
C# 字节到字符串的介绍
在这篇文章中,我们将学习如何将一个字节数组转换为字符串。有很多方法可以帮助我们实现这一目标。其中一个常见的方法是使用System命名空间中的BitConverter类。在本专题中,我们将学习C#的字节到字符串。
BitConverter.ToString()方法以其所有的重载形式使其很容易将字节[]转换为字符串。这个方法基本上是将数字值(只不过是byte[]的一个元素)转换为其等价的十六进制形式的字符串。重载的形式如下。
- ToString(Byte[])。
- ToString(Byte[], Int32);
- ToString(Byte[], Int32, Int32)。
语法与解释
以下是使用BitConverter.ToString()方法将byte[]转换为字符串的语法。
public static string ToString(byte[] byteArray);
上述方法接收一个字节数组作为输入,并返回一个包含一些十六进制对的字符串。这些对中的每一个都用连字符隔开,代表byteArray中的相应元素。
public static string ToString(byte[] byteArray, int startingIndex);
这里,ToString()方法需要两个参数;byteArray是要转换为字符串的字节数组,startingIndex是你要开始转换的字节数组中的一个元素的索引。
public static string ToString(byte[] byteArray, int startingIndex, int length);
这里,ToString()方法需要三个参数;byteArray是要转换为字符串的字节数组,startingIndex是你要执行转换的字节数组中的元素索引,length是你要从startingIndex开始转换的字节数组元素的数量。
如何在C#中转换字节到字符串?
如前所述,在C#中,有许多方法可以将字节数组转换为字符串。其中一个常见的方法是使用BitConverter.ToString()方法。在C#中System命名空间下的BitConverter类包含了几种将字节数组转换为基础数据类型的方法,因此我们可以使用这个类的ToString()方法将byte[]转换为字符串。这个方法有三种重载形式,如下所示。
ToString(byte[]);
该方法用于将整个字节数组中每个元素的数值转换为字符串,转换后的字符串将包含十六进制对,每个对用连字符分隔,每个对代表相应的字节数组元素。
ToString(byte[], Int32);
该方法将字节子数组中每个元素的数值转换为其对应的十六进制字符串对。该方法的整数参数指定了子数组的起始索引。
ToString(byte[], Int32, Int32);
该方法将字节数组中部分或全部元素的数值转换为其十六进制字符串对。要转换的元素通过使用该方法的第二和第三个参数来指定;第二个参数指定了我们需要开始转换的起始索引,第三个参数指定了要取的元素的长度,即从前面指定的起始索引开始,要取的转换元素的数量。
除此以外,我们可以使用System.Text命名空间中的Encoding类来转换字节数组。除此之外,我们还可以使用System.Text命名空间中的Encoding类来将字节数组转换为UTF-8或ASCII字符集和编码的字符串。该类提供的GetString()方法用于将字节数组中的字节解码为字符串。
- UTF8.GetString(byte[])。
- ASCII.GetString(byte[])。
编码类提供的其他编码方案包括Unicode、UTF32、UTF7等。
另一种实现这种转换的方法是使用Convert.ToBase64String()方法,用于将字节数组内的字节转换为字符串。
ToBase64String(byte[]);
我们也可以使用MemoryStream来转换字节数组为字符串。但是,首先,我们需要使用MemoryStream类将字节数组转换为字节流;然后,我们可以使用StreamReader类读取整个字节流,然后可以在ReadToEnd()方法的帮助下将这个字节流返回为字符串。现在让我们在下面提供的语句的帮助下理解这个问题。
using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream(bytes)) { using (StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader(memoryStream)) { return streamReader.ReadToEnd(); } }
上述语句中的'bytes'是一个要转换为字符串的字节数组。因此,首先,我们在'memoryStream'对象中得到了作为字节流的字节数组。然后,我们使用StreamReader类读取这个流,并使用ReadToEnd()方法将该流作为字符串返回,该方法读取该流并返回字符串值。
字节到字符串的例子 C#
下面提到了不同的例子。
例子#1
使用BitConverter类将字节数组转换为字符串的例子。
代码。
using System; using System.Globalization; using System.Text; using System.IO; public class Program { public static void Main() { string resultedStr = string.Empty; //defining byte array byte[] bytes = new byte[5] { 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 }; //printing byte array before conversion Console.Write("Byte array before conversion: "); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++) { Console.Write(" " + bytes[i]); } //converting byte array to string resultedStr = BitConverter.ToString(bytes); //printing string after conversion Console.WriteLine("\nResulted string after conversion: {0}", resultedStr); Console.ReadLine(); } }
输出。

例子#2
使用Encoding类和MemoryStream类将字节数组转换为字符串的例子。
代码。
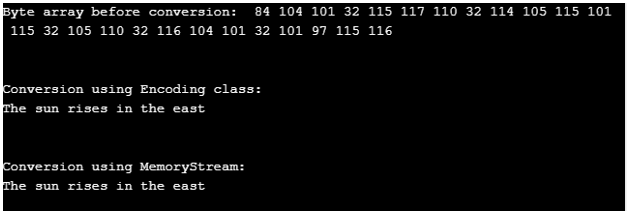
using System; using System.Globalization; using System.Text; using System.IO; namespace ConsoleApp4 { public class Program { public static void Main() { string str = "The sun rises in the east"; //converting string to array of bytes byte[] bytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(str); //printing byte array before conversion Console.Write("Byte array before conversion: "); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++) { Console.Write(" " + bytes[i]); } //converting byte array to string using Encoding class str = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(bytes); //printing resulted string after conversion Console.WriteLine("\n"); Console.Write("\nConversion using Encoding class: \n{0}", str); //converting byte array to string using MemoryStream class Console.WriteLine("\n"); Console.WriteLine("\nConversion using MemoryStream: "); using (MemoryStream memoryStream = new MemoryStream(bytes)) { using (StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader(memoryStream)) { Console.Write(streamReader.ReadToEnd()); } } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
输出。
结论
在C#中,我们可以使用BitConverter、Encoding、MemoryStream等类将一个字节数组转换为字符串。由BitConverter类提供的结果字符串包括十六进制对。使用Encoding类,我们可以使用相同的编码方案将字符串转换为byte[]和byte[]转换为字符串。
推荐文章
这是一份关于C#的字节到字符串的指南。在这里,我们讨论了如何在C#中把字节转换为字符串,以及与代码和输出有关的例子。你也可以看看下面的文章来了解更多