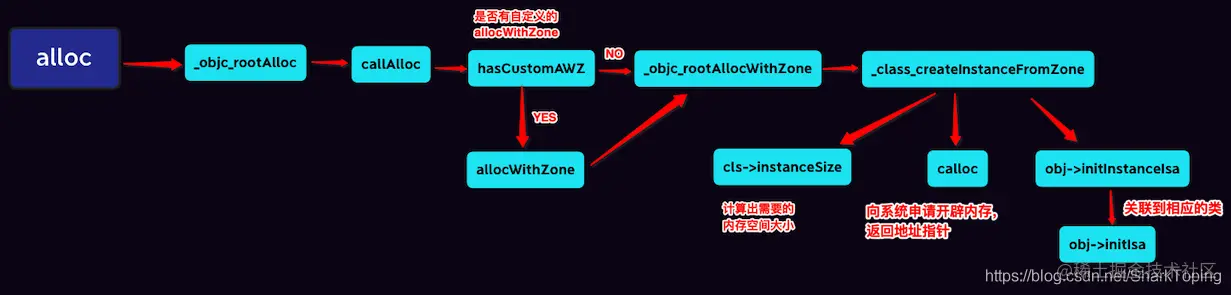
1.创建对象 [LGPerson alloc]将调用底层的alloc函数创建对象
2.进入符号断点,找到objc_alloc
找到objc_alloc的方法
1.符号断点 libobjc.A.dylib`objc_alloc:
2.汇编 跟流程 - 符号断点: objc_alloc(最长使用)
3.符号断点 确定未知 : libobjc.A.dylib`+[NSObject alloc]:
4.alloc创建对象的时候会调用内部 _objc_rootAlloc函数
id
_objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)
{
return callAlloc(cls, false, true);
}
5.从_objc_rootAlloc进一步调用callAlloc函数、当前对象没有自定义的allocWithZone方法的话、会走快速创建方法;有自定义的allocWithZone方法,调用之后也会走 _objc_rootAllocWithZone方法
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
{
#if __OBJC2__
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {//hasCustomAWZ :自定义的allocWithZone
return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(cls, nil);
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) {
return ((id(*)(id, SEL, struct _NSZone *))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(allocWithZone:), nil);
}
return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(alloc));
}
6.经过快速创建继续走 _objc_rootAllocWithZone方法、
id
_objc_rootAllocWithZone(Class cls, malloc_zone_t *zone __unused)
{
// allocWithZone under __OBJC2__ ignores the zone parameter
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, 0, nil,
OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC);
}
7.最终创建对象为 _class_createInstanceFromZone 方法
cls->instanceSize 计算需要的内存空间大小
calloc 向系统申请开辟内存,返回地址指针
obj->initInstanceIsa 关联到相应的类
_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,
int construct_flags = OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_NONE,
bool cxxConstruct = true,
size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)
{
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
// Read class's info bits all at once for performance
bool hasCxxCtor = cxxConstruct && cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
size_t size;
//计算出需要的内存空间大小
size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
id obj;
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
//向系统申请开辟内存,返回地址指针
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (slowpath(!obj)) {
if (construct_flags & OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC) {
return _objc_callBadAllocHandler(cls);
}
return nil;
}
//关联到相应的类
if (!zone && fast) {
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
} else {
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
if (fastpath(!hasCxxCtor)) {
return obj;
}
construct_flags |= OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_FREE_ONFAILURE;
return object_cxxConstructFromClass(obj, cls, construct_flags);
}
8.zone不存在时、且canAllocNonpointer为true时。走 obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor),zone存在时、走 obj->initIsa(cls) 方法
inline void
objc_object::initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
ASSERT(hasCxxDtor == cls->hasCxxDtor());
initIsa(cls, true, hasCxxDtor);
}
inline void
objc_object::initIsa(Class cls)
{
initIsa(cls, false, false);
}
9.最后使用initIsa方法做了赋值操作
objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool nonpointer, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!isTaggedPointer());
//nonpointer 表示是否对isa指针开启指针优化 0 纯isa指针、1:不止是类对象地址,isa包含了类对象,对象的引用等
if (!nonpointer) {
isa = isa_t((uintptr_t)cls);
} else {
ASSERT(!DisableNonpointerIsa);
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
isa_t newisa(0);
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
ASSERT(cls->classArrayIndex() > 0);
newisa.bits = ISA_INDEX_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.indexcls = (uintptr_t)cls->classArrayIndex();
#else
newisa.bits = ISA_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.shiftcls = (uintptr_t)cls >> 3;
#endif
// This write must be performed in a single store in some cases
// (for example when realizing a class because other threads
// may simultaneously try to use the class).
// fixme use atomics here to guarantee single-store and to
// guarantee memory order w.r.t. the class index table
// ...but not too atomic because we don't want to hurt instantiation
isa = newisa;
}
}
10.ISA_BITFIELD 涉及的变量含义
nonpointer: 表示是否对指针开启指针优化、0:纯isa指针,1:不止是类对象地址,isa中包含了类信息,对象的引用计数等。
has_assoc: 关联对象标志位,0没有,1存在
has_cxx_dtor: 该对象是否有C++或者Objc的析构器,如果有析构函数,则需要做析构逻辑,如果没有,则可以更快的释放对象。
shiftcls: 存储类指针的值。开启指针优化的情况下,在arm64架构中有33位用来存储类指针。
magic: 用于调试器判断当前对象是真的对象还是没有初始化的空间。
weakly_referenced:标志对象是否被指向或者曾经指向一个ARC的弱变量,没有弱引用的对象可以更快释放。
deallocating: 标志对象是否正在释放对象。
has_sidetable_rc:当对象引用计数大于10时,则需要借用该变量存储进位
extra_rc: 当表示该对象的引用计数值,实际上是引用计数减1。如果对象的引用计数为10,那么extra_rc为9。如果引用计数大于10,则需要使用has_sidetable_rc。
最后是alloc流程图