队列
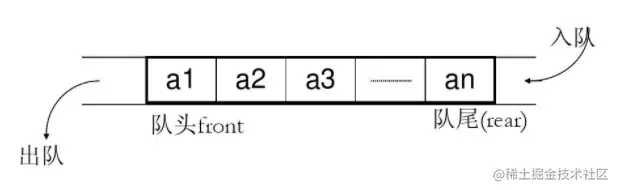
队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,
和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。
进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
简介
队列的数据元素又称为队列元素。
在队列中插入一个队列元素称为入队,
从队列中删除一个队列元素称为出队。
因为队列只允许在一端插入,在另一端删除,
所以只有最早进入队列的元素才能最先从队列中删除,
故队列又称为先进先出(FIFO—first in first out)
特征
就一句话:先进先出(First In First Out),头删尾插
手撸代码
入队
判断队列没满才可以放入队列
public void push(int x) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满了!");
return;
}
this.quere[this.rear] = x;
this.rear ++;
System.out.println("【" + x + "】进入队列!");
}
出队
队列不为空才可出队
public void pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列已空!");
return;
}
System.out.println( "已出队列:【" + this.quere[this.front] +"】");
this.quere[this.front] = 0;
this.front ++;
}
完整演示
public class NewQueue{
private int front = 0;
private int rear = 0;
private int size = 0;
private int[] quere;
public NewQueue (int length) {
this.quere = new int[length];
this.size = length;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.front == this.rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.rear == this.size - 1;
}
public void push(int x) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满了!");
return;
}
this.quere[this.rear] = x;
this.rear ++;
System.out.println("【" + x + "】进入队列!");
}
public void pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列已空!");
return;
}
System.out.println( "已出队列:【" + this.quere[this.front] +"】");
this.quere[this.front] = 0;
this.front ++;
}
public void reset() {
for (int i = this.front; i < this.rear; i++) {
this.quere[i] = 0;
}
this.front = 0;
this.rear = 0;
System.out.println("队列已重置!");
}
public void showQueue() {
System.out.println("打印队列!");
for (int i = this.front; i < this.rear; i++) {
System.out.print(quere[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewQueue newQueue = new NewQueue(6);
newQueue.push(1);
newQueue.push(2);
newQueue.pop();
newQueue.push(3);
newQueue.push(4);
newQueue.push(5);
newQueue.pop();
newQueue.showQueue();
newQueue.reset();
}
}
总结
本文实现的是顺序队列,真正表示队列的是头指针front与尾指针rear之间的存储空间,
由于头指针front与尾指针rear是动态变化的,所以当front与rear指向同一位置时,表示一个空队列
当rear指向的位置是定义队列的最后位置时表示队列已满,即使front不一定出现在定义队列的首位时,也表示队列已满
当队列已满再添加元素进去时,则会出现队满溢出情况,但是front前面可能还存在空间,这种情况就称之为‘假溢出’
适用场景
最熟悉的是Java里面的线程池,以及各种消息中间件