Android API 11 源码查看
Zygote进程创建?
总结一下ZygoteInit的main方法都做了哪些事情:
1.创建了一个Server端的Socket
2.预加载类和资源
3.启动了SystemServer进程
4.等待AMS请求创建新的应用程序进程
最后再总结一下Zygote进程启动公做了几件事:
1.创建AndroidRuntime并调用其start方法,启动Zygote进程。
2.创建Java虚拟机并为Java虚拟机注册JNI方法。
3.通过JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数进入Zygote的java框架层。
4.通过registerZygoteSocket方法创建服务端Socket,并通过runSelectLoop方法等待AMS的请求来创建新的应用程序进程。
5.启动SystemServer。
SystemServer进程创建过程?
1.runSelectLoop函数处理AMS 发送的请求进程
SystemServer进程:
1.启动Binder线程池
2.创建了SystemServiceManager(用于对系统服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理)
3.启动了各种服务
SystemServer 怎么关联 AMS的(AMS什么时候创建的)?
AMS怎么关联了ATMS的?
ActivityManager是什么?
根据类的介绍来看:ActivityManager 就是一个管理类,是对Activity管理、运行时功能管理和运行时数据结构的封装,进程(Process)、应用程序/包、服务(Service)、任务(Task)信息等:
ActivityManager mActivityManager = (ActivityManager)getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
获取实例,从而获取ActivityManager管理的 进程,包名,服务等内容。
public List<RunningAppProcessInfo> getRunningAppProcesses() {
}
@Deprecated
public List<RunningServiceInfo> getRunningServices(int maxNum)
throws SecurityException {
}
@Deprecated
public List<RunningTaskInfo> getRunningTasks(int maxNum)
throws SecurityException {
}
AMS作用?
AMS 和 ATMS 区别?看出来 ATMS 初始化也是在AMS 里面进行,而且包含了对他的管理
Android 桌面(Launcher)启动流程?
**AMS怎么管理得四大组件?**
**Activity启动流程?**
**Activity先创建还是Application先创建?** [流程启动代码说明参考这个](https://www.freesion.com/article/83351017344/) **OnCreate调用方法** 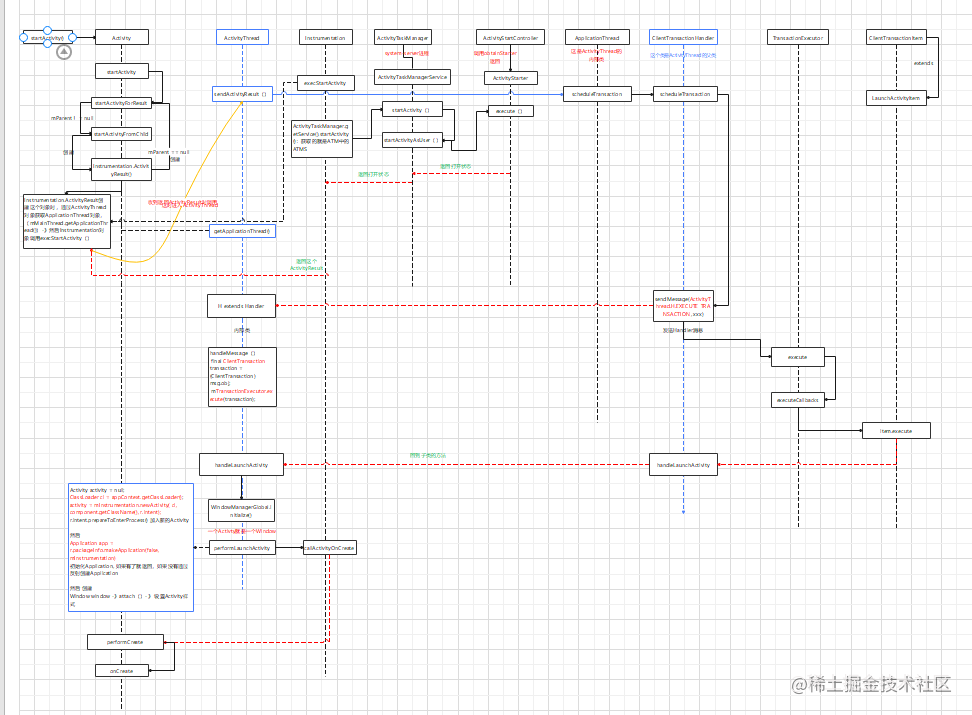 **OnResume调用方法**
Activity启动完成 查看启动流程全面
Activity 先创建 那么 Application 的onCreate方法在哪里运行?
从栈顶Activity的onPause到启动activityon的Resume过程
ActivityStack.startPausingLocked()
IApplicationThread.schedulePauseActivity()
ActivityThread.sendMessage()
ActivityThread.H.sendMessage();
ActivityThread.H.handleMessage()
ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity()
ActivityThread.performPauseActivity()
Activity.performPause()
Activity.onPause()
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token)
ActivityManagerService.activityPaused()
ActivityStack.activityPausedLocked()
ActivityStack.completePauseLocked()
ActivityStack.resumeTopActivitiesLocked()
ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked()
ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked()
ActivityStack.startSpecificActivityLocked
Application 的创建流程?
startActivity到怎么创建进程
这表文章写了关于启动的整个流程包含了怎么创建的应用进程
AMS就是ActivityManagerService,是由zygote进程孵化出第一个java进程system_server,在com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit类的main 方法中:
//ZygoteInit main方法 6件事:1.registerZygoteSocket,
//2.调用preload加载资源,3.利用gcAndFinalize初始化gc,4.启动SystemServer,
//5.调用runSelectLoop运行Zygote进程选择的looper,6.关闭和清理zygote sockets
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
Runnable caller;
try {
RuntimeInit.preForkInit();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
//开始system-server
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
//加载资源
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
//初始化GC
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
if (!isRuntimeRestarted) {
if (isPrimaryZygote) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
} else if (zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME)) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
}
}
Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);
//创建一个 Socket
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
if (startSystemServer) {
//创建system-server 进程
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
if (zygoteServer != null) {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
}
}
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
//fork 进程
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
+ "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010,3011",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
//解析args指令
parsedArgs = new ZygoteArguments(args);
Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
if (Zygote.nativeSupportsTaggedPointers()) {
/* Enable pointer tagging in the system server. Hardware support for this is present
* in all ARMv8 CPUs. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_TBI;
}
/* Enable gwp-asan on the system server with a small probability. This is the same
* policy as applied to native processes and system apps. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.GWP_ASAN_LEVEL_LOTTERY;
if (shouldProfileSystemServer()) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
/* Request to fork the system server process */
//去fork 一个进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
//当创建子进程的时候 pid 进程Id 为0
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
//通知创建进程完成
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits,
permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Set the Java Language thread priority to the default value for new apps.
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
private static native int nativeForkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities);
nativeForkSystemServer创建system_server进程,创建成功后 调用 handleSystemServerProcess
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs) {
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
// Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
// prevents it.
if (shouldProfileSystemServer() && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) {
try {
Log.d(TAG, "Preparing system server profile");
prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerClasspath);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e);
}
}
}
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
String[] args = parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, amendedArgs, 2, args.length);
args = amendedArgs;
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected return from WrapperInit.execApplication");
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
//通过反射会调用到SystemServer 的 main 函数
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mDisabledCompatChanges,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
这时 从 Zygote 进入 system-server进程, SystemServer 的 main:
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
//5件事:1、初始化设置一些系统属性;2、准备MainLooper;
//3、初始化system context对象;4、创建system service manager;
//5、调用startBootstrapServices(),startCoreServices(),startOtherServices()启动各种service
private void run() {
// 初始化一些系统属性
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// The system server should always load safe labels
PackageItemInfo.forceSafeLabels();
// Default to FULL within the system server.
SQLiteGlobal.sDefaultSyncMode = SQLiteGlobal.SYNC_MODE_FULL;
// Deactivate SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags until settings provider is initialized
SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags.init(null);
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Within the system server, when parceling exceptions, include the stack trace
Parcel.setStackTraceParceling(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
//准备Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
Looper.getMainLooper().setSlowLogThresholdMs(
SLOW_DISPATCH_THRESHOLD_MS, SLOW_DELIVERY_THRESHOLD_MS);
SystemServiceRegistry.sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf = true;
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
//创建SystemServer的上下文SystemContext 并且ActivityThread 在这里面进行初始化
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
// Call per-process mainline module initialization.
ActivityThread.initializeMainlineModules();
//实例化一个SystemServiceManager对象
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
//开启一些系统服务
startBootstrapServices(t);
startCoreServices(t);
startOtherServices(t);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
在SystemServer的run方法里面 需要关注的时
startBootstrapServices(t); 和 startOtherServices(t);
这个时候才进入到android.app.ActivityThread 的main 方法里面