View的绘制过程
- Q:知道了activity_main.xml是如何添加到DecorView的,那这个DecorView是如何添加到Window的呢?
- 简单回顾下Phonewindow#setCountView的过程
1.创建好DecorView
2.先确定好activtiy的父布局即mContentParent是 #generateLayout得到的
3.在generateLayout方法中通过判断确定好layoutResource(系统预设的xml布)局
4.找到在layoutResource中id为com.android.internal.R.id.content的ViewGroup赋值给mContentParent
5.layoutResource通过mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource)方法layoutResource把添加进了DecorView
6.最后将activity_main添加到mContentParent,到这里就结束了整个流程,并没有将DecorView添加到window的步骤。
- 关于LayoutInflater#inflate
- 大体可以理解将xml解析出来,通过LayoutInflater#createViewFromTag方法根据名称反射实例化view后添加到ViewGroup root,子view添加通过rInflateChildren循环找到view添加到ViewGroup
正式开始分析
- 直接进入ActivityThread#handleResumeActivity
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean finalStateRequest, boolean isForward,
String reason) {
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
final ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, finalStateRequest, reason);
if (r == null) {
return;
}
if (mActivitiesToBeDestroyed.containsKey(token)) {
return;
}
final Activity a = r.activity;
if (localLOGV) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " + a.mStartedActivity
+ ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow + ", finished: " + a.mFinished);
}
final int forwardBit = isForward
? WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityTaskManager.getService().willActivityBeVisible(
a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
if (!a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);
} else {
}
}
}
- 进入WindowManagerImpl#addView,这里又调用了WindowManagerGlobal#addView
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow,
mContext.getUserId());
}
- 进入WindowManagerGlobal#addView
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) {
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
- 进入ViewRootImpl#setView了,篇幅太长只保留了关键的代码requestLayout()和mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView,
int userId) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
requestLayout();
try {
mOrigWinpatibility(mWindowAttributes);
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mTmpFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, inputChannel,
mTempInsets, mTempControls);
setFrame(mTmpFrame);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mAdded = false;
mView = null;
mAttachInfo.mRootView = null;
inputChannel = null;
mFallbackEventHandler.setView(null);
unscheduleTraversals();
setAccessibilityFocus(null, null);
throw new RuntimeException("Adding window failed", e);
} finally {
if (restore) {
attrs.restore();
}
}
view.assignParent(this);
}
}
}
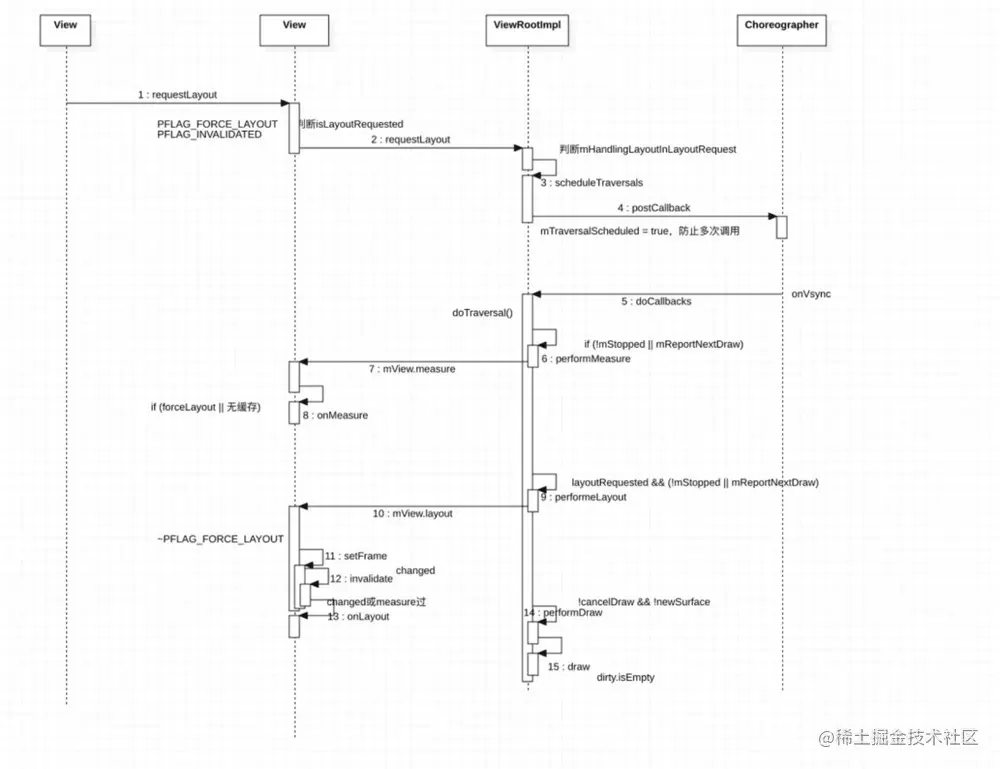
- ViewRootImpl#requestLayout()方法,requestLayout()这个一下子就熟悉起来了,自定义view的时候应该都用到过特别是viewgroup,实际最后调用的方法就是这里了,先丢个坑在这,后续讲解下
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
mLayoutRequested = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
- checkThread这有个经典的问题,为啥不能在子线程更新ui。
- 这里判断了当前ViewRootImpl是不是在同一个线程执行,不是就抛出异常,而ViewRootImpl刚好是在主线程创建的#Activity#main方法创建了主线程->Looper.prepareMainLooper();,刚好handleResumeActivity创建ViewRootImpl就是在主线程,严格意义上来说,是不能不同线程更新ui。
void checkThread() {
if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) {
throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException(
"Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.");
}
}
- ViewRootImpl#scheduleTraversals,接着分析scheduleTraversals
- 这样也比较眼熟,网上找屏幕刷新机制都会提到这个。这个方法是屏幕刷新最重要的方法,推荐个相关文章
@UnsupportedAppUsage
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
- 回到正文这里,这里传入了一个Runnable,所以最终会掉到这个doTraversal()
final TraversalRunnable mTraversalRunnable = new TraversalRunnable();
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
if (mProfile) {
Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor");
}
performTraversals();
if (mProfile) {
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
mProfile = false;
}
}
}
private void performTraversals() {
windowSizeMayChange |= measureHierarchy(host, lp, res,
desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
performDraw()
}
- #measureHierarchy 这里进行了3次预测量,当view的宽度设置为WRAP_CONTENT时会预测量2次
private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp,
final Resources res, final int desiredWindowWidth, final int desiredWindowHeight) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag,
"Measuring " + host + " in display " + desiredWindowWidth
+ "x" + desiredWindowHeight + "...");
boolean goodMeasure = false;
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
final DisplayMetrics packageMetrics = res.getDisplayMetrics();
res.getValue(com.android.internal.R.dimen.config_prefDialogWidth, mTmpValue, true);
int baseSize = 0;
if (mTmpValue.type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {
baseSize = (int)mTmpValue.getDimension(packageMetrics);
}
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": baseSize=" + baseSize
+ ", desiredWindowWidth=" + desiredWindowWidth);
if (baseSize != 0 && desiredWindowWidth > baseSize) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": measured ("
+ host.getMeasuredWidth() + "," + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ ") from width spec: " + MeasureSpec.toString(childWidthMeasureSpec)
+ " and height spec: " + MeasureSpec.toString(childHeightMeasureSpec));
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState()&View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
goodMeasure = true;
} else {
baseSize = (baseSize+desiredWindowWidth)/2;
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": next baseSize="
+ baseSize);
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": measured ("
+ host.getMeasuredWidth() + "," + host.getMeasuredHeight() + ")");
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState()&View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Good!");
goodMeasure = true;
}
}
}
}
if (!goodMeasure) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth() || mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight()) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
if (DBG) {
System.out.println("======================================");
System.out.println("performTraversals -- after measure");
host.debug();
}
return windowSizeMayChange;
}
- 根据上面3次的测量条件可以在加上下面的一次最多测量4次 最少测量2次,按照预测的方法来说,将width不要设置成WRAP_CONTENT会快一点(手动狗头)
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
- 这里mView.measure实际上是DecorView,所以onMeasure的时候实际调用的是DecorView#onMeasure然后DecorView继承自FrameLayout,先通过自己宽高模式啥的的一番计算调用了 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);所以直接去看FrameLayout的onMeasure
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
- 上门就是测量的过程,先预测量宽高,不管结果如何再去测量一次确定一下啊,然后循环去调用子view的测量
- 测量看完,看看performLayout,这里思路和上面测量一样的
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
mScrollMayChange = true;
mInLayout = true;
final View host = mView;
if (host == null) {
return;
}
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) {
Log.v(mTag, "Laying out " + host + " to (" +
host.getMeasuredWidth() + ", " + host.getMeasuredHeight() + ")");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "layout");
try {
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
- host就是DecorView而他继承了FrameLayout,FrameLayout就是viewGroup
- viewGroup#layout->View#layotu->View#onLayout
- 所以最终执行的是FrameLayout#onlayout
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
}
}
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
if (DBG) {
Log.d(VIEW_LOG_TAG, this + " View.setFrame(" + left + "," + top + ","
+ right + "," + bottom + ")");
}
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
invalidate(sizeChanged);
}
return changed;
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false );
}
void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) {
final int count = getChildCount();
final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground();
final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground();
final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground();
final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height);
}
}
}
- 这里绘制流程和布局流程都是一个套路,看看performDraw
private void performDraw() {
if (mAttachInfo.mDisplayState == Display.STATE_OFF && !mReportNextDraw) {
return;
} else if (mView == null) {
return;
}
try {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if (usingAsyncReport && !canUseAsync) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.setFrameCompleteCallback(null);
usingAsyncReport = false;
}
} finally {
mIsDrawing = false;
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
Surface surface = mSurface;
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnDraw();
if (!dirty.isEmpty() || mIsAnimating || accessibilityFocusDirty) {
if (mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer != null && mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.isEnabled()) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this);
} else {
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset,
scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) {
return false;
}
}
}
if (animating) {
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
scheduleTraversals();
}
return useAsyncReport;
}
- 上面ViewRootImpl#draw方法打了2个注释会走view.onDraw方法,先分析第一个
void draw(View view, AttachInfo attachInfo, DrawCallbacks callbacks) {
final Choreographer choreographer = attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mChoreographer;
choreographer.mFrameInfo.markDrawStart();
updateRootDisplayList(view, callbacks);
}
private void updateViewTreeDisplayList(View view) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_DRAWN;
view.mRecreateDisplayList = (view.mPrivateFlags & View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED)
== View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.mPrivateFlags &= ~View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
view.mRecreateDisplayList = false;
}
public RenderNode updateDisplayListIfDirty() {
final RecordingCanvas canvas = renderNode.beginRecording(width, height);
try {
if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE) {
buildDrawingCache(true);
Bitmap cache = getDrawingCache(true);
if (cache != null) {
canvas.drawBitmap(cache, 0, 0, mLayerPaint);
}
} else {
computeScroll();
canvas.translate(-mScrollX, -mScrollY);
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) {
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().draw(canvas);
}
if (isShowingLayoutBounds()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
} else {
draw(canvas);
}
}
} finally {
renderNode.endRecording();
setDisplayListProperties(renderNode);
}
} else {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
}
return renderNode;
}
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
int saveCount;
drawBackground(canvas);
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
onDraw(canvas);
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
onDrawForeground(canvas);
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
if (isShowingLayoutBounds()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
return;
}
}
- onDraw这个就不用说了,看下dispatchDraw怎么绘制子view的,dispatchDraw是抽象的方法所以先找下DecorView和FrameLayout有没有实现,没有找到所以直接接着找ViewGroup
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(preorderedList, children, childIndex);
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
}
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
- 上面ViewRootImpl#draw提到调用drawSoftware的方法,一样的套路
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) {
try {
mView.draw(canvas);
drawAccessibilityFocusedDrawableIfNeeded(canvas);
} finally {
}
return true;
}
- 到这里测量绘制的流程就完结了,setview中mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser就是把window添加到wms显示了。通过view.assignParent(this);给DecorView设置了父类,所以说ViewRootImpl是整个界面的爸爸。
分析下requestLayout和invalidate
当调用xxxView#requestLayout的时候会发生什么
public void requestLayout() {
if (mMeasureCache != null) mMeasureCache.clear();
if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == null) {
ViewRootImpl viewRoot = getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRoot != null && viewRoot.isInLayout()) {
if (!viewRoot.requestLayoutDuringLayout(this)) {
return;
}
}
mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = this;
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) {
mParent.requestLayout();
}
if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == this) {
mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = null;
}
}
- 看到这个重点就有一个递归的过程了,上面分析知道了ViewRootImpl是整个页面的爸爸,所以这个重点代码其实就是递归找ViewRootImpl并执行requestLayout方法了。
- 可以抽象看成:子view找爸爸viewgroup->viewgroup(DecorView)找爸爸ViewRootImpl,在让这个最后的爸爸执行requestLayout方法
- 至于requestLayout上面就有分析了不多重复了,有一个注意的一点的是不一定会去执行onDraw(),触发onDraw一般是因为layout过程中发现l,t,r,b和以前不一样或者动画在执行
- requestLayout流程图
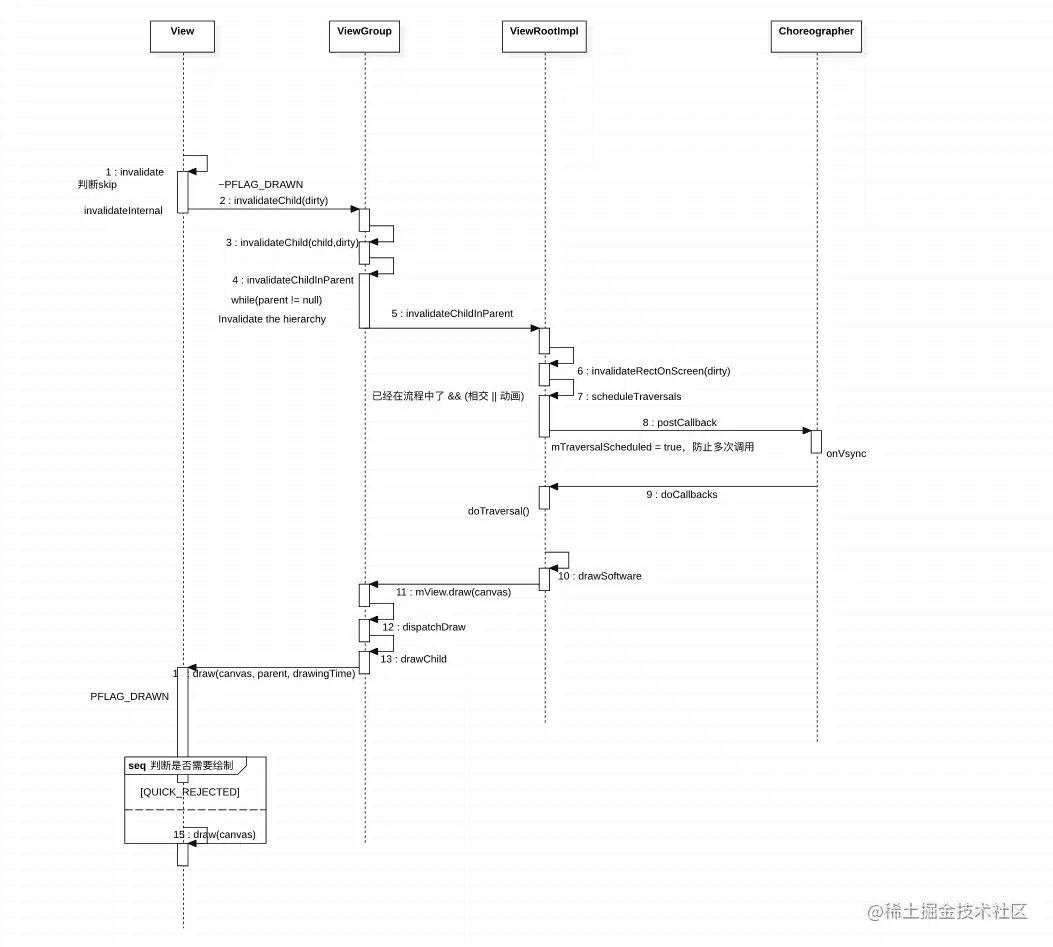
当调用xxxView#invalidate的时候会发生什么
public void invalidate() {
invalidate(true);
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) {
invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,
boolean fullInvalidate) {
if (mGhostView != null) {
mGhostView.invalidate(true);
return;
}
if (skipInvalidate()) {
return;
}
mPrivateFlags4 &= ~PFLAG4_CONTENT_CAPTURE_IMPORTANCE_MASK;
mContentCaptureSessionCached = false;
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)
|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED
|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {
final ViewParent p = mParent;
if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {
final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
damage.set(l, t, r, b);
p.invalidateChild(this, damage);
}
}
}
@Deprecated
@Override
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
ViewParent parent = this;
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
} while (parent != null);
}
}
- 调用了view.invalidate最终会循环调用parent.invalidateChildInParent。所以会找到页面的爸爸ViewRootImpl执行invalidateChildInParent和上面逻辑相似。至于viewgroup的invalidateChildInParent只是在设置脏区大小啥的
public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) {
checkThread();
if (DEBUG_DRAW) Log.v(mTag, "Invalidate child: " + dirty);
if (dirty == null) {
invalidate();
return null;
} else if (dirty.isEmpty() && !mIsAnimating) {
return null;
}
invalidateRectOnScreen(dirty);
return null;
}
- scheduleTraversals后面也不用说啥了又是doTraversal->performTraversals然后又是一通判断是否要执行measure、layout和draw
- invalidate流程图