HTMLElement
1. clientHeight / clientWidth
- 1.只读属性
- 2.对于没有定义 CSS 或者内联布局盒子的元素为 0
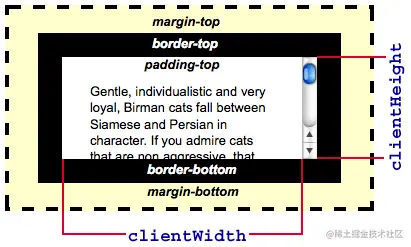
- 3.否则,它是元素内部的高度(单位像素),包含内边距,但不包括水平滚动条、边框和外边距
- 4.即一个元素由内到外分别由 height + padding + border + margin 组成,而 clientHeight 只取前面的 height 和 padding
2. offsetHeight / offsetHeight
- 1.只读属性
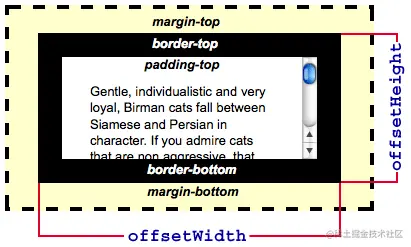
- 2.一个元素由内到外分别由 height + padding + border + margin 组成,而 offsetHeight 由 height + padding + border 组成
3. scrollHeight / scrollWidth
- 1.只读属性
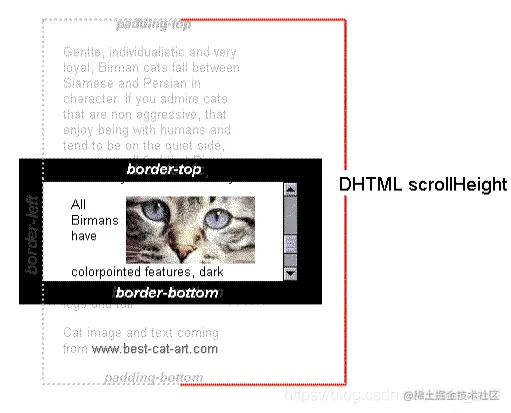
- 2.scrollHeight 和元素本身的高度无关
- 3.scrollHeight 代表包括当前不可见部分的元素的高度;而可见部分的高度其实就是 clientHeight
- 4.在没有垂直滚动条的情况下,scrollHeight 可视为 clientHeight
4. scrollTop / scrollLeft
- 1.可读可写
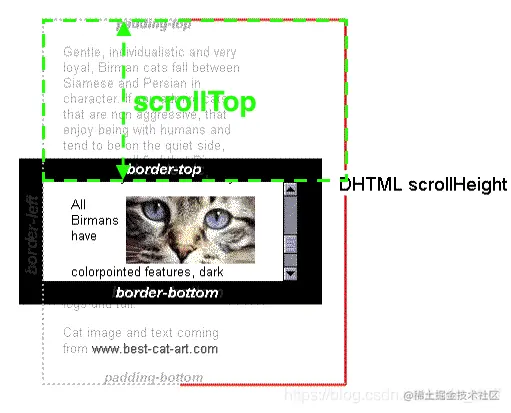
- 2.scrollTop 值是这个元素的内容顶部(卷起来的)到它的视口可见内容(的顶部)的距离
- 3.当一个元素的内容没有产生垂直方向的滚动条,那么它的 scrollTop 值为 0
- 4.element.scrollTop = intValue; // 设置滚动的距离
5. offsetTop / offsetLeft

- 1.只读属性
- 2.返回当前元素相对于其 offsetParent 元素的顶部内边距的距离。与有没有滚动条没有关系
offsetParent
- 1.只读属性
- 2.返回一个指向最近的(指包含层级上的最近)包含该元素的定位元素或者最近的 table,td,th,body 元素
- 3.当元素的 style.display 设置为 "none" 时,offsetParent 返回 null
- 4.offsetParent 很有用,因为 offsetTop 和 offsetLeft 都是相对于其内边距边界的
6. getBoundingClientRect()
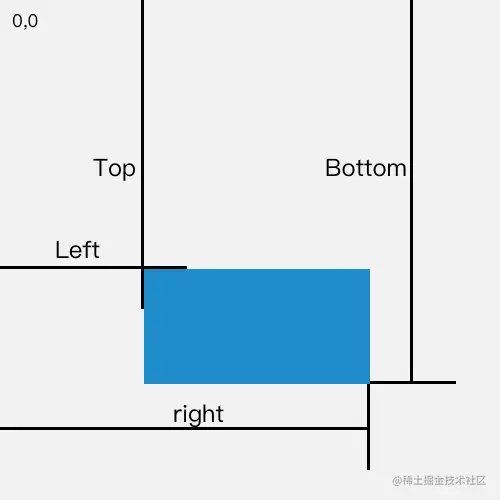
- 1.方法返回元素的大小及其相对于视口的位置
- 2.拥有left, top, right, bottom, x, y, width, height这几个以像素为单位的只读属性用于描述整个边框
- 3.除了width 和 height 以外的属性是相对于视图窗口的左上角来计算的

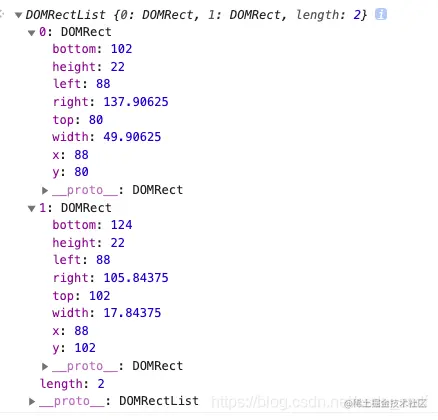
7.getClientRects()
- 1.获取元素占据页面的所有矩形集合(元素的大小及其相对于视口的位置)
- 2.行内元素会产生自动换行这类看似分割整体的歧义,所以,会把行内元素根据它换行划分成多个盒子边界矩形
Window
1.scrollX / scrollY
- 1.只读属性
- 2.返回文档/页面水平方向滚动的像素值
- 3.可调用 Window.scroll()方法,滚动窗口至文档中的特定位置
- 4.pageXOffset 属性是 scrollX 属性的别名
if (window.scrollX > 400) {
window.scroll(0, 0);
}
window.pageXOffset == window.scrollX;
2.innerWidth / innerHeight
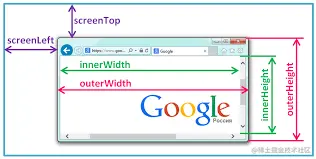
- 1.只读属性
- 2.表示浏览器窗口的视口(viewport)高度/宽度
3.outerWidth / outerHeight
- 1.只读属性,没有默认值。
- 2.表示整个浏览器窗口的宽度,包括侧边栏(如果存在)、窗口镶边(window chrome)和调正窗口大小的边框(window resizing borders/handles)
- 3.要改变一个窗口的大小,可参考 window.resizeBy() 和 window.resizeTo()
4.screenTop / screenLeft
-
- 只读属性
-
- 返回用户浏览器的上边界(左边框)到屏幕最顶端(左边屏幕边缘)的 CSS 像素数
附上测试代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>测试元素宽高</title>
</head>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="test1" style="display: inline; background-color: red;"></div>
<div id="test2" style="width: 200px;height: 200px;overflow: scroll; background-color: red;">
<div id="test2_1" style="width: 200px;height: 400px; background-color: royalblue;"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
const clientWidth1 = document.getElementById('test1').clientWidth
const clientHeight1 = document.getElementById('test1').clientHeight
console.log('client inline', clientWidth1, clientHeight1)
const clientWidth2 = document.getElementById('test2').clientWidth
const clientHeight2 = document.getElementById('test2').clientHeight
console.log('clinet o', clientWidth2, clientHeight2)
const clientWidth2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').clientWidth
const clientHeight2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').clientHeight
console.log('client i', clientWidth2_1, clientHeight2_1)
const offsetWidth2 = document.getElementById('test2').offsetWidth
const offsetHeight2 = document.getElementById('test2').offsetHeight
console.log('offset o', offsetWidth2, offsetHeight2)
const offsetWidth2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').offsetWidth
const offsetHeight2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').offsetHeight
console.log('offset i', offsetWidth2_1, offsetHeight2_1)
const scrollWidth2 = document.getElementById('test2').scrollWidth
const scrollHeight2 = document.getElementById('test2').scrollHeight
console.log('scorll o', scrollWidth2, scrollHeight2)
const scrollWidth2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').scrollWidth
const scrollHeight2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').scrollHeight
console.log('scorll i', scrollWidth2_1, scrollHeight2_1)
document.getElementById('test2').scrollTop = 100
const scrollTop2 = document.getElementById('test2').scrollTop
console.log('scorllTop o', scrollTop2)
console.log('scorllTop o ----', scrollTop2)
document.getElementById('test2_1').scrollTop = 100
const scrollTop2_1 = document.getElementById('test2_1').scrollTop
console.log('scorllTop i', scrollTop2_1)
console.log('scorllTop i ----', scrollTop2_1)
</script>
</html>