实现光线追踪:
- Renderer.cpp 中的 Render():这里你需要为每个像素生成一条对应的光线,然后调用函数 castRay() 来得到颜色,最后将颜色存储在帧缓冲区的相应像素中。
- Triangle.hpp 中的 rayTriangleIntersect(): v0, v1, v2 是三角形的三个 顶点,orig 是光线的起点,dir 是光线单位化的方向向量。tnear, u, v 是你需 要使用我们课上推导的 Moller-Trumbore 算法来更新的参数。
渲染函数:
```
void Renderer::Render(const Scene& scene)
{
std::vector<Vector3f> framebuffer(scene.width * scene.height);
float scale = std::tan(deg2rad(scene.fov * 0.5f));
float imageAspectRatio = scene.width / (float)scene.height;
Vector3f eye_pos(0);
int m = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < scene.height; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < scene.width; ++i)
{
float x;
float y;
float nx=(i+0.5f)/(scene.width/2.0f)-1.0f;
float ny=-((j+0.5f)/(scene.height/2.0f)-1.0f);
x=nx*scale*imageAspectRatio;
y=ny*scale;
Vector3f dir = Vector3f(x, y, -1);
dir=normalize(dir);
framebuffer[m++] = castRay(eye_pos, dir, scene, 0);
}
UpdateProgress(j / (float)scene.height);
}
FILE* fp = fopen("binary.ppm", "wb");
(void)fprintf(fp, "P6\n%d %d\n255\n", scene.width, scene.height);
for (auto i = 0; i < scene.height * scene.width; ++i) {
static unsigned char color[3];
color[0] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].x));
color[1] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].y));
color[2] = (char)(255 * clamp(0, 1, framebuffer[i].z));
fwrite(color, 1, 3, fp);
}
fclose(fp);
}
```
对Möller Trumbore算法的简单运用求三角形和线的交点
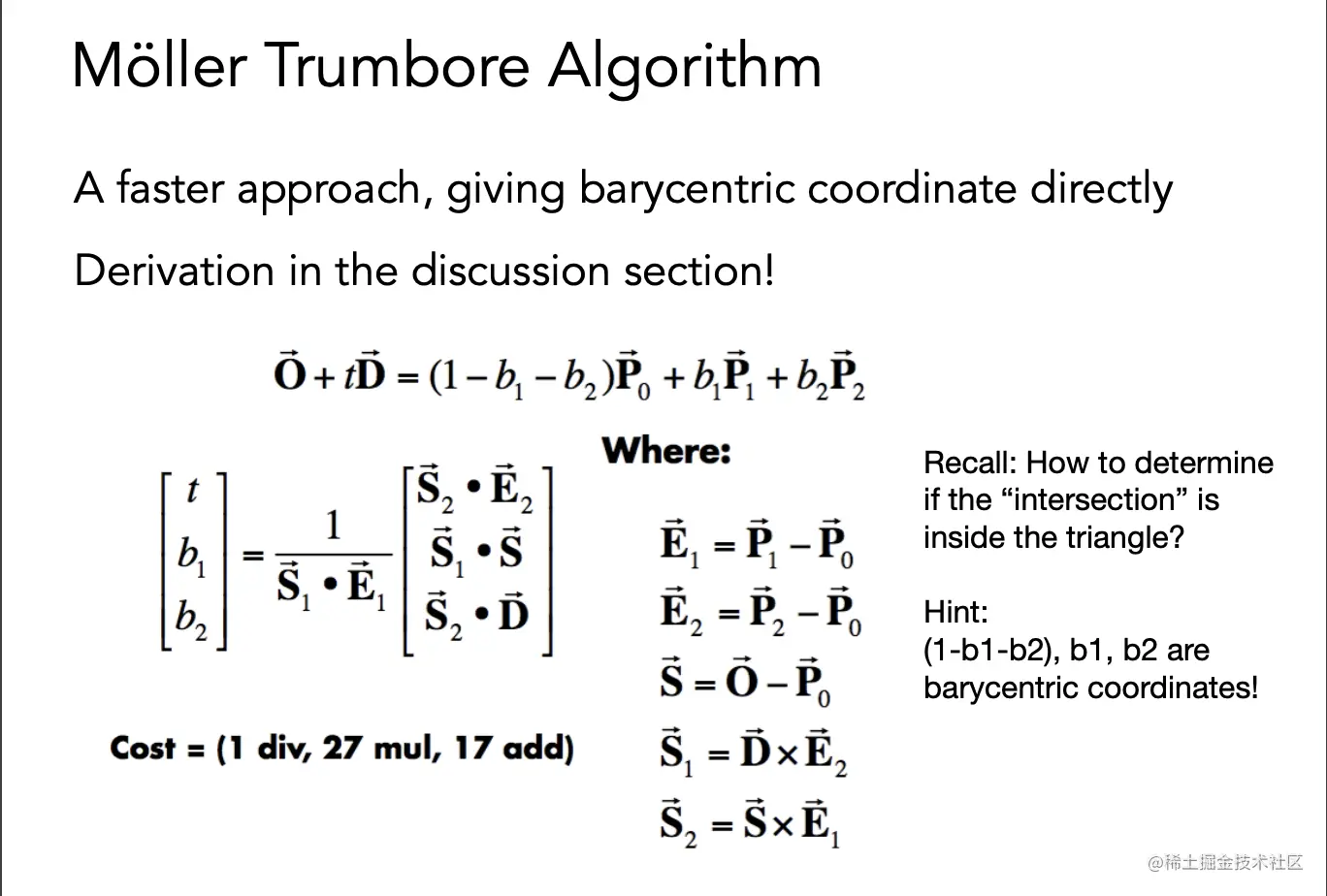
//求三角形和射线的交点,并把相应数据写入对应变量
bool rayTriangleIntersect(const Vector3f& v0, const Vector3f& v1, const Vector3f& v2, const Vector3f& orig,
const Vector3f& dir, float& tnear, float& u, float& v)
{
// TODO: Implement this function that tests whether the triangle
// that's specified bt v0, v1 and v2 intersects with the ray (whose
// origin is *orig* and direction is *dir*)
// Also don't forget to update tnear, u and v.
//对Möller Trumbore算法应用
Vector3f e1=v1-v0
Vector3f e2=v2-v0
Vector3f s=orig-v0
Vector3f s1= crossProduct(dir,e2)
Vector3f s2= crossProduct(s,e1)
float s1e1=1.f/ dotProduct(s1,e1)
Vector3f mv(dotProduct(s2,e2), dotProduct(s1,s), dotProduct(s2,dir))
float t=s1e1*mv.x
float b1=s1e1*mv.y
float b2=s1e1*mv.z
if(t>0&&b1>0&&b2>0&&(1-b1-b2)>0){
tnear=t
u=b1
v=b2
return true
}
return false
}