kernel如何得到uboot启动信息
 \
\
一、uboot的的配置和编译
**
**
1、配置:make smdk6410_config
SRCTREE := $(CURDIR)
MKCONFIG := $(SRCTREE)/mkconfig
smdk6410_config : unconfig
@$(MKCONFIG) $(@:_config=) arm s3c64xx smdk6410 samsung s3c6410
mkconfig smdk6410 arm s3c64xx smdk6410 samsung s3c6410
s0 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6
生成如下两个文件:
include/config.mk include/config.h
建立两个软链接文件:
ln -s asm-arm asm
ln -s arch-smdk6410 asm-arm/arch
2、make
在编译到最后看到了如下一句:
“arm-linux-ld -Bstatic -T /home/uboot/u-boot-6410/board/samsung/smdk6410/u-boot.lds -Ttext 0xc7e00000 ........”
通过上述可知,uboot.bin的链接地址为:0xc7e00000(整个地址是在board/samsung/smdk6410/config.mk定义),链接脚本为:u-boot.lds
注意:u-boot.lds中定义了个“.u_boot_cmd”段,地址范围从__u_boot_cmd_start到__u_boot_cmd_end
二、uboot的源码分析:
uboot重要的功能如下:
1)关看门狗
2)初始化时钟
3)初始化SDRAM
4)初始化flash
5)初始化网卡、usb、串口等
6)加载内核并且启动内核喂你好你在干麻耶
从 u-boot.lds中可以看出“start.o”放在最前面,那么也就注定start.s是整个uboot第一个运行的文件,这样我们就可以从start.s开始分析uboot。
start.s做了如下的功能:
1)进入设置为svc
2)关看门狗
3)屏蔽中断
4)初始化
5)设置stack
6)时钟
7)代码重定位,从nand flash 到 sd ram
8)清bss段
9)start_armboot
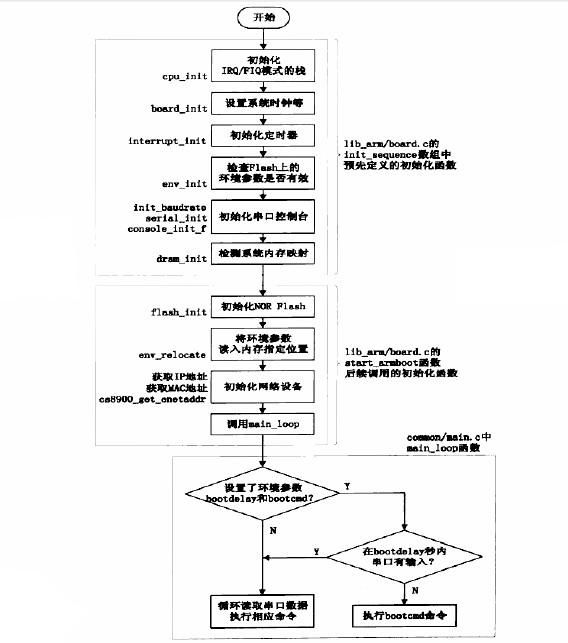
在进入了start_armboot之后工作流程如下图:
最后,从env变量中获取到bootcmd参数(nand read 0xc0008000 0x100000 0x500000;bootm 0xc0008000),执行到了” nand read 0xc0008000 0x100000 0x500000”命令,从nand flash 中将内核到内存中,之后就执行bootm 0xc0008000。最后将会调用如下函数:
do_bootm ->do_bootm_linux->theKernel
1、do_bootm:从0x500000中读取UImage的头部,填充到一个全局变量header 中。结构定义为:
[cpp] view plain copy
- typedef struct image_header {
- uint32_t ih_magic;
- uint32_t ih_hcrc;
- uint32_t ih_time;
- uint32_t ih_size;
- uint32_t ih_load;
- uint32_t ih_ep;
- uint32_t ih_dcrc;
- uint8_t ih_os;
- uint8_t ih_arch;
- uint8_t ih_type;
- uint8_t ih_comp;
- uint8_t ih_name[IH_NMLEN];
- } image_header_t;
其中我们关心的是“ih_load”和“ih_ep”两个成员,ih_load指定了内核应该在内存的地址,ih_ep指定了执行内核时的入口地址。
2、知道了内核的在内存的地址和内核的入口地址,我们就可以开始启动内核了,但是在启动内核之前,还需要一些信息(如: bootargs,内存的大小、串口的波特率等)告诉内核。这些信息的收集就由“do_bootm_linux”收集。将信息收集好后,怎么样告诉内核呢?很简单,就是按照双方约定内存地址中开辟一块内存,按照双方约定的格式存储就好了!存储的格式如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- struct tag_header {
- u32 size;
- u32 tag;
- };
-
- struct tag {
- struct tag_header hdr;
- union {
- struct tag_core core;
- struct tag_mem32 mem;
- struct tag_videotext videotext;
- struct tag_ramdisk ramdisk;
- struct tag_initrd initrd;
- struct tag_serialnr serialnr;
- struct tag_revision revision;
- struct tag_videolfb videolfb;
- struct tag_cmdline cmdline;
-
-
- struct tag_acorn acorn;
-
-
- struct tag_memclk memclk;
- } u;
- };
添加这些信息首先调用setup_start_tag (bd),添加完后调用setup_end_tag (bd)。
那这内存地址是在哪里呢?我们定义一个gd全局变量,内存地址保存在gd->bd-> bi_boot_params 中,对gb赋值是在函数“start_armboot”!gd的结构体的定义如下:
[cpp] view plain copy
- typedef struct bd_info {
- int bi_baudrate;
- unsigned long bi_ip_addr;
- unsigned char bi_enetaddr[6];
- struct environment_s *bi_env;
- ulong bi_arch_number;
- ulong bi_boot_params;
- struct
- {
- ulong start;
- ulong size;
- } bi_dram[CONFIG_NR_DRAM_BANKS];
- #ifdef CONFIG_HAS_ETH1
-
- unsigned char bi_enet1addr[6];
- #endif
- } bd_t
-
- typedef struct global_data {
- bd_t *bd;
- unsigned long flags;
- unsigned long baudrate;
- unsigned long have_console;
- unsigned long reloc_off;
- unsigned long env_addr;
- unsigned long env_valid;
- unsigned long fb_base;
- #ifdef CONFIG_VFD
- unsigned char vfd_type;
- #endif
- #if 0
- unsigned long cpu_clk;
- unsigned long bus_clk;
- unsigned long ram_size;
- unsigned long reset_status;
- #endif
- void **jt;
- } gd_t;
3、有了上述信息和配置后我们就可以开始启动内核,调用
theKernel (0, bd->bi_arch_number, bd->bi_boot_params),之后我们的linux内核就开始工作了,uboot的使命就完成了!
以下参考:blog.csdn.net/songqqnew/a…
从uboot启动内核的形式theKernel (0, machid, bd->bi_boot_params)
可以看出uboot给内核传递了3个参数,第1个是0,第2个是机器码,第3个是参数列表在SDRAM的起始位置
刚好满足一下调用内核的条件
• R0=0。
• R1=机器类型ID;
• R2=启动参数标记列表在RAM 中起始基地址
①在 uboot/board/davinci/dm365evm的board_init函数中uboot中:
机器码:
gd->bd->bi_arch_number = MACH_TYPE_DAVINCI_DM365_EVM
而#define MACH_TYPE_DAVINCI_DM365_EVM 1939 定义在arch\arm\include\asm\Mach-types.h中
kernel中:
需对应内核的linux/arch/arm/mach-davinci/Board-dm365-evm.c中一行代码
MACHINE_START(DAVINCI_DM365_EVM, "DaVinci_DM365x_EVM")
而DAVINCI_DM365_EVM定义在linux/asm
#define DAVINCI_DM365_EVM 1939
注:
machine type 不匹配
在内核自解压完成以后内核会首先会进入 bl __lookup_machine_type函数(在arch/arm/kernel/head.S中),检查machine_type是否匹配,如果不匹配会跳入__error_a函数(在arch/arm/kernel/head-common.S中),导致启动失败
②指定参数位置:
在uboot:
uboot/board/davinci/dm365evm 的board_init函数中
gd->bd->bi_boot_params=PHYS_SDRAM_1+0x100 //
#definde PHYS_SDRAM_1 0x80000000 定义在include\configs\Davin_dm365evm.h
在kernel中:
对应内核的linux/arch/arm/mach-davinci/Board-dm365-evm.c中一行代码.boot_params = (0x80000100),
如果uboot没有给出gd->bd->bi_boot_params的值,则linux默认去这个地址寻址tag
如果uboot给出了gd->bd->bi_boot_params的值,则linux则按照uboot的给的这个地址去寻址tag
所以即使uboot中设置 gd->bd->bi_boot_params = 0x30000000或 0x30000200或 0x300000300(或许设置一个空闲的内存区就可以)
而内核的.boot_params = S3C2410_SDRAM_PA + 0x100,(就用不到了也能顺利启动内核,已试过
在试验中发现uboot中设置gd->bd->bi_boot_params=0或将gd->bd->bi_boot_params注释掉,都未能顺利启动内核。貌似在uboot必须为gd->bd->bi_boot_params指定一个值才行,而linux的.boot_params 始终都没有用到。
gd是一个全局结构体指针,用于uboot中各个文件中重要的参数传递,其成员见blog.csdn.net/songqqnew/a…
看一下uboot在sdram 0x30000100处给内核传递了什么东东,见blog.csdn.net/songqqnew/a…
参考嵌入式Linux应用开发完全手册ch15.1 p243