中介者模式
- 案例,智能家庭包括多个设备,在看电视时,协同工作
- Mediator Pattern,行为型模式,子系统内部不发生关系,用户通过中介获得结果,中介分别与子系统发生关系
- 使各个子系统不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,独立他们之间的交互
- MVC,View通过Controller与Model交互
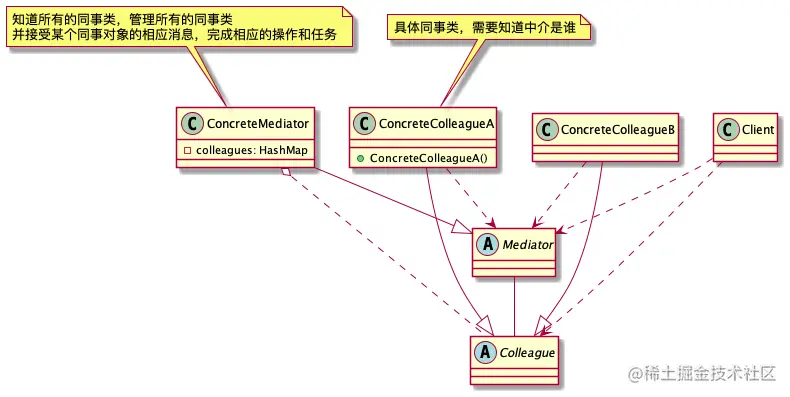
- 案例类图
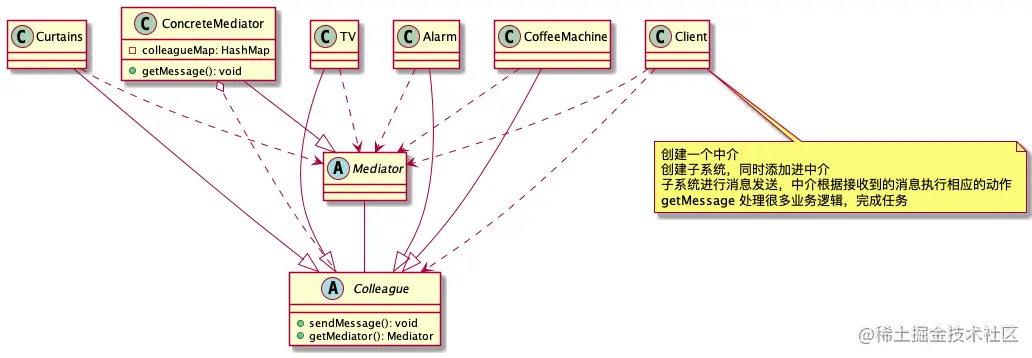
- 抽象中介类,注册子系统,处理核心业务
public abstract class Mediator {
public abstract void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague);
public abstract void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName);
}
public class ConcreteMediator extends Mediator {
private HashMap<String, Colleague> colleagueMap;
private HashMap<String, String> interMap;
public ConcreteMediator() {
colleagueMap = new HashMap<>();
interMap = new HashMap<>();
}
@Override
public void Register(String colleagueName, Colleague colleague) {
colleagueMap.put(colleagueName, colleague);
if (colleague instanceof Alarm) {
interMap.put("Alarm", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
interMap.put("CoffeeMachine", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof TV) {
interMap.put("TV", colleagueName);
} else if (colleague instanceof Curtains) {
interMap.put("Curtains", colleagueName);
}
}
@Override
public void GetMessage(int stateChange, String colleagueName) {
if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Alarm) {
if (stateChange == 0) {
((CoffeeMachine) (colleagueMap.get(interMap
.get("CoffeeMachine")))).StartCoffee();
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StartTv();
} else if (stateChange == 1) {
((TV) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("TV")))).StopTv();
}
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof CoffeeMachine) {
((Curtains) (colleagueMap.get(interMap.get("Curtains"))))
.UpCurtains();
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof TV) {
} else if (colleagueMap.get(colleagueName) instanceof Curtains) {
}
}
}
public abstract class Colleague {
private Mediator mediator;
public String name;
public Colleague(Mediator mediator, String name) {
this.mediator = mediator;
this.name = name;
}
public Mediator GetMediator() {
return this.mediator;
}
public abstract void SendMessage(int stateChange);
}
public class Alarm extends Colleague {
public Alarm(Mediator mediator, String name) {
super(mediator, name);
mediator.Register(name, this);
}
public void SendAlarm(int stateChange) {
SendMessage(stateChange);
}
@Override
public void SendMessage(int stateChange) {
GetMediator().GetMessage(stateChange, name);
}
}
小结
- 多个类相互耦合形成网状结构,中介者将网状结构分离为星状结构,进行解耦
- 减少类间依赖,降低耦合,符合迪米特原则
- 但是,中介者承担了较多责任,会比较复杂
备忘录模式
- 案例,游戏角色状态恢复,角色有攻击力和防御力,大战Boss前需要保存自身的状态,大战后状态下降,要在大战Boss前恢复
- Memento Pattern,行为型模式,在不破坏封装性的前提,捕获一个对象的内部状态,在该对象之外保存这个状态
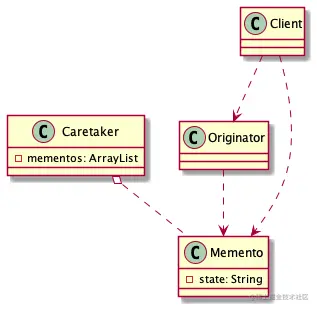
- 角色,需要保存状态的对象
public class Originator {
private String state;
public Memento saveStateMemento() {
return new Memento(state);
}
public void getStateFromMemento(Memento memento) {
state = memento.getState();
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
public class Memento {
private String state;
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public Memento(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
- 备忘录对象管理对象,保存多个角色的多个状态下的多个备忘录对象
public class Caretaker {
private Map<Originator, List<Memento>> map = new HashMap<>();
public void add(Originator originator, Memento memento) {
map.putIfAbsent(originator, new ArrayList<>());
map.get(originator).add(memento);
}
public Memento get(Originator originator, int idx) {
return map.get(originator).get(idx);
}
}
案例
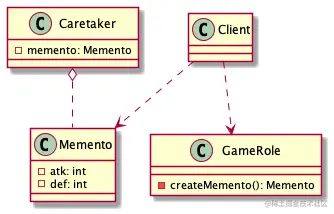
public class Caretaker {
private Memento memento;
public Memento getMemento() {
return memento;
}
public void setMemento(Memento memento) {
this.memento = memento;
}
}
public class Memento {
private int atk;
private int def;
public Memento(int atk, int def) {
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
}
public class GameRole {
private int atk;
private int def;
public GameRole(int atk, int def) {
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public Memento createMemento() {
return new Memento(atk, def);
}
public void recoverGameRoleFromMemento(Memento memento) {
this.atk = memento.getAtk();
this.def = memento.getDef();
}
public void display() {
System.out.println(atk + " - " + def);
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
小结
- 一种状态恢复机制,可以回到某个历史状态,实现信息的封装,不需要关心状态的保存细节
- 适用于后悔药、游戏存档、撤销/回退、数据库的事物管理
- 可以和原型模式配合使用,可以直接通过
原型模式快速的复制一个对象,直接把对象保存下来