前言
_objc_init是runtime初始化的函数,在os_objec_init之后调用
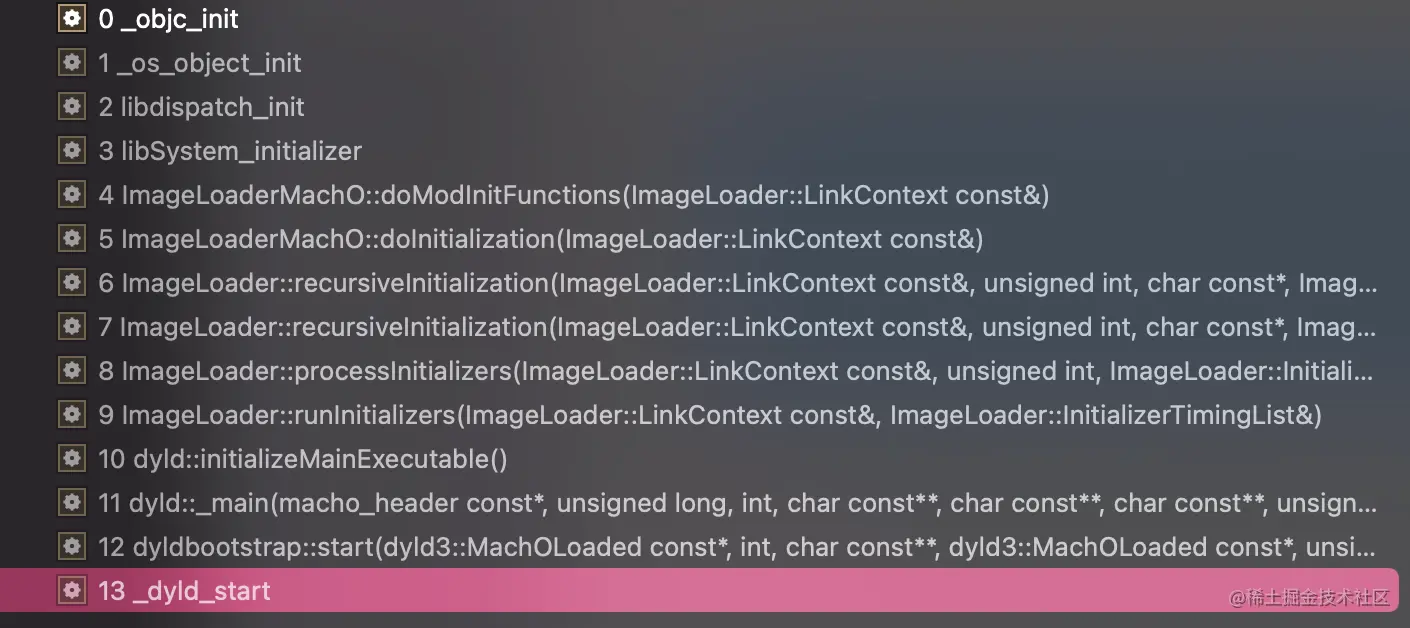
_objc_init里的具体实现
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
environ_init();
tls_init();
static_init();
runtime_init();
exception_init();
#if __OBJC2__
cache_t::init();
#endif
_imp_implementationWithBlock_init();
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
#if __OBJC2__
didCallDyldNotifyRegister = true;
#endif
}
分析
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
- 这个很好理解,用一个静态变量标记有没初始化过,已经初始化了的话,直接
return
environ_init();
- 环境变量初始化,这个可以配置在
xcode里,根据自己的需求在lldb打印出自己需要调试的变量
- 在终端输入
export OBJC_HELP=1 和 export OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS=1,可以打印出环境变量和对应的描述
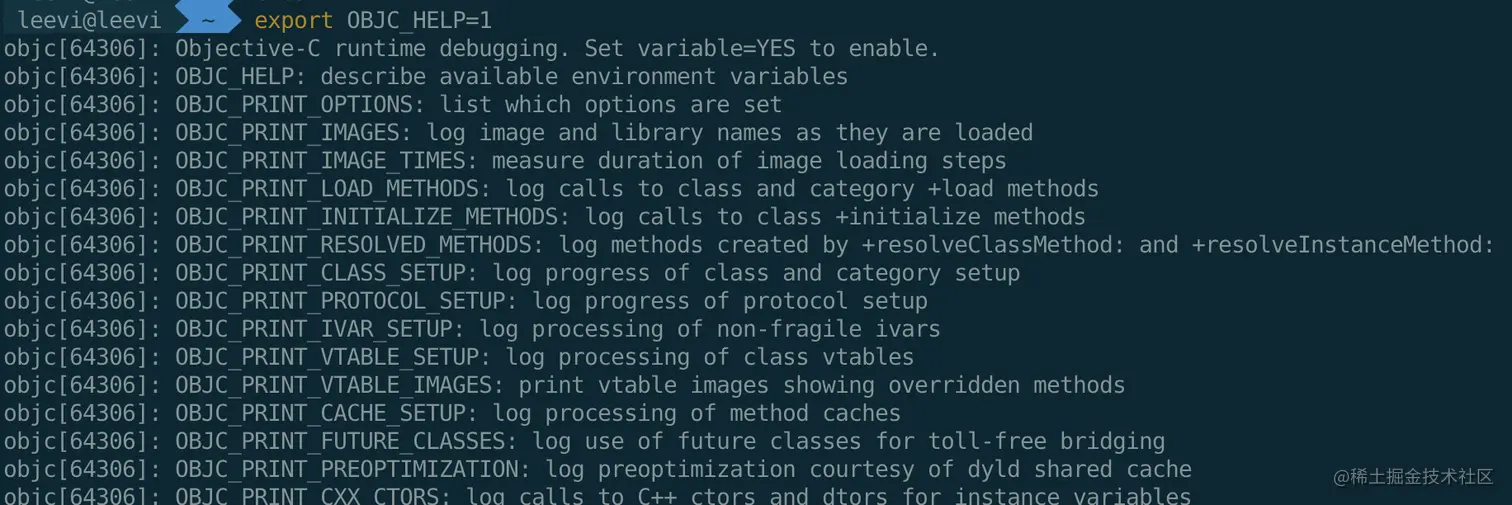
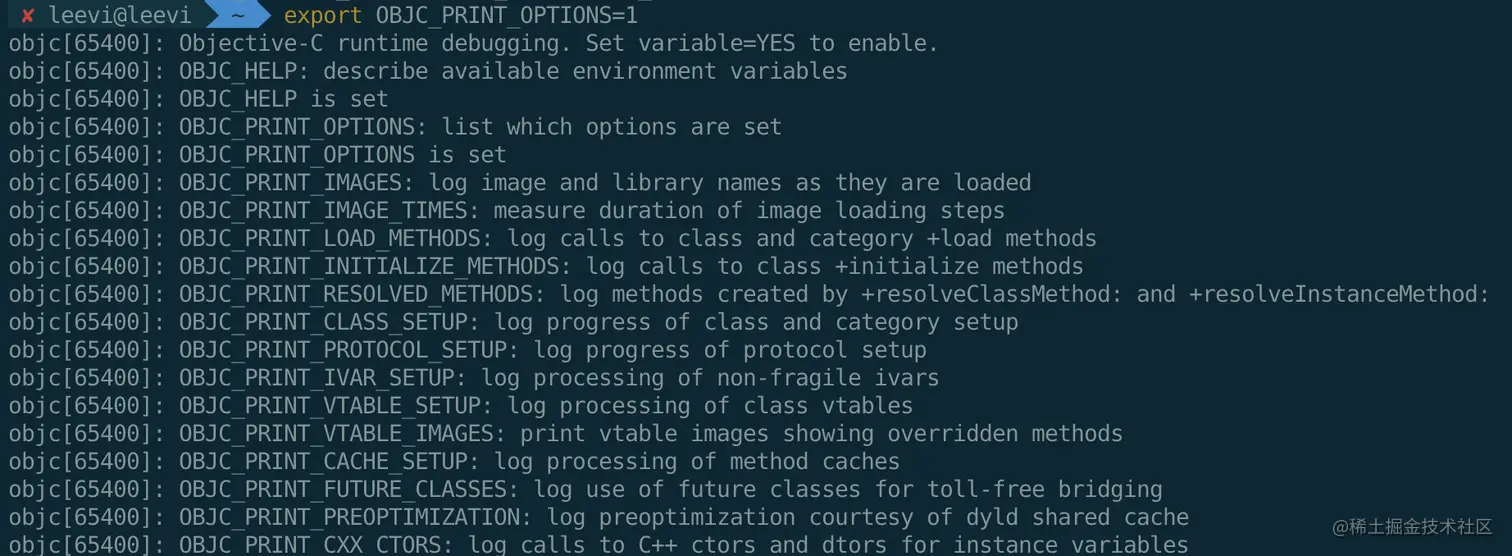
- 然后可以在
xcode配置, 下面配置了打印所有调用load方法的地方
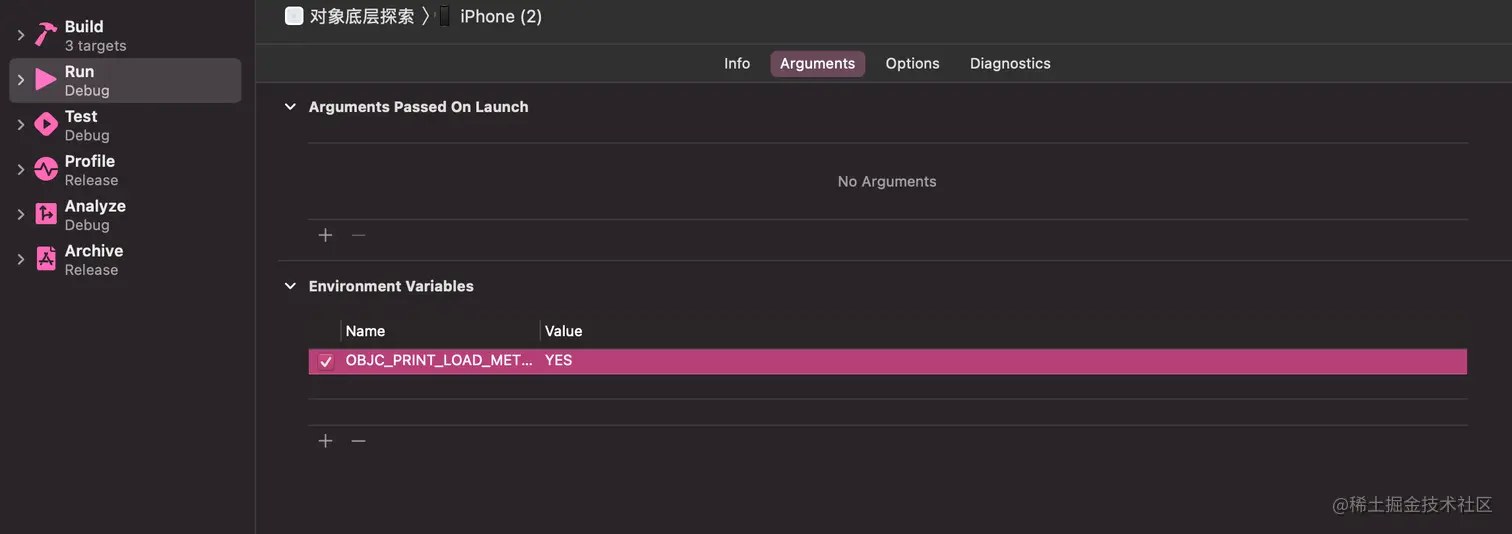
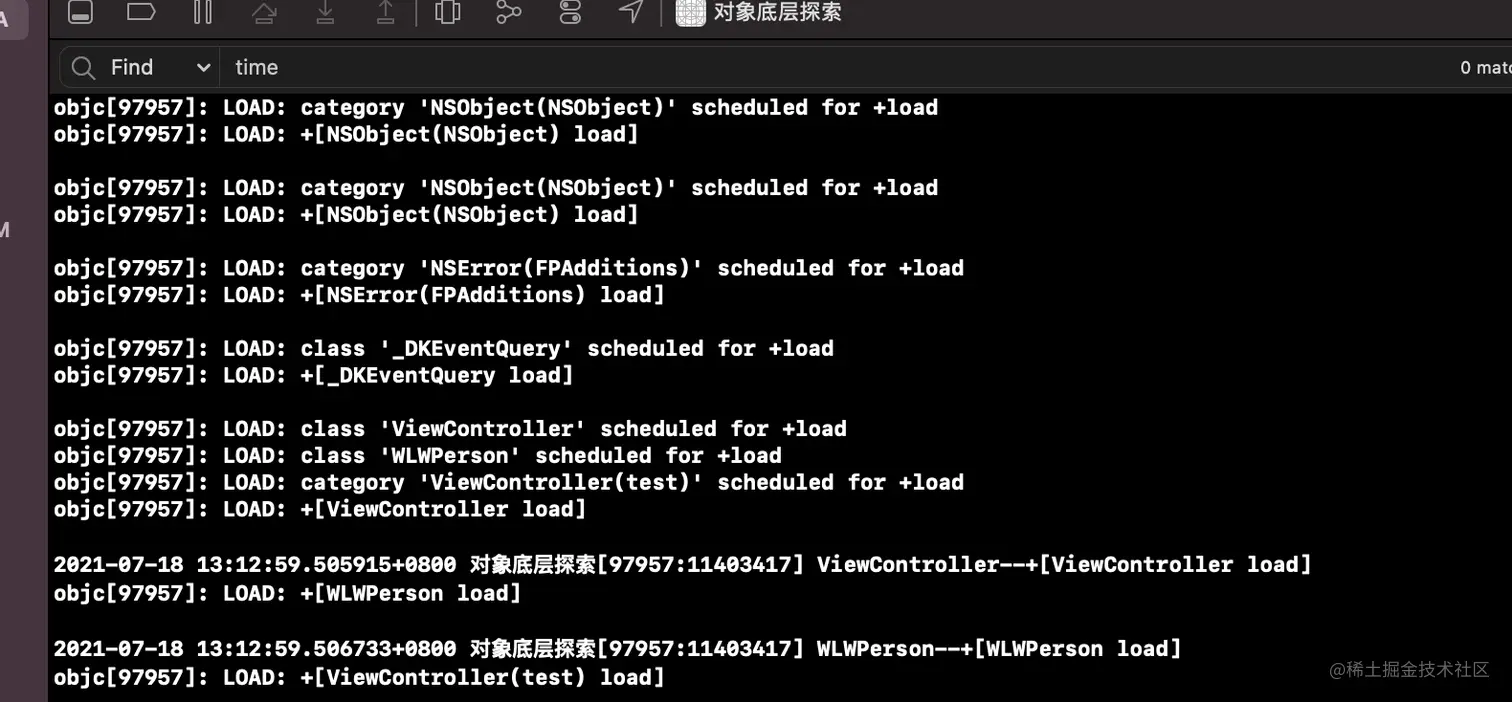
dyld 环境变量
const char* const * DYLD_FRAMEWORK_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES;
const char* const * LD_LIBRARY_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_VERSIONED_LIBRARY_PATH;
const char* const * DYLD_VERSIONED_FRAMEWORK_PATH;
bool DYLD_PRINT_LIBRARIES_POST_LAUNCH;
bool DYLD_BIND_AT_LAUNCH;
bool DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS;
bool DYLD_PRINT_STATISTICS_DETAILS;
bool DYLD_PRINT_OPTS;
bool DYLD_PRINT_ENV;
bool DYLD_DISABLE_DOFS;
bool hasOverride;
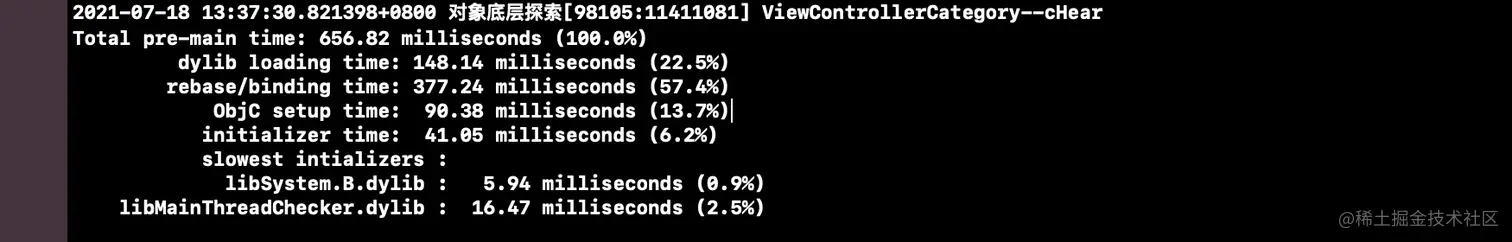
tls_init();
void tls_init(void)
{
#if SUPPORT_DIRECT_THREAD_KEYS
pthread_key_init_np(TLS_DIRECT_KEY, &_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);
#else
_objc_pthread_key = tls_create(&_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);
#endif
}
- 线程Key的绑定
- 设置析构函数
_objc_pthread_destroyspecific
static_init();
- 调用
libobjc 中的所有 C++ 构造函数,在 dylb调用构造函数之前
__attribute__((constructor))
static void defineLockOrder() {
}
runtime_init();
void runtime_init(void)
{
objc::unattachedCategories.init(32);
objc::allocatedClasses.init();
}
- 初始化了两张
表
unattachedCategories: 未被识别的分类表allocatedClasses: 已经开辟的所有类和元类的表
exception_init();
static void _objc_terminate(void)
{
if (PrintExceptions) {
_objc_inform("EXCEPTIONS: terminating");
}
if (! __cxa_current_exception_type()) {
(*old_terminate)();
}
else {
@try {
__cxa_rethrow();
} @catch (id e) {
(*uncaught_handler)((id)e);
(*old_terminate)();
} @catch (...) {
(*old_terminate)();
}
}
}
- 下面的
ar数组是越界,我们可以用NSSetUncaughtExceptionHandler(&fn)来抛出异常,找到有用的信息,传给我们的服务器,以便分析
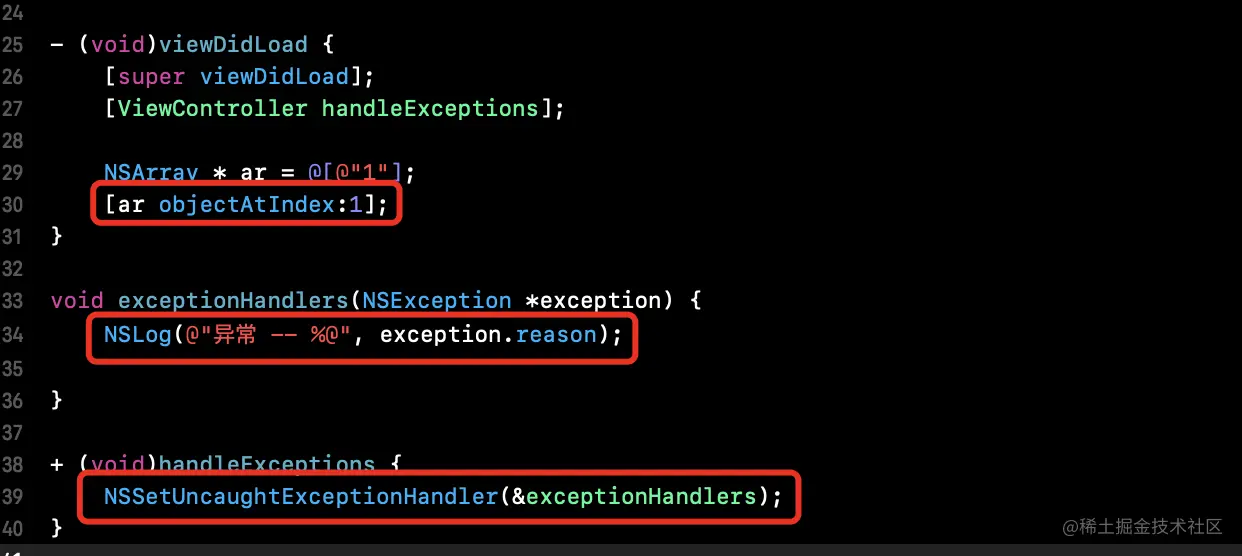
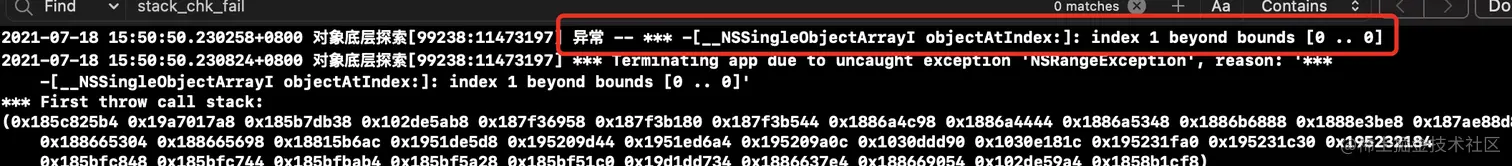
uncaught_handler是在objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler赋值的
/***********************************************************************
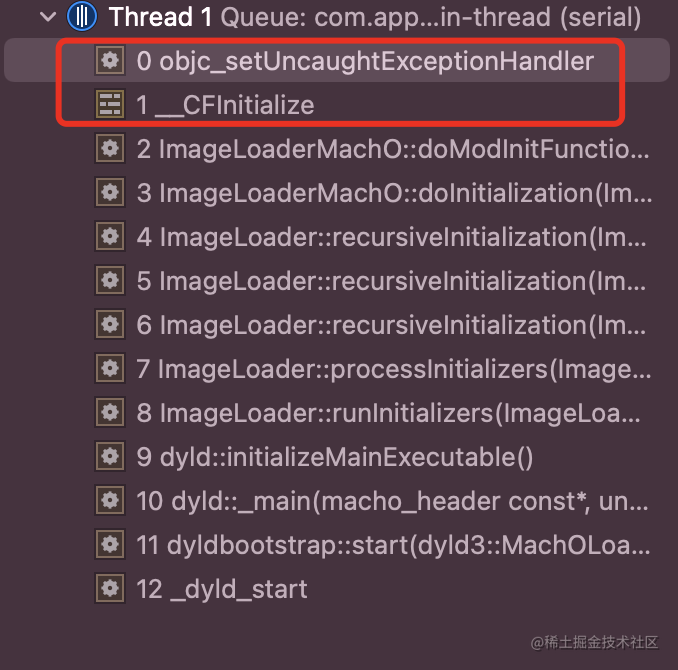
* objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler
* Set a handler for uncaught Objective-C exceptions.
* Returns the previous handler.
**********************************************************************/
objc_uncaught_exception_handler
objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler(objc_uncaught_exception_handler fn)
{
objc_uncaught_exception_handler result = uncaught_handler;
uncaught_handler = fn;
return result;
}
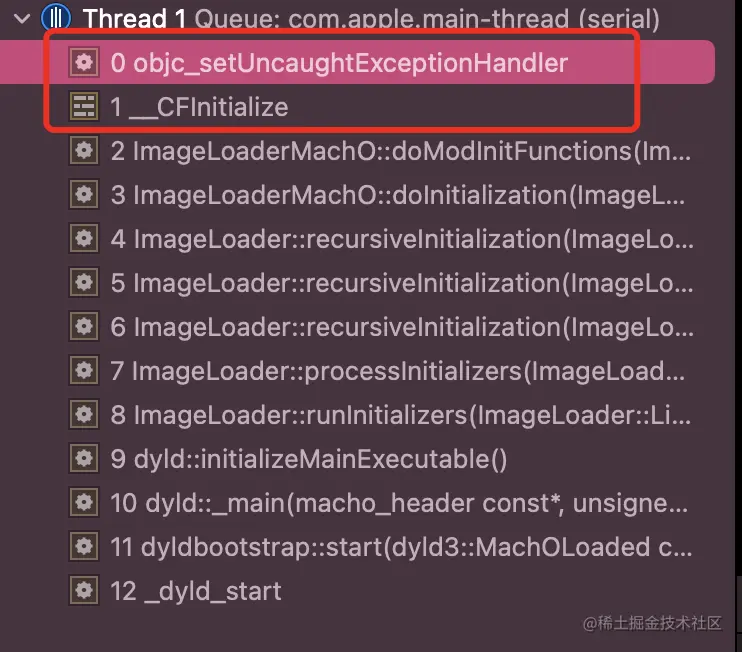
objc_setUncaughtExceptionHandler在CoreFoundtion初始化之后就调用了- 这个具体的流程还需要在具体探索一下,目前只研究到这了
cache_t::init();
void cache_t::init()
{
#if HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES
mach_msg_type_number_t count = 0;
kern_return_t kr;
while (objc_restartableRanges[count].location) {
count++;
}
kr = task_restartable_ranges_register(mach_task_self(),
objc_restartableRanges, count);
if (kr == KERN_SUCCESS) return;
_objc_fatal("task_restartable_ranges_register failed (result 0x%x: %s)",
kr, mach_error_string(kr));
#endif
}
HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES
#if TARGET_OS_SIMULATOR || defined(__i386__) || defined(__arm__) || !TARGET_OS_MAC
# define HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES 0
#else
# define HAVE_TASK_RESTARTABLE_RANGES 1
#endif
_imp_implementationWithBlock_init();
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
- 交给
dyld 调用 mao_images, load_images, unmap_image, 具体可以看应用程序加载