变量&常量&运算符
变量

public class Demo03 {
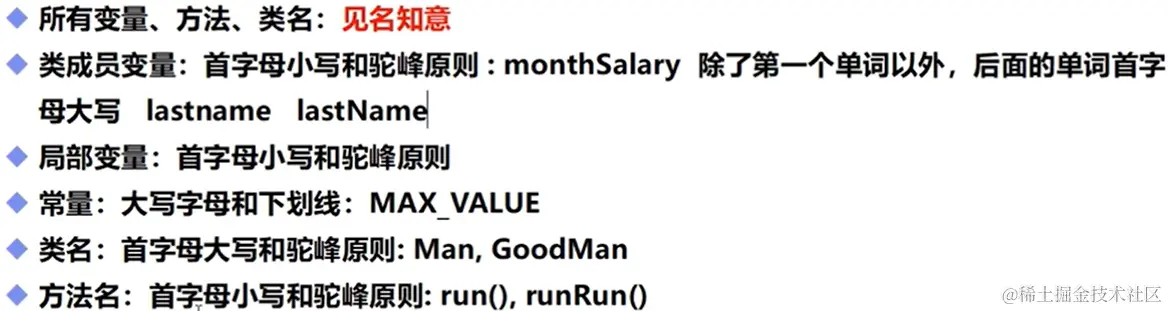
static double salary = 10000;
String name;
int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 10;
System.out.println(i);
Demo03 demo03 = new Demo03();
System.out.println(demo03.age);
System.out.println(demo03.name);
System.out.println(salary);
}
}
常量
public class Demo04 {
static final double PI = 17;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(PI);
}
}
运算符
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 二元运算符的注意事项
int a = 10
int b = 20
// 因为a,b都是整数型 所以最后的输出类型也是整数型
System.out.println(a/b)
System.out.println(a/(double)b)
long w = 12345671
int x = 123
short y = 10
byte z = 8
// 只有long类型和double类型的数据 经过计算之后 还是long类型或double类型的数据 ,其余都是int类型的数据
System.out.println(w+x+y+z)
System.out.println(x+y+z)
System.out.println(y+z)
// 幂运算 (使用一些工具类来操作)
double pow = Math.pow(2,3)
System.out.println(pow)
// 逻辑运算符
boolean i = true
boolean j = false
System.out.println("(i&&j):"+(i&&j))
System.out.println("(i||j):"+(i||j))
System.out.println("!(i&&j):"+!(i&&j))
// 短路运算 c&&d c判断出来已经是错的了 代码不会再向后运行 即c++ 不会被执行
int c = 5
boolean d = (c<1)&&(c++<2)
System.out.println(d)
System.out.println(c)
// 位运算
/*
A = 0001 1010
B = 1010 0010
A&B = 0000 0010 都为1 的时候才是1
A/B = 1011 1010 都为0 的时候才是0
A^B = 0100 0111 一样的才是1 不一样的是0
~B = 0101 1101 1变成0 0变成1
面试题:2*8如何用最快的方法计算出16 2*2*2*2 (位运算的效率极高)
>> 相当于*2
<< 相当于/2
0000 0000 0
0000 0001 1
0000 0010 2
0000 0100 4
0000 1000 8
0001 0000 16
*/
System.out.println(2<<3)
// 字符串连接符 (面试题:为何会出现以下的结果)
int q = 10
int p = 20
// ""+q+p 如果“”在前面,字符串进行拼接
// q+p+"" 如果“”在后面,q+p进行正常的运算
System.out.println(""+q+p)
System.out.println(q+p+"")
// 三元运算符
// x ?y : z 如果x==true,则结果为y 否则结果为z
int score = 80
int score2 = 100
int result = (score>score2)?score:score2
System.out.println(result)
}
}