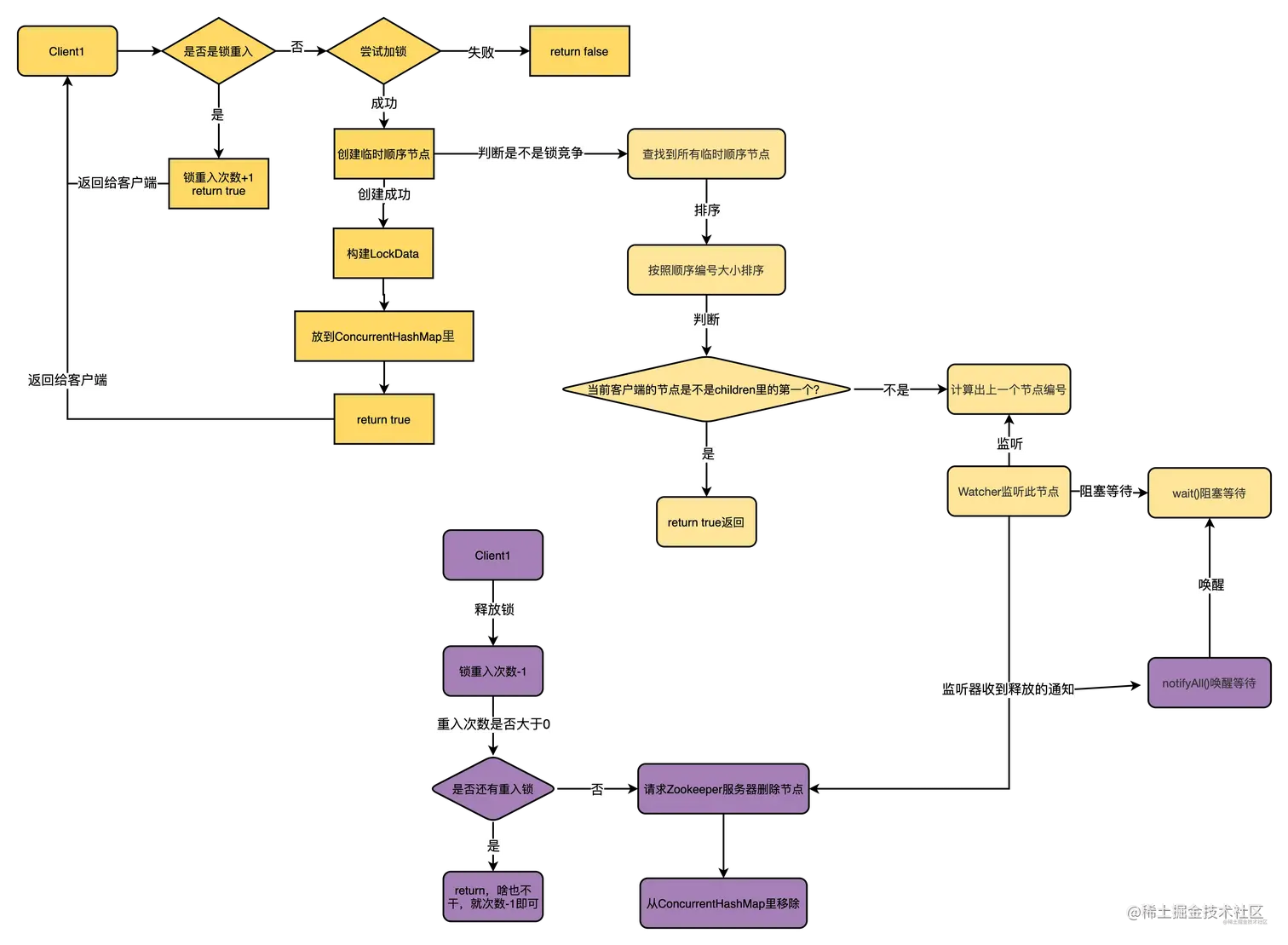
原理
- ZooKeeper通过临时节点实现加锁,解锁,重入等操作。
- 临时节点续期
- ZooKeeper的节点是通过session心跳来续期的,比如客户端1创建了一个节点, 那么客户端1会和ZooKeeper服务器创建一个Session,通过这个Session的心跳来维持连接。如果ZooKeeper服务器长时间没收到这个Session的心跳,就认为这个Session过期了,也会把对应的节点删除。简单来说就是:当客户端宕机后,临时节点会随之消亡。
- 锁类型:公平锁,顺序抢占。来一个请求新建一个节点名称:node_01,node_02,node_03,01抢到锁后,02等待,01释放后,02抢锁,以此类推。
- 到期处理:删除临时节点
代码
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
return internalLock(time, unit);
}
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
if ( lockPath != null ) {
LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {
try {
ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e ) {
}
return null;
}
public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception {
return client
.create()
.creatingParentContainersIfNeeded()
.withProtection()
.withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL)
.forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);
}
private static class LockData {
final Thread owningThread;
final String lockPath;
final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
}
- 互斥逻辑
- 查找到所有临时顺序节点,然后按照编号从小到大排序
- 判断当前客户端是不是 children 里的第一个,不是的话就代表不能加锁,那就计算出上一个节点编号,然后开启一个 Watcher 监听这个节点(刚计算出来的上一个节点)
- wait() 。
private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception {
boolean haveTheLock = false;
try {
while ((client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock) {
List<String> children = getSortedChildren();
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1);
PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
if (predicateResults.getsTheLock() ) {
haveTheLock = true;
} else {
String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();
synchronized(this) {
try {
client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);
wait();
} catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e ) {}
}
}
}
}
return haveTheLock;
}
public void release() throws Exception {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
int newLockCount = lockData.lockCount.decrementAndGet();
if ( newLockCount > 0 ) {
return;
}
try {
internals.releaseLock(lockData.lockPath);
}
finally {
threadData.remove(currentThread);
}
}
整体流程