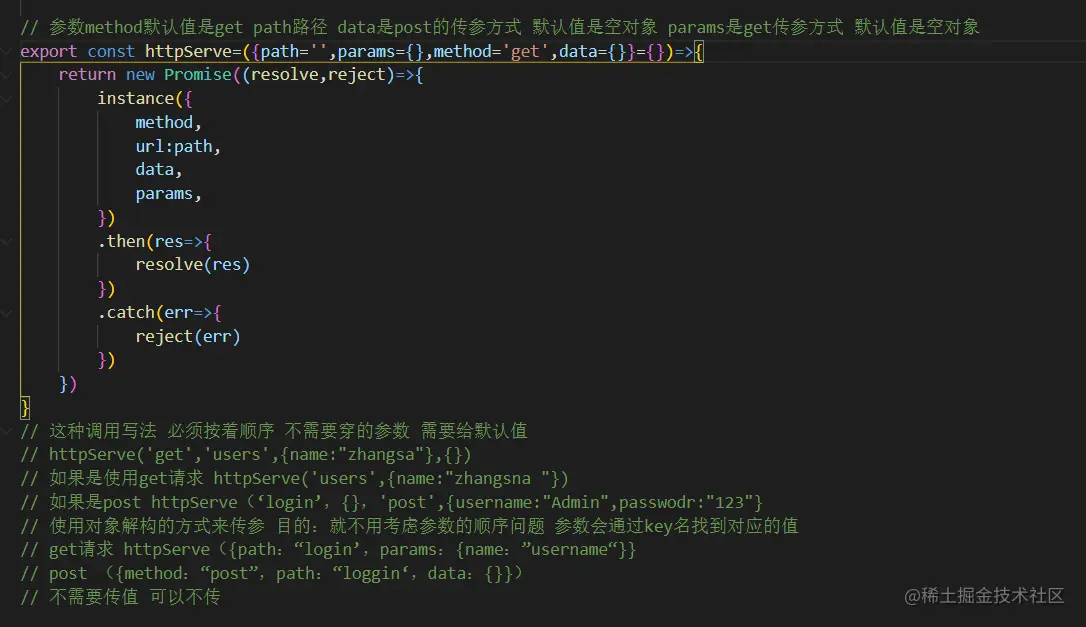
- 使用对象解构的方式来传参 目的:就不用考虑参数的顺序问题 参数会通过key名找到对应的值 不用传的参 直接不写
// 局部axios请求
let instance=axios.create({
baseURL:"",
timeout:5000,
})
// 局部的请求拦截器
instance.interceptors.request.use(
config => {
// 每次发送请求之前判断是否存在token
// 如果存在,则统一在http请求的header都加上token,这样后台根据token判断你的登录情况,此处token一般是用户完成登录后储存到localstorage里的
localStorage.token && (config.headers.Authorization = localStorage.token)
return config
},
error => {
return Promise.error(error)
})
// 局部响应拦截器axios.
instance.interceptors.response.use(response => {
return response
}, error => {
return error
})
// 参数method默认值是get path路径 data是post的传参方式 默认值是空对象 params是get传参方式 默认值是空对象
export const httpServe=({path='',params={},method='get',data={}}={})=>{
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
instance({
method,
url:path,
data,
params,
})
.then(res=>{
resolve(res)
})
.catch(err=>{
reject(err)
})
})
}
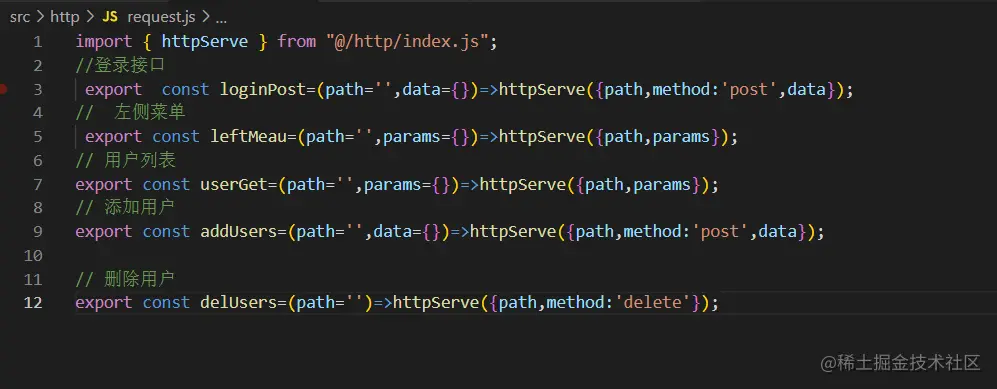
import { httpServe } from "@/http/index.js";
//登录接口
export const loginPost=(path='',data={})=>httpServe({path,method:'post',data});
// 左侧菜单
export const leftMeau=(path='',params={})=>httpServe({path,params});
// 用户列表
export const userGet=(path='',params={})=>httpServe({path,params});
// 添加用户
export const addUsers=(path='',data={})=>httpServe({path,method:'post',data});
// 删除用户
export const delUsers=(path='')=>httpServe({path,method:'delete'});