一起养成写作习惯!这是我参与「掘金日新计划 · 4 月更文挑战」的第3天,点击查看活动详情。
1.1 反射概述
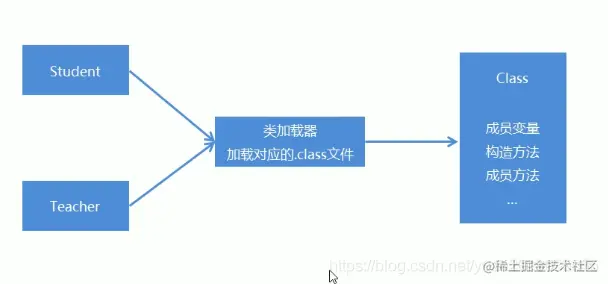
- Java反射机制:是指在运行时去获取一个类的变量和方法信息。然后通过获取到的信息来创建对象,调用方法的一种机制。由于这种动态性,可以极大的增强程序的灵活性,程序不用在编译期就完成确定,在运行期仍然可以扩展
1.2 反射获取Class类的对象
- 我们要想通过反射去使用一个类,==首先我们要获取到该类的字节码文件对象==,也就是类型为Class类型的对象这里我们提供三种方式获取Cass类型的对象
-
1、使用类的class属性来获取该类对应的Class对象。举例: Student.class将会返回Student类对应的Class对象
-
2、调用对象的getClass()方法, 返回该对象所属类对应的Class对象
该方法是Object类中的方法,所有的Java对象都可以调用该方法
-
3、使用Class类中的静态方法forName(StringclassName), 该方法需要传入字符串参数,该字符串参数的值是某个类的全路径,也就是完整包名的路径
package test;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<Student> c1 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c1);
Class<Student> c2 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c1 == c2);
Student s = new Student();
Class<? extends Student> c3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(c1 == c3);
Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("test.Student");
System.out.println(c1 == c4);
}
}
1.3 反射获取构造方法并使用
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() | 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组 |
Constructor<?> [] getDeclaredConstructors [dɪˈkleəd] | 返回所有构造方法对象的数组 |
Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>...parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共构造方法对象 |
Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?> ...parameterTypes) | 返回单个构造方法对象 |
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
| T newInstance(Object...initargs) | 根据指定的构造方法创建对象 |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
Constructor<?>[] cons1 = c.getConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons1) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Constructor<?>[] cons2 = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons2) {
System.out.println(con);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Constructor<?> con1 = c.getConstructor();
Object obj1 = con1.newInstance();
System.out.println(obj1);
}
}
1.4 反射获取成员变量并使用
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
| Field[ ] getFields() | 返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组 |
| Field[ ] getDeclaredFields() | 返回所有成员变量对象的数组 |
| Field getField(String name) | 返回单个公共成员变量对象 |
| Field getDeclaredField(String name) | 返回单个成员变量对象 |
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
| void set(Object obj, Object value) | 给obj对象的成员变量赋值为value |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
Field[] fields1 = c.getFields();
for(Field field:fields1) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Field[] fields2 = c.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field:fields2) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("--------");
Field addressField = c.getField("address");
System.out.println(addressField);
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
addressField.set(obj,"成都");
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
1.5 反射获取成员方法并使用
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
| Method[ ] getMethods() | 返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的 |
| Method[ ] getDeclaredMethods() | 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的 |
| Method getMethod(String name, Class<?> .. parameterTypes) | 返回单个公共成员方法对象 |
| Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?> .. parameterTypes) | 返回单个成员方法对象 |
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|
| Object invoke(Object obj, Objet... args) | 调用obj对象的成员方法,参数是args,返回值是Object类型 |
package test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
Class<?> c = Class.forName("test.Student");
Method[] methods1 = c.getMethods();
for(Method method:methods1) {
System.out.println(method);
}
System.out.println("---------");
Method[] methods2 = c.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method method:methods2) {
System.out.println(method);
}
Method m = c.getMethod("method1");
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
m.invoke(obj);
}
}