又到了金三银四的春招了,前端仔也是在积极的准备面试,刷算法、刷面经、回顾项目.....。在面试中也是遇到了许许多多的原题,最最最频繁遇到的就是:遇到过跨域嘛?怎么解决?看的多自然也能随便回答出几种
- jsonp解决
- nginx反向代理
- CORS解决跨域
- vue-cli代理服务器
....
其实还有很多,但是常用的就是这几种,惭愧的是,自己原来有一招鲜,吃遍天的想法,就试过CORS、vue-cli、jsonp这几种,今天整理下这些方法,并实践测试一波!
1.什么是跨域请求拦截?
在开始解决问题之前,我们先要知道问题是什么。所谓的跨域其实是浏览器的保护策略,被称为同源策略,如果没了这个策略。浏览器就很容易受到攻击(XXS,CSRF),简单的说,就是没有了跨域资源限制的话,你的身份信息如cookie这些就可以有办法被获得,进行伪造,或者直接在你登录A网站的时候,偷偷的让你给B网站发送请求,模拟你的操作。那么这个策略的标准是什么呢? 域名+协议+端口 只要有一个不同,那么就是跨域请求!
2.jsonp解决跨域
原理:同源策略限制了资源的加载,但是不是所有的资源的加载!
<img src="xxx"/>
<link src="xxx"/>
<script src="xxx"/>
这些标签加载的资源是不受影响的,所以jsonp就是借助这个来发起请求,获取对应的资源!
1.搭建简易服务器
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request", function (req, res) {
console.log("接收到了请求,客户端的地址为:", req.socket.remoteAddress);
res.end("hello world");
});
server.listen(5000, function () {
console.log("服务器启动成功!");
});
服务器搭建的非常随意,不过能接受请求,返回数据就行了,大行不顾细谨。
2.前端页面来发起请求
2.1跨域请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
fetch("http://localhost:5000").then((res)=>{
console.log(res);
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
依旧朴实无华的代码,模拟产生了跨域请求(端口号不同产生了跨域)!
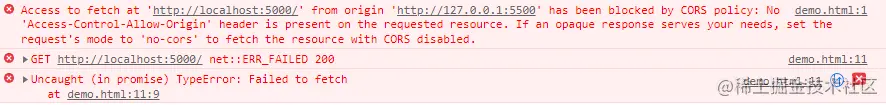
2.2jsonp模拟解决
简单改一下服务器的代码
const http = require("http");
const urllib = require("url");
const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request", function (req, res) {
console.log("接收到了请求,客户端的地址为:", req.socket.remoteAddress);
const param = urllib.parse(req.url, true);
if (param.query.callback) {
let result = param.query.callback + "('helloworld')";
res.end(result);
} else {
res.end("hello world");
}
});
server.listen(5000, function () {
console.log("服务器启动成功!");
});
简单改一下前端代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function getSomething(data) {
console.log(data);
}
</script>
<script src="http://localhost:5000?callback=getSomething"></script>
</body>
</html>
结果很显,我们成功获得了helloworld数据,完成了跨域的请求,通过script标签不受同源策略的影响,传递一个回调函数给服务器,服务器返回改回调的执行形式,script就是自动执行指定的回调,获取得到函数的形式参数就是所要的数据!
3.nginx反向代理解决跨域请求
原理:要知道跨域请求是限制服务器和浏览器的,而服务器和服务器之间是不会有同源策略的,如果我们能将不同源的请求转发到和浏览器同源的服务器,服务器再进行请求,是不是就解决了跨域请求了呢?说干就干!
1.下载安装nginx
2.修改配置文件
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
# 这里是访问的域名
server_name a.com;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
# 这里是前端的IP和端口
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5500;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
# 这里是后端的接口地址
location /tset/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:5500;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
配置完成后重新启动nginx就可以正常访问了
以下是常用的nginx的命令
start nginx 开启 nginx -s stop 停止 nginx -s reload 重新加载
3.CORS解决跨域
通过给响应头添加字段完成跨域请求
1.简单请求直接添加access-control-allow-origin
所谓的简单请求要求如下
- 请求方法为 GET、POST 或者 HEAD
- 请求头的取值范围: Accept、Accept-Language、Content-Language、Content-Type(只限于三个值`application/x-www-form-urlencoded`、`multipart/form-data`、`text/plain`)
我们简单的修改下服务端的代码就完成请求的发送
const http = require("http");
const urllib = require("url");
const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request", function (req, res) {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
console.log("接收到了请求,客户端的地址为:", req.socket.remoteAddress);
const param = urllib.parse(req.url, true);
if (param.query.callback) {
let result = param.query.callback + "('helloworld')";
res.end(result);
} else {
res.end("hello world");
}
});
server.listen(5000, function () {
console.log("服务器启动成功!");
});
这里的*表示什么域名都可以访问,你可以根据需要进行设置。
2.非简单请求
显然不是简单请求那就是非简单请求了嘛
非简单请求相对而言会有些不同,体现在两个方面: 预检请求和响应字段。
我们增加以下字段就行了
Access-Control-Request-Method: PUT
Access-Control-Request-Headers: X-Custom-Header
当然这里的put和X-Custom-Header根据你的需求来就好了!
如果请求中你还需要携带cookie的话那么就要加这个字段
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials:true
前端要配合设置
withCredentials
4.vue-cli代理服务器
原理:通过代理服务器,我们将请求给到代理服务器,服务器再转发到服务器上,由于服务器和服务器不存在跨域的问题,所以一样可以解决跨域资源的访问。
module.exports = {
pages: {
index: {
entry: "src/main.js",
},
},
lintOnSave: false,
devServer: {
proxy: {
"/test": {
target: "http://localhost:5000",
pathRewrite: { "^/test": "" },
},
"/index": {
target: "http://localhost:5000",
pathRewrite: { "^/index": "" },
},
},
},
};