
LINQ联盟简介
LINQ Union用于检索两个集合/序列之间的不同元素;它结合两个或多个元素集合,最后返回唯一的元素作为结果。LINQ联盟是一个扩展方法,它需要两个集合来结合这两个集合,并返回两个集合中的不同元素。LINQ Union只支持方法语法,不支持查询语法。Union方法同时出现在Queryable类和Enumerable类中。
语法。
让我们看看LINQ联合方法的语法,如下所示。
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Union<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> first, IEnumerable<TSource> second); public static IEnumerable<TSource> Union<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> first, IEnumerable<TSource> second, IEqualityComparer<TSource> comparer);
如果你正在处理复杂类型的联合集合,那么你必须使用IEqualityComparer接口来得到一个准确的结果,否则,你将得到不正确的结果。
联盟在LINQ中如何工作?
在LINQ的联合方法中,它只支持方法语法;查询语法在联合方法中是不可用的。在union方法中,Queryable和Enumerable类将被接受。Union操作者或方法主要用于将多个集合合并成一个单独的集合,它只返回唯一的元素,因此它从集合中删除重复的值。让我们看一个例子,如下
举例来说。
Collection X= {20, 40, 60, 80, 100} Collection Y= {20, 40, 70} var _result = X.Union(Y);
结果是 = {20, 40, 60, 70, 80, 100} 在这个结果集合中,元素20和40同时出现在两个集合中,所以在结果中它只返回一次,因为唯一的元素只被显示,它消除了重复。让我们看看唯一方法的工作流程如下。
static public void Main() { string[] Department1 = { "JAVA", "DOTNET", "PHYTHON", "ANDROID" }; string[]Department2 = { "JAVA", "ANDROID", "DESIGNING" }; var unionResult = Department1.Union(Department2); foreach (var items in unionResult) { Console.WriteLine(items); } }
在上面的编码中,有两个元素集合Courses_1和Courses_2,其中包含课程名称,如下所示。
string[]Department1 = { "JAVA", "DOTNET", "PHYTHON", "ANDROID" }; string[]Department2 = { "JAVA", "ANDROID", "DESIGNING" };
我们必须从这两个集合中只返回唯一的元素,它删除了两个集合中的重复元素,为了获得所有唯一的元素,我们需要使用Union()方法。
var unionResult = Department1.Union(Department2);
它只从集合中返回唯一的元素,其中它删除了集合中存在的重复元素,它只返回一次;让我们看看下面的结果。
Result is {"JAVA", "DOTNET","DESIGNING", "PHYTHON", "ANDROID"};
IEqualityComparer接口的用法
这里我们为union方法引入了IEqualityComparer接口,因为union方法不能区分两种类型是否相等;它不能处理复杂类型的集合,所以它只返回错误的结果。为此,我们必须建立一个新的比较器类来实现IEqualityComparer接口以得到一个准确的结果。IEqualityComparer接口有两个不同的方法GetHashCode和Equals方法,我们需要强制性地实现这两个方法。让我们看看IEqualityComparer接口的一个例子,让我们假设Book类包含BookID和BookName。
class BookComparer : IEqualityComparer<Book> { public bool Equals(Book x, Book y) { if (x.BookID == y.BookID && x.BookName.ToLower() == y. BookName.ToLower()) return true; return false; } public int GetHashCode(Student obj) { return obj. BookID.GetHashCode(); } }
现在可以将BookComparer类发送到Union扩展方法中以获得准确的结果
List<BookClass> BookList_1 = new List< BookClass >(); BookList _1.Add(new BookClass { BookID = 1001, BookName = "The Writer" }); BookList _1.Add(new BookClass { BookID = 1002, BookName = " Success " }); BookList _1.Add(new BookClass { BookID = 1003, BookName = "Life Secret " }); List< BookClass > BookList _2 = new List< BookClass >(); BookList _2.Add(new BookClass { BookID = 1002, BookName = "Success" }); BookList _3.Add(new BookClass { BookID = 1005, BookName = "Team Lead " }); var _resultUnion = BookList _1.Union(BookList _2, new BookComparer()); foreach (BookClass res in _resultUnion) Console.WriteLine(res. BookName);
结果将是 "The Writer, Success, Life Secret, Team Lead",它只返回集合中唯一的元素,其中删除了重复元素。
例子
当处理复杂类型的联合集合时,你必须使用IEqualityComparer接口来获得一个准确的结果。IEqualityComparer接口有两个不同的方法GetHashCode和Equals方法,我们需要强制性地实现这两个方法。让我们看看一个示例程序。
程序
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Console_LINQUnion { class Linq_Union { internal class DoctorClass { public int DoctorID { get; set; } public string DoctorName { get; set; } } // UNION Operator with IEqualityComparer internal class DoctorComparer : IEqualityComparer<DoctorClass> { public bool Equals(DoctorClass a, DoctorClass b) { if(a.DoctorID==b.DoctorID&&b.DoctorName.ToLower()==b.DoctorName.ToLower()) { return true; } return false; } public int GetHashCode(DoctorClass obj) { return obj.DoctorID.GetHashCode(); } } public class Program { public static void Main(string[] args) { List<DoctorClass> DoctorList_1 = new List<DoctorClass>(); DoctorList_1.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1001, DoctorName = "Smith" }); DoctorList_1.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1002, DoctorName = "Rio" }); DoctorList_1.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1003, DoctorName = "Dev" }); DoctorList_1.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1004, DoctorName = "Jack" }); DoctorList_1.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1005, DoctorName = "Ricky" }); List<DoctorClass> DoctorList_2 = new List<DoctorClass>(); DoctorList_2.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1002, DoctorName = "Rio" }); DoctorList_2.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1003, DoctorName = "Dev" }); DoctorList_2.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1007, DoctorName = "Peter" }); DoctorList_2.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1009, DoctorName = "Raj" }); DoctorList_2.Add(new DoctorClass { DoctorID = 1001, DoctorName = "Smith" }); var _resultUnion = DoctorList_1.Union(DoctorList_2, new DoctorComparer()); Console.WriteLine("USING LINQ-UNION WITH IEqualityComparer"); Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------\n"); Console.WriteLine("List of Unique Doctor-Names\n"); foreach (DoctorClass val in _resultUnion) Console.WriteLine(val.DoctorName); Console.ReadLine(); } } } }
输出。
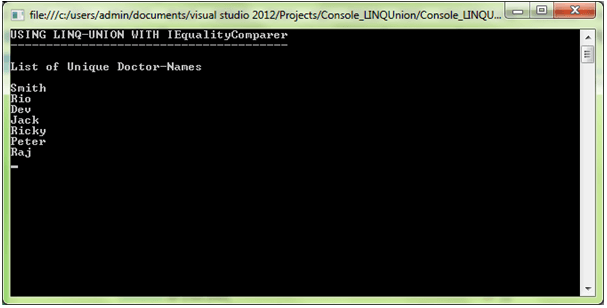
结论
文章中的LINQ联盟主要是用来组合元素的集合,并返回不同的元素作为结果,当处理复杂类型的庞大数据时,我们需要实现IEqualityComparer接口。希望这篇文章能通过程序化地看到这些例子,毫无疑问地帮助我们。
推荐文章
这是一篇关于LINQ联盟的指南。在这里,我们讨论了简介、语法、LINQ中如何联合工作?例子,以及代码实现。你也可以看看下面的文章,以了解更多的信息
The postLINQ Unionappeared first onEDUCBA.