一、表达式判断
- 之前登录用户权限判断底层实现都是调用 access(表达式)
public ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry access(String attribute) {
if (this.not) {
attribute = "!" + attribute;
}
interceptUrl(this.requestMatchers, SecurityConfig.createList(attribute));
return ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer.this.REGISTRY;
}
- access(表达式)
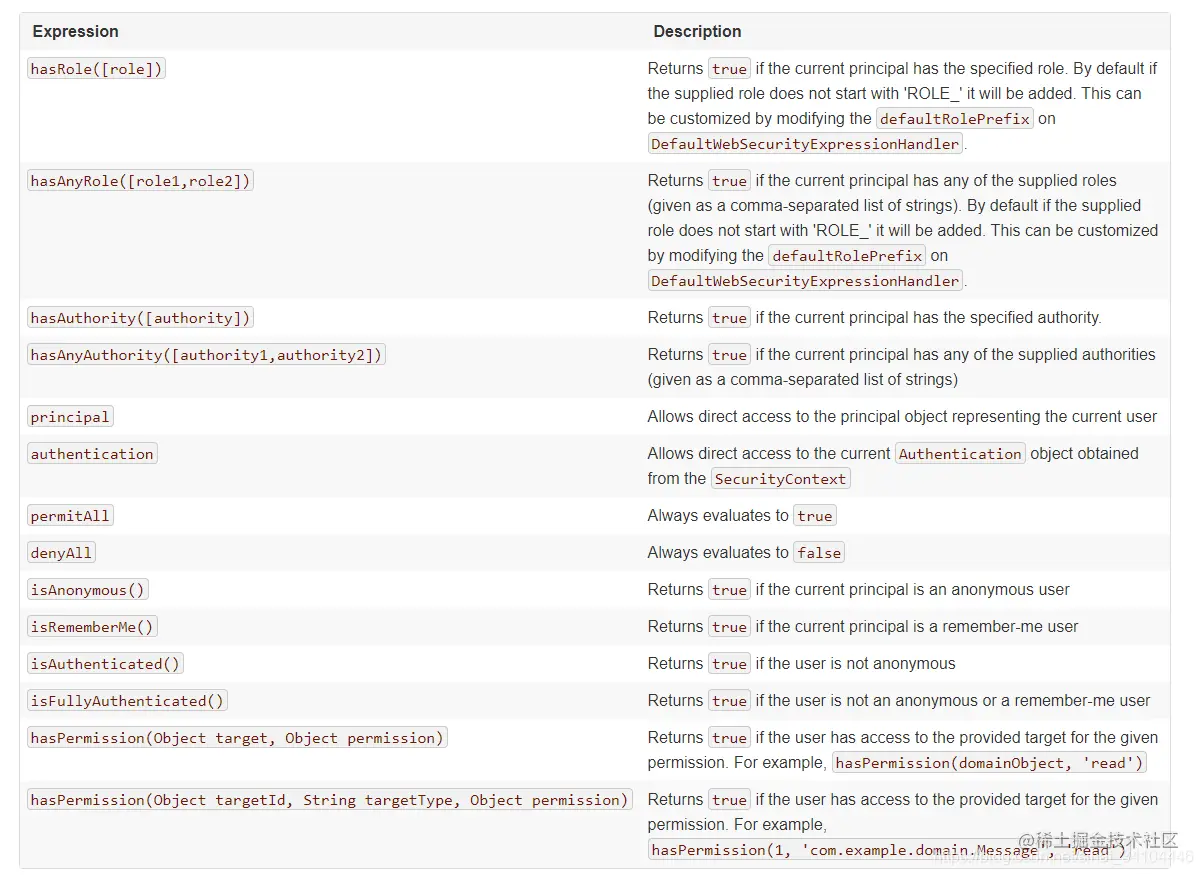
1.1 access()方法使用
- access()中的方法为上述表格中的方法,也就是下面的写法中把方法名称直接放到access中
- 例如 .antMatchers("/xxx.html").access("hasRole('xxx')") ,中access的参数就是下面的antMatchers("/xxx.html") 后的方法名放放到表达式中
- .antMatchers("/xxx.html").hasRole("xxx")
- .antMatchers("/xxx.html").hasAnyRole("xxx, xxx")
- .antMatchers("/xxx.html").hasAuthority("xxx")
- .antMatchers("/xxx.html").hasAnyAuthority("xxx, xxx")
- .antMatchers("/xxx.html").hasIpAddress("xxx")
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/root.html").access("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')");
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/admin.html").access("hasAnyAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN', 'ROLE_USER')");
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/root.html").access("hasRole('ADMIN')");
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/admin.html").access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN', 'USER')");
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/ip.html").access("hasIpAddress('127.0.0.1')");
- 按照之前方式访问,权限正常控制,推荐使用方法名直接调用方式,方便调整且IDE可以检查方法名是否错误
1.2 自定义处理方法
- 上述都是使用内置的方法进行处理,可以指定自定义方法处理
- 自定义授权处理器接口
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public interface CustomAuthenticationHandler {
boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication);
}
- 实现自定义授权处理器接口
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AdvanceCustomAuthenticationHandler implements CustomAuthenticationHandler {
private static final String ACCESS_ROLE = "ROLE_ADMIN";
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication) {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) principal;
System.out.println(String.format("获取到授权信息【{%s}】", JsonUtil.toJson(userDetails)));
return userDetails.getAuthorities().stream()
.map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.anyMatch(authority -> authority.equals(ACCESS_ROLE));
}
return false;
}
}
- 在 http.authorizeRequests() 中指定对应匹配规则的处理器
- 通过 @<beanName>.<methodName> 调用
- 其中HttpServletRequest request, Authentication authentication调用时自动注入
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/advance.html")
.access("@advanceCustomAuthenticationHandler.hasPermission(request, authentication)")
- 正常访问,当使用admin登录时将会报403,使用root登录时正常访问