Lua打印表的定义
Lua是一种可扩展以及轻量级的编程语言。这种语言采用C语言,从一开始就被设计成可以集成到C语言和其他传统编程语言的软件。在Lua中,表被认为是唯一的数据结构,它创造了几种类型,如字典和数组。此外,它使用关联数组,也可以用数字和字符串进行索引。表的特点是它没有任何固定的大小,也可以根据需求来增长。Lua中的表几乎被用于所有的表示法中,比如包的表示法。
语法。
Lua中的表既不是变量也不是值。相反,它们被认为是对象,它使用{},也被称为构造函数表达式来创建一个空表。
- 表的初始化
tb = {}
- 表的赋值
tb[1]= "Hai"
-删除引用
tb = nil
这里,tb是表的名称。
如何在Lua中打印表?
现在,我们将看到如何在Lua中打印表。
正如已经讨论过的,我们可以创建空表和带有字符串以及数字索引的表。首先,我们将看到如何打印表的类型。
-- create an empty table
tb = {}
print("The type of the table created is: ",type(tb))
使用上述命令,一个空表被创建,它的类型可以通过type()方法被识别。
现在,我们将看到如何在表的索引1中设置数值 "一",在索引果中设置数值 "苹果"。
tb[1]= "one"
tb["fruit"] = "Apple"
print("Element in the table which is at index 1 is ", tb[1])
print("Element in the table which is at index 1]fruit is ", tb["fruit"])
最后,print()被用来打印表格。
表的操作方法
下面是Lua中用于表操作的一些方法。
- concat(table [, sep [, i [, j]])
表中的字符串将根据给定的参数被串联起来。
- insert(table, [pos,] val)
值val将被插入到表的所述位置。
- maxn (table)
将会返回最大的数字索引。
- remove (table [, pos])
值将被从表中删除。
- sort (table [, comp])
表将根据比较器参数进行排序,该参数是可选的。
示例
现在,我们可以看到一些关于Lua表的示例程序。
例子#1:Lua程序创建一个表并打印元素
-- create an empty table
tb = {}
print("The type of the table created is: ",type(tb))
tb[1]= "one"
tb["fruit"] = "Apple"
print("Element in the table which is at index 1 is ", tb[1])
print("Element in the table which is at index 1]fruit is ", tb["fruit"])
输出示例。
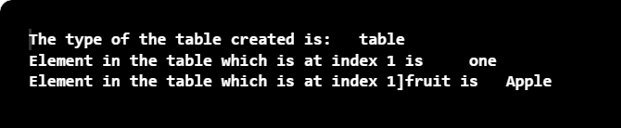
在这个程序中,一个空表被创建,元素被添加到索引1和 "水果 "中。
Example #2: Lua程序创建一个新的表并将其引用到旧的表中
-- create an empty table
tb = {}
print("The type of the table created is: ",type(tb))
tb[1]= "one"
tb["fruit"] = "Apple"
print("Element in the table which is at index 1 is ", tb[1])
print("Element in the table which is at index 1]fruit is ", tb["fruit"])
--create another table and refer it to the table which is created first
tbnew = tb
print("Element at index 1 in the table tbnew is ", tbnew[1])
print("Element at index fruit in the table tbnew is ", tbnew["fruit"])
tbnew[1] = "two"
print("Element at index 1 in the table tbnew is ", tbnew[1])
输出示例。
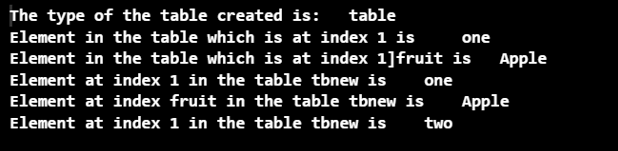
在这个程序中,一个空表被创建,元素被添加到索引1和 "水果"。后来,一个新的表被创建,并被引用到旧的表上。然后,索引处的元素被打印出来。
例子#3:连接元素的Lua程序
Animals = { "Horse" , "Buffalo" , "Cat" , "Deer" }
-- Print the concatenated string of the table
print("The string which is concatenated is ",table.concat(Animals))
-- Print the concatenated character
print("The string after concatenating with / is ",table.concat(Animals,"/ "))
-- Print the concatenated strings based on index
print("The string after concatenating based on index is: ",
table.concat(Animals,"/ ", 1,4))
输出示例。
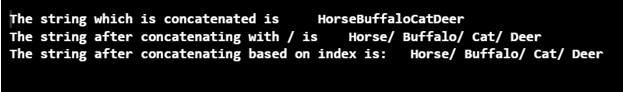
在这个程序中,创建了一个表,使用concat()方法将元素连接起来。
例四:插入新元素的Lua程序
Animals = { "Horse" , "Buffalo" , "Cat" , "Deer" }
-- insert string at the end
table.insert(Animals,"Dog")
--insert string at index 4
table.insert(Animals , 4 , "Cow" )
-- Print the concatenated string of the table
print("The string which is concatenated is ",table.concat(Animals))
-- Print the concatenated character
print("The string after concatenating with / is ",table.concat(Animals,"/ "))
-- Print the concatenated strings based on index
print("The string after concatenating based on index is: ",
table.concat(Animals,"/ ", 1,4))
输出示例。

在这个程序中,创建了一个表,并将元素插入其中。之后,使用concat()方法将它们连接起来。
例五:寻找最大元素数的Lua程序
Animals = { "Horse" , "Buffalo" , "Cat" , "Deer" }
-- insert string at the end
table.insert(Animals,"Dog")
--insert string at index 4
table.insert(Animals , 4 , "Cow" )
-- Print the concatenated string of the table
print("The string which is concatenated is ",table.concat(Animals))
-- Print the concatenated character
print("The string after concatenating with / is ",table.concat(Animals,"/ "))
-- Print the concatenated strings based on index
print("The string after concatenating based on index is: ",
table.concat(Animals,"/ ", 1,4))
print("The maximum number of items in the Animals table is",table.maxn(Animals))
print("The last item in the Animals table is", Animals[6])
--remove the table
table.remove(Animals)
输出示例:

在这个程序中,创建了一个表,并确定了元素的最大数量。最后,该表被删除。
总结
Lua中的表被认为是唯一的数据结构,它创建了几种类型,如字典和数组。在这篇文章中,不同的方面如语法、方法、工作和Lua表的例子都得到了详细的解释。