generate the dataset for the network
trainX, trainY, testX, testY, scaler = get_fib_XY(1200, time_steps, 0.7)
# Train the network
model_RNN.fit(trainX, trainY, epochs=epochs, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# Evalute model
train_mse = model_RNN.evaluate(trainX, trainY)
test_mse = model_RNN.evaluate(testX, testY)
# Print error
print("Train set MSE = ", train_mse)
print("Test set MSE = ", test_mse)
# Add attention layer to the deep learning network
class attention(Layer):
def __init__(self,**kwargs):
super(attention,self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self,input_shape):
self.W=self.add_weight(name='attention_weight', shape=(input_shape[-1],1),
initializer='random_normal', trainable=True)
self.b=self.add_weight(name='attention_bias', shape=(input_shape[1],1),
initializer='zeros', trainable=True)
super(attention, self).build(input_shape)
def call(self,x):
# Alignment scores. Pass them through tanh function
e = K.tanh(K.dot(x,self.W)+self.b)
# Remove dimension of size 1
e = K.squeeze(e, axis=-1)
# Compute the weights
alpha = K.softmax(e)
# Reshape to tensorFlow format
alpha = K.expand_dims(alpha, axis=-1)
# Compute the context vector
context = x * alpha
context = K.sum(context, axis=1)
return context
def create_RNN_with_attention(hidden_units, dense_units, input_shape, activation):
x=Input(shape=input_shape)
RNN_layer = SimpleRNN(hidden_units, return_sequences=True, activation=activation)(x)
attention_layer = attention()(RNN_layer)
outputs=Dense(dense_units, trainable=True, activation=activation)(attention_layer)
model=Model(x,outputs)
model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='adam')
return model
# Create the model with attention, train and evaluate
model_attention = create_RNN_with_attention(hidden_units=hidden_units, dense_units=1,
input_shape=(time_steps,1), activation='tanh')
model_attention.summary()
model_attention.fit(trainX, trainY, epochs=epochs, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# Evalute model
train_mse_attn = model_attention.evaluate(trainX, trainY)
test_mse_attn = model_attention.evaluate(testX, testY)
# Print error
print("Train set MSE with attention = ", train_mse_attn)
print("Test set MSE with attention = ", test_mse_attn)
摘要
在本教程中,你发现了如何使用Keras在深度学习网络中添加一个自定义的注意力层。
具体来说,你学到了。
- 如何重写Keras的
Layer类。 - 向注意力层添加权重时,需要使用
build()方法。 call()方法是指定注意力层的输入到输出的映射所需要的。- 如何在使用SimpleRNN构建的深度学习网络中添加一个自定义的注意力层。