Pandas DataFrame被非常普遍地用于存储表格数据。很多时候,我们需要迭代数据框架的行来执行各种操作。这是一种导航DatraFrame的方式。
在这篇文章中,你将了解到一些最流行的方法,这些方法将帮助你根据需求访问DataFrame的行。你还会了解到在各种情况下使用这些方法的一些实用技巧。
创建一个基本的数据框架
让我们从创建一个简单的数据框架开始
# Create a DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# Create the data of the DataFrame as a dictionary
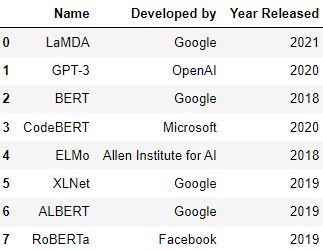
data_df = {'Name': ['LaMDA', 'GPT-3', 'BERT', 'CodeBERT', 'ELMo', 'XLNet', 'ALBERT', 'RoBERTa'],
'Developed by': ['Google', 'OpenAI', 'Google', 'Microsoft',
'Allen Institute for AI', 'Google', 'Google', 'Facebook'],
'Year Released': [2021, 2020, 2018, 2020, 2018, 2019, 2019, 2019]}
# Create the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data_df)
df
使用索引标签来迭代行
使用for循环,我们可以迭代DataFrame的行。下面的例子打印了DataFrame中每一行的'Name'列值。
# Use index labels to iterate over the rows values
for i in range(len(df)):
print(df['Name'][i])
LaMDA
GPT-3
BERT
CodeBERT
ELMo
XLNet
ALBERT
RoBERTa
使用loc()方法来迭代行数
.loc() 方法是用来通过使用索引标签来访问DataFrame的行和列。
你可以通过使用.loc() 方法指定DataFrame的行和列的标签来迭代DataFrame的行。
# Pass the index labels the rows or columns of the DataFrame to the loc() function to iterate over them
for i in range(len(df)):
print(df.loc[i, 'Name'], df.loc[i, 'Developed by'])
LaMDA Google
GPT-3 OpenAI
BERT Google
CodeBERT Microsoft
ELMo Allen Institute for AI
XLNet Google
ALBERT Google
RoBERTa Facebook
使用iloc()方法来迭代行数
.iloc.() 方法用于通过使用DataFrame中的整数值位置来访问DataFrame的行和列。
因此,通过指定行和列索引的整数值,你可以迭代pandas DataFrame的行。
# Pass the integer-value locations of the rows or columns of the DataFrame to the iloc() function to iterate over them
for i in range(len(df)):
print(df.iloc[i, 0], df.iloc[i, 1])
LaMDA Google
GPT-3 OpenAI
BERT Google
CodeBERT Microsoft
ELMo Allen Institute for AI
XLNet Google
ALBERT Google
RoBERTa Facebook
使用iterrows()方法来迭代行数
iterrows() 方法被用来遍历pandas DataFrame的行。它返回一个元组,其中包含行的索引标签和作为pandas系列的行的内容。
# Iterate over the row values using the iterrows() method
for ind, row in df.iterrows():
print(row)
print('\n') # Use the escape character '\n' to print an empty new line.
Name LaMDA
Developed by Google
Year Released 2021
Name: 0, dtype: object
Name GPT-3
Developed by OpenAI
Year Released 2020
Name: 1, dtype: object
Name BERT
Developed by Google
Year Released 2018
Name: 2, dtype: object
Name CodeBERT
Developed by Microsoft
Year Released 2020
Name: 3, dtype: object
Name ELMo
Developed by Allen Institute for AI
Year Released 2018
Name: 4, dtype: object
Name XLNet
Developed by Google
Year Released 2019
Name: 5, dtype: object
Name ALBERT
Developed by Google
Year Released 2019
Name: 6, dtype: object
Name RoBERTa
Developed by Facebook
Year Released 2019
Name: 7, dtype: object
现在,我们已经涵盖了最简单的方法。
使用 itertuples() 方法
itertuples() 方法将一个pandas DataFrame的行作为命名的tuples进行迭代。当你使用这个方法时,会返回一个元组,该元组的第一个元素是行索引标签,第二个元素是以pandas系列形式存在的行值。
- 语法: pandas.DataFrame.itertuples(index=True, name='Pandas')
- 目的: 在一个数据框架的行上进行迭代
- 参数:
- index: 布尔值(默认:True)。用于指定是否应返回该行的索引标签。如果值为'True',那么索引标签将作为元组的第一个索引被返回。
- name: 字符串或无(默认:'Pandas')。 我们用它来指定给元组的名称。
- **返回:**一个迭代器
# Iterate over the row values using the itertuples() method
for row in df.itertuples():
print(row)
Pandas(Index=0, Name='LaMDA', _2='Google', _3=2021)
Pandas(Index=1, Name='GPT-3', _2='OpenAI', _3=2020)
Pandas(Index=2, Name='BERT', _2='Google', _3=2018)
Pandas(Index=3, Name='CodeBERT', _2='Microsoft', _3=2020)
Pandas(Index=4, Name='ELMo', _2='Allen Institute for AI', _3=2018)
Pandas(Index=5, Name='XLNet', _2='Google', _3=2019)
Pandas(Index=6, Name='ALBERT', _2='Google', _3=2019)
Pandas(Index=7, Name='RoBERTa', _2='Facebook', _3=2019)
使用iteritems()方法
iteritems() 方法是用来迭代一个DataFrame的列。当你使用这个方法时,它会返回一个元组,其中第一个元素是列的标签,第二个元素是以pandas系列形式存在的列值。
# Iterate over the column values using the iteritems() method
for col in df.iteritems():
print('element at index 0:', col[0])
print('element at index 1:', col[1])
element at index 0: Name
element at index 1: 0 LaMDA
1 GPT-3
2 BERT
3 CodeBERT
4 ELMo
5 XLNet
6 ALBERT
7 RoBERTa
Name: Name, dtype: object
element at index 0: Developed by
element at index 1: 0 Google
1 OpenAI
2 Google
3 Microsoft
4 Allen Institute for AI
5 Google
6 Google
7 Facebook
Name: Developed by, dtype: object
element at index 0: Year Released
element at index 1: 0 2021
1 2020
2 2018
3 2020
4 2018
5 2019
6 2019
7 2019
Name: Year Released, dtype: int64
使用items()方法
items() 方法与iteritems() 方法类似。这个方法也会返回一个元组,列名是第一个元素,列值是第二个元素。
# Iterate over the column values using the items() method
for col in df.items():
print('element at index 0:', col[0])
print('element at index 1:', col[1])
element at index 0: Name
element at index 1: 0 LaMDA
1 GPT-3
2 BERT
3 CodeBERT
4 ELMo
5 XLNet
6 ALBERT
7 RoBERTa
Name: Name, dtype: object
element at index 0: Developed by
element at index 1: 0 Google
1 OpenAI
2 Google
3 Microsoft
4 Allen Institute for AI
5 Google
6 Google
7 Facebook
Name: Developed by, dtype: object
element at index 0: Year Released
element at index 1: 0 2021
1 2020
2 2018
3 2020
4 2018
5 2019
6 2019
7 2019
Name: Year Released, dtype: int64
使用apply()函数
你可以使用apply() 函数对一个DataFrame的所有值进行某种操作。
- 语法: pandas.DataFrame.apply(func, axis=0, raw=False, result_type=None, args=(), kwds)
- 目的: 沿DataFrame的某一轴应用一个函数。
- 参数:
- func: 表示将在DataFrame上应用的函数或操作。
- axis: 0 或 1(默认为 0)。这个参数指定了DataFrame的方向,函数将沿着这个方向应用。
- raw: 布尔值(默认为假)。它用于指定行或列是以pandas系列还是numpy数组的形式传递。设置值为True可以将行或列作为一个numpy数组传递。如果要将行或列作为pandas系列传递,请将该参数的值设为False。
- result_type: expand or reduce or broadcast or None(默认:None)。 它决定了系列或numpy数组的返回方式。
1.expand参数将列表式的结果变成不同的列。
2.reduce参数返回一个pandas系列。它所执行的功能与expand参数相反。3.3.broadcast参数用于将结果广播给原始DataFrame的形状。4.4.None参数的返回值取决于应用该函数后的返回值。
- args(): 它用于指定位置参数,与数组或系列一起传递给func中指定的函数。
- kwds: 用于指定额外的关键字参数,这些参数将被func参数中指定的函数使用。
- 返回: 一个pandas系列或一个DataFrame。
通过将index labels 方法与此方法相结合,你可以使用apply() 函数来迭代pandas DataFrame的列值。
# Iterate over the column values using the apply() method
print(df.apply(lambda row: row['Name'] + ', ' + row['Developed by'], axis=1))
0 LaMDA, Google
1 GPT-3, OpenAI
2 BERT, Google
3 CodeBERT, Microsoft
4 ELMo, Allen Institute for AI
5 XLNet, Google
6 ALBERT, Google
7 RoBERTa, Facebook
dtype: object
实用提示
- 记住,
loc()函数接受行或列的标签,iloc()函数接受整数值的行或列的位置来迭代pandas DataFrame。 iterrows(),iteritems(), 和items()方法返回一个生成器对象。因此,我们不能直接访问这些。你可以通过使用一个循环来迭代它们的值。- 请记住,
iterrows()和itertuples()方法迭代的是 DataFrame 的行值,而iteritems()和items()方法迭代的是 DataFrame 的列值。
测试你的知识
Q1: iterrows() 方法返回一个列表,其中第一个元素是行标签,第二个元素是以pandas系列形式存在的行值。真的还是假的?
答案: 错。iterrows() 方法返回一个元组,其中第一个元素是行标签,第二个元素是以pandas系列形式存在的行值。
Q2: 哪个函数或方法在迭代DataFrame时需要行或列标签?
答案:loc()方法。
Q3: 写出代码,使用apply()函数遍历DataFramedf中'col_1'和'col_2'的列值。
答案: print(df.apply(lambda row: row['col_1'] + ', ' + row['col_2'],axis=1))
Q4: 编写代码,使用itertuples()方法遍历DataFramedf的行值。
答案:
for row in df.itertuples():
print(row)
Q5: 编写代码,遍历数据框架df第二列的所有行。
答案:
for i in range(len(df)):
print(df.iloc[i,1])