从0到1打造一款安卓app之12-ViewModel+NavHostFragment+StateFlow 单向数据流示例
1.参考资料
2.Flow和StateFlow 、 SharedFlow的区别
flow的基本知识
flow的常见构建器有
flowOf()和 flow{}
public fun <T> flow(@BuilderInference block: suspend FlowCollector<T>.() -> Unit): Flow<T> = SafeFlow(block)
用法
flow {
eimt(1)
emit(2)
}
public fun <T> flowOf(vararg elements: T): Flow<T> = flow {
for (element in elements) {
emit(element)
}
}
flowOf(1,2,3,4)
各种集合转成流 asFlow
public fun <T> Array<T>.asFlow(): Flow<T> = flow {
forEach { value ->
emit(value)
}
}
public fun IntArray.asFlow(): Flow<Int> = flow {
forEach { value ->
emit(value)
}
}
public fun LongArray.asFlow(): Flow<Long> = flow {
forEach { value ->
emit(value)
}
}
public fun IntRange.asFlow(): Flow<Int> = flow {
forEach { value ->
emit(value)
}
}
public fun LongRange.asFlow(): Flow<Long> = flow {
forEach { value ->
emit(value)
}
}
callbackFlow
public fun <T> callbackFlow(@BuilderInference block: suspend ProducerScope<T>.() -> Unit): Flow<T> = CallbackFlowBuilder(block)
//使用示例
fun main() {
fun getData(): Flow<String> = callbackFlow<String> {
send("start")
var count = 0
while (count++ < 10) {
delay(1000)
send(count.toString())
}
send("over")
close()
// awaitClose()
}
runBlocking {
getData()
.catch { e ->
emit("收到了异常 ${e.message}")
}.collect {
println("it:$it")
}
}
}
冷流flow
1.不收集就不会发送数据
2.多个收集方多次收集时,会从头开始发送重复的数据
private fun flowCreate(): Flow<Int> = flow {
for (i in 1..3) {
println("flow emit $i")
delay(100)
emit(i)
}
}
fun main() = runBlocking {
val _flow = flowCreate()
println("start delay")
delay(2000)
println("在收集之前,并不会发出值")
println("start collect1")
_flow.collect{
println("flow collect1 $it")
}
println("\nstart collect2\n")
_flow.collect{
println("flow collect2 $it")
}
}
start delay
在收集之前,并不会发出值
start collect1
flow emit 1
flow collect1 1
flow emit 2
flow collect1 2
flow emit 3
flow collect1 3
start collect2
flow emit 1
flow collect2 1
flow emit 2
flow collect2 2
flow emit 3
flow collect2 3
热流SharedFlow、StateFlow
StateFlow是SharedFlow的子类,区别在于前者有多了一个value属性,可以直接获取到值(只读)
MutableStateFlow、 MutableSharedFlow分别是上面两者的子类,MutableStateFlow有一个value值可读可写
直接创建
val sharedFlow = MutableSharedFlow<String>(replay = 0,extraBufferCapacity=1,onBufferOverflow= BufferOverflow.DROP_LATEST)
val _state = MutableStateFlow(value = "start")
stateIn 把冷流转换成热流
public fun <T> Flow<T>.stateIn(
scope: CoroutineScope,
started: SharingStarted,
initialValue: T
): StateFlow<T> {
val config = configureSharing(1)
val state = MutableStateFlow(initialValue)
val job = scope.launchSharing(config.context, config.upstream, state, started, initialValue)
return ReadonlyStateFlow(state, job)
}
/**
* Starts the upstream flow in a given [scope], suspends until the first value is emitted, and returns a _hot_
* [StateFlow] of future emissions, sharing the most recently emitted value from this running instance of the upstream flow
* with multiple downstream subscribers. See the [StateFlow] documentation for the general concepts of state flows.
*
* @param scope the coroutine scope in which sharing is started.
*/
public suspend fun <T> Flow<T>.stateIn(scope: CoroutineScope): StateFlow<T> {
val config = configureSharing(1)
val result = CompletableDeferred<StateFlow<T>>()
scope.launchSharingDeferred(config.context, config.upstream, result)
return result.await()
}
把上面的例子稍微修改一下
private fun flowCreate(): Flow<Int> = flow {
for (i in 1..3) {
println("flow emit $i")
delay(100)
emit(i)
}
}
fun main() = runBlocking<Unit> {
val _flow = flowCreate().stateIn(this)
println("start delay")
delay(2000)
println("在收集之前,就已经发出值了")
launch {
println("start collect1")
_flow.onCompletion {
println("onCompletion")
}.collect{
println("flow collect1 $it")
}
}
launch {
println("\nstart collect2\n")
_flow.collect{
println("flow collect2 $it")
}
}
}
输出结果
flow emit 1
flow emit 2
start delay
flow emit 3
在收集之前,就已经发出值了
start collect1
flow collect1 3
start collect2
flow collect2 3
组合多个Flow的操作符
zip
val nums2 = (1..3).asFlow().onEach { delay(300) }
val strs2 = flowOf("one","two","three").onEach { delay(400) }
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
nums2.zip(strs2){ a,b ->
"$a -> $b"
}.collect{
println("$it at ${System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime} ms from start")
}
输出结果
1 -> one at 403 ms from start
2 -> two at 804 ms from start
3 -> three at 1204 ms from start
combine
val nums4 = (1..3).asFlow().onEach { delay(300) } // numbers 1..3 every 300 ms
val strs4 = flowOf("one", "two", "three").onEach { delay(400) } // strings every 400 ms
val startTime4 = System.currentTimeMillis() // remember the start time
nums4.combine(strs4) { a, b -> "$a -> $b" } // compose a single string with "combine"
.collect { value -> // collect and print
println("$value at ${System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime4} ms from start")
}
输出结果
1 -> one at 416 ms from start
2 -> one at 619 ms from start
2 -> two at 818 ms from start
3 -> two at 921 ms from start
3 -> three at 1220 ms from start
单向数据流 (UDF)
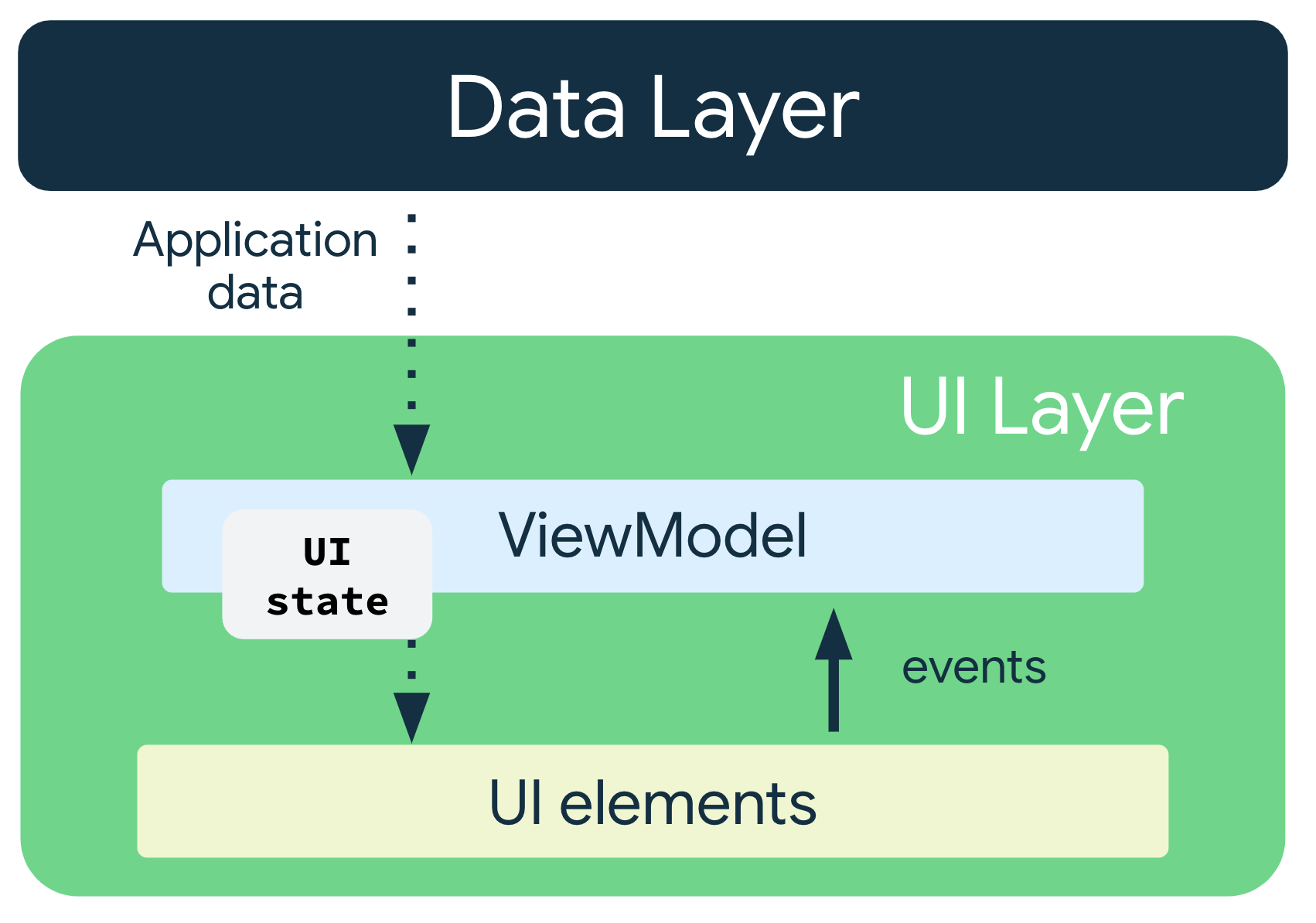
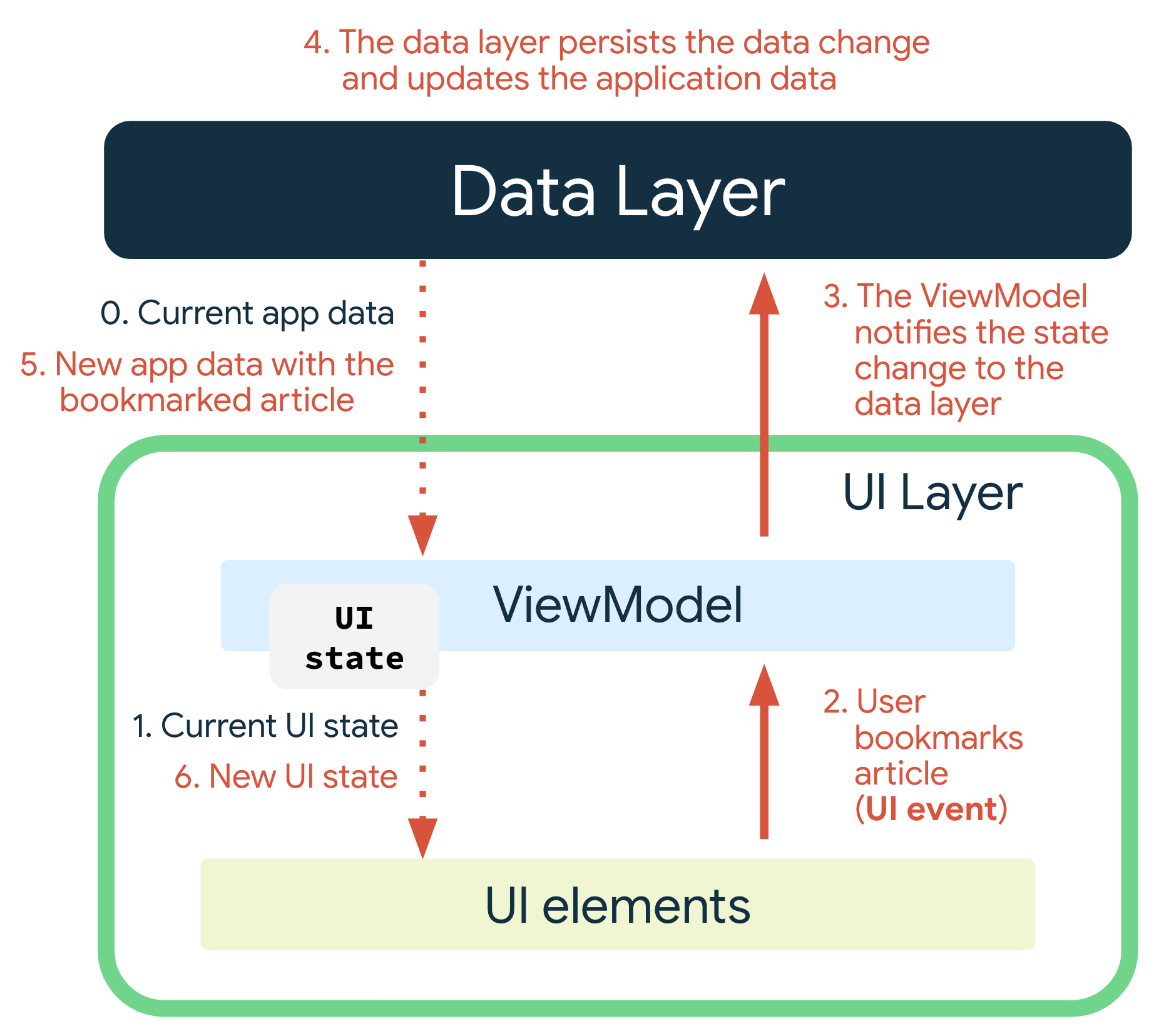
UDF 在应用架构中的运作方式图示
ViewModel+NavHostFragment+StateFlow 单向数据流示例
实现一个简单示例
1.启动app时,先显示一个LoadingFragment,三秒后跳转到登录界面LoginFragment
2.登录界面有一个登录按钮,点击后弹出正在登录提示框,登录成功后跳转到主页
3.登录界面和主页MainFragment显示时间,10秒更新一次
4.主页有一个按钮,点击一次,就累加一次并把点击次数持久化到本地,下次直接读取显示
5.LoadingFragment,LoginFragment,MainFragment共享一个ViewModel实例
ClickCounterSource
存储并读取点击数
class ClickCounterSource(val context: Context) {
private val EXAMPLE_COUNTER = longPreferencesKey("example_counter")
fun getCounterFlow(): Flow<Long> = context.dataStore.data
.map { preferences ->
preferences[EXAMPLE_COUNTER] ?: 0
}
suspend fun incrCount() = context.dataStore.edit { settings ->
val currentCounterValue = settings[EXAMPLE_COUNTER] ?: 0
settings[EXAMPLE_COUNTER] = currentCounterValue + 1
}
}
UserSource
模拟用户登录,并在内存中保存userInfo信息
class UserSource {
private val _userInfo = MutableLiveData<String>("")
val userInfo: Flow<String> = _userInfo.asFlow().onEach {
Log.d("UserSource","UserSource value:$it")
}
suspend fun getUserById() {
delay(3000)
Log.d("UserSource","getUserById")
_userInfo.value = "kotlin"
}
}
定义ViewModel和ViewModelProvider.Factory
class MainViewModel(
context: Application,
val clickCounterSource: ClickCounterSource,
val userSource: UserSource,
) : AndroidViewModel(context) {
private val timeFlow = flow<Long> {
while (true) {
emit(System.currentTimeMillis())
delay(10 * 1000)
}
}
private val loadingFow = MutableLiveData(true).apply {
viewModelScope.launch {
delay(3000)
value = false
}
}.asFlow()
val mainUiState: StateFlow<MainUiState> = combine(
loadingFow,
timeFlow,
clickCounterSource.getCounterFlow(),
userSource.userInfo
) { loadingFow, time, counter, userInfo ->
if (loadingFow) {
MainUiState.Loading
} else {
MainUiState.MainState(userName = userInfo, date = Date(time), count = counter)
}
}.stateIn(
scope = viewModelScope,
started = SharingStarted.WhileSubscribed(),
initialValue = MainUiState.Loading
)
fun login() {
viewModelScope.launch {
userSource.getUserById()
}
}
fun incrCount() {
viewModelScope.launch {
clickCounterSource.incrCount()
}
}
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d("MainViewModel", "onCleared")
}
companion object {
class MainViewModelFactory(val context: Context) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {
override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>, extras: CreationExtras): T {
return MainViewModel(
context = context.applicationContext as Application,
clickCounterSource = ClickCounterSource(context),
userSource = UserSource(),
) as T
}
}
}
}
MainActivity,主要负责切换Fragment
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
val viewModel: MainViewModel by viewModels {
MainViewModel.Companion.MainViewModelFactory(this@MainActivity)
}
private lateinit var navController: NavController
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val navHostFragment = supportFragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.nav_host_container) as NavHostFragment
navController = navHostFragment.navController
navController.addOnDestinationChangedListener { controller, destination, arguments ->
Log.d("MainActivity", "addOnDestinationChangedListener:${destination.label}")
}
lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.mainUiState.collect {
updateView(it)
}
}
}
}
private fun updateView(mainUiState: MainUiState) {
if (mainUiState is MainUiState.Loading) {
if (getString(R.string.loadingScreenLabel) != navController.currentDestination?.label)
navController.navigate(R.id.loadingScreen)
} else if (mainUiState is MainUiState.MainState) {
updateTime(mainUiState.date)
if (mainUiState.isLogined) {
if (getString(R.string.mainScreenLabel) != navController.currentDestination?.label) {
navController.navigate(R.id.mainScreen)
}
} else {
if (getString(R.string.loginScreenLabel) != navController.currentDestination?.label) {
navController.navigate(R.id.loginScreen)
}
}
}
return
}
private fun updateTime(time: Date) {
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.tvTime).setText(time.toString())
}
}
LoadingFragment
简单的显示一个等待框
class LoadingFragment : Fragment() {
private var param1: String? = null
private var param2: String? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
arguments?.let {
param1 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM1)
param2 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM2)
}
}
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_loading, container, false)
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance(param1: String, param2: String) =
LoadingFragment().apply {
arguments = Bundle().apply {
putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1)
putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2)
}
}
}
}
LoginFragment
使用activityViewModels,和Activity使用同一个ViewMode实例
调用mainViewModel.login()方法,并且监听是否登录成功
class LoginFragment : Fragment() {
private var param1: String? = null
private var param2: String? = null
private val mainViewModel: MainViewModel by activityViewModels() {
MainViewModel.Companion.MainViewModelFactory(requireContext())
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
arguments?.let {
param1 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM1)
param2 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM2)
}
}
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_login, container, false)
}
private var alertDialog: AlertDialog? = null
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
view.findViewById<Button>(R.id.btnLogin).setOnClickListener {
alertDialog = AlertDialog.Builder(requireContext())
.setMessage("正在登录,请稍候...")
.create()
.apply {
show()
}
mainViewModel.login()
}
lifecycleScope.launch {
viewLifecycleOwner.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
mainViewModel.mainUiState.collect {
if (it is MainUiState.MainState && it.isLogined) {
alertDialog?.run {
dismiss()
}
}
}
}
}
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance(param1: String, param2: String) =
LoginFragment().apply {
arguments = Bundle().apply {
putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1)
putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2)
}
}
}
}
MainFragment
调用 viewModel.incrCount()方法,累加点击数并监听变化
class MainFragment : Fragment() {
private var param1: String? = null
private var param2: String? = null
private val viewModel: MainViewModel by activityViewModels {
MainViewModel.Companion.MainViewModelFactory(requireContext())
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
arguments?.let {
param1 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM1)
param2 = it.getString(ARG_PARAM2)
}
}
private fun updateView(state: MainUiState) {
if (state is MainUiState.MainState) {
view?.apply {
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.tvUserName).text = "登录成功:${state.userName}"
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.tvCount).text = state.count.toString()
}
}
}
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank, container, false)
}
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch {
viewLifecycleOwner.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
viewModel.mainUiState.collect {
updateView(state = it)
}
}
}
view.findViewById<Button>(R.id.btnCounter).setOnClickListener {
viewModel.incrCount()
}
}
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun newInstance(param1: String, param2: String) =
MainFragment().apply {
arguments = Bundle().apply {
putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1)
putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2)
}
}
}
}