前言
vue3核心compiler源码地址Vue 3 Template Explorer- 本文只是描述一下思路, 源码做的太多, 因为vue3引入
Block的概念(Block Tree)
- block的作用就是为了收集动态节点 将树的递归 拍平成了有一个数组
dynamicChildren
- 在
createVnode的时候 会判断这个节点是动态的 就让外层的block收集起来
- 所以
transform这一步的 PatchFlags 对不同的动态节点进行描述
- 为了diff的时候只diff动态的节点, 减少比对, 同时不像vue2遇到孩子 就要递归操作, 虽然vue2做了静态标记
- 只是比对是静态 就跳过, vue3 在这一块做了很大的性能提升
- vue3 可以直接写render函数
h('div') 但是并不好 如果dom元素太多 不好维护
- 也可以jsx语法 会转成
h('div') 没有优化
- 用vue3的template 转化为的render函数 具备优化特点的
patchFlag blockTree
- template -> render函数
-
- 把
html解析成抽象语法树ast(描述语法本身)
-
- 转化
ast语法树 加标记和进行优化 transform
-
- 生成
render函数(字符串拼接)
示例
<script src="../node_modules/@vue/compiler-dom/dist/compiler-dom.global.js"></script>
<script>
const { baseCompile } = VueCompilerDOM
const template = `
<div >tom {{ age }}</div>
<span>123456</span>
`
let res = baseCompile(template)
console.log("🚀 ~ res", res)
</script>
最终要的字符串
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache, $props, $setup, $data, $options) {
with (_ctx) {
const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, createVNode: _createVNode, Fragment: _Fragment, openBlock: _openBlock, createBlock: _createBlock } = _Vue
return (_openBlock(), _createBlock(_Fragment, null, [
_createVNode("div", null, "tom " + _toDisplayString(age), 1 ),
_createVNode("span", null, "123456")
], 64 ))
}
}
compile.ts
import { generate } from "./codegen"
import { baseParse } from "./parse"
import { getBaseTransformPreset, transform } from "./transform"
export function baseCompile(template) {
const ast = baseParse(template)
const nodeTransforms = getBaseTransformPreset()
transform(ast, nodeTransforms)
return generate(ast)
}
export const enum PatchFlags {
TEXT = 1,
CLASS = 1 << 1,
STYLE = 1 << 2,
PROPS = 1 << 3,
FULL_PROPS = 1 << 4,
HYDRATE_EVENTS = 1 << 5,
STABLE_FRAGMENT = 1 << 6,
KEYED_FRAGMENT = 1 << 7,
UNKEYED_FRAGMENT = 1 << 8,
NEED_PATCH = 1 << 9,
DYNAMIC_SLOTS = 1 << 10,
DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT = 1 << 11,
HOISTED = -1,
BAIL = -2
}
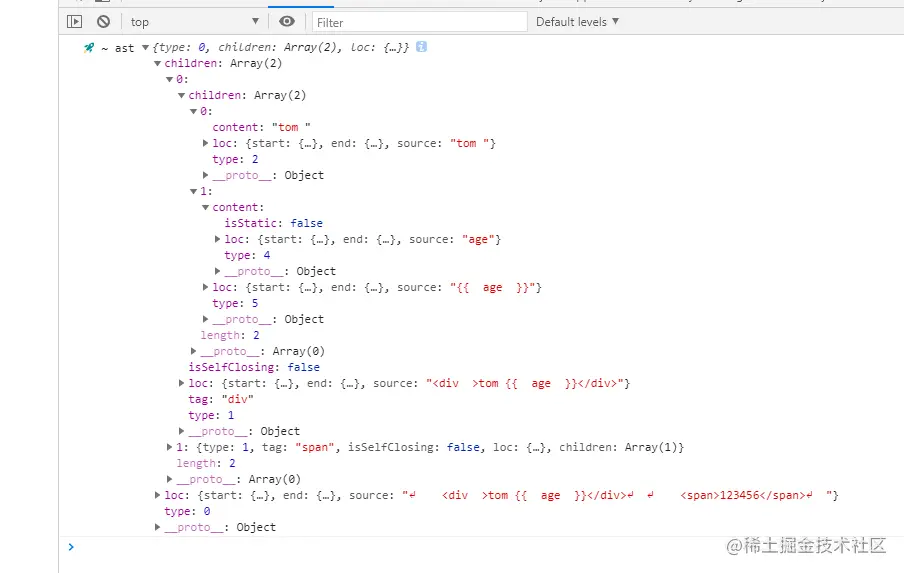
1.html 转化 ast(parse.ts)
AST Explorer网址- 可以根据上面的网站, 将语言选择vue, 左面输入html, 右面显示解析的ast语法树
- vue3源码的编译成ast语法树 处理的情况很多(vue3比vue2编译部分做了许多优化部分) 这里只是抽出了 核心部分
- 从以下三方面 做了词法解析(以下面的示例为主)
- 最后通过递归的形式 将所有标签都组装起来
- 核心方法是
parseChildren, 通过循环方式, 解析一点词法 就将html字符串, 截掉一点(方法advanceBy)
- 直到解析的html字符串为空, 跳出循环
- vue3支持外层不用包裹一个根元素, 它会把你创建一个, 返回最终的结果
* 文本ast语法树
* 假如html: `hello`
{
type: 2,
content: 'hello',
loc: {
start: { column: 1, line: 1, offset: 0 },
end: { column: 6, line: 1, offset: 5 },
source: 'hello'
}
}
================================================
* 表达式ast语法树
* 假如html: `{{aaa}}`
{
type: 5,
content: {
type: 4,
isStatic: false,
content: 'aaa',
loc: {
start: { column: 3, line: 1, offset: 2 },
end: { column: 6, line: 1, offset: 5 },
source: 'aaa'
}
},
loc: {
start: { column: 1, line: 1, offset: 0 },
end: { column: 8, line: 1, offset: 7 },
source: '{{aaa}}'
}
}
================================================
* 标签ast语法树
* 假如html: `<div></div>`
{
type: 1,
isSelfClosing: false,
children: [],
loc: {
start: { column: 1, line: 1, offset: 0 },
end: { column: 12, line: 1, offset: 11 },
source: '<div></div>'
}
}
================================================
* 根 自己创建的, 将所有标签都包裹起来
{
type: 0,
children: [ ... ],
loc: {
start: { ... },
end: { ... },
source: '...'
}
}
export const enum NodeTypes {
ROOT,
ElEMENT,
TEXT,
SIMPLE_EXPRESSION = 4,
INTERPOLATION = 5,
COMPOUND_EXPRESSION = 8,
TEXT_CALL = 12,
VNODE_CALL = 13,
JS_CALL_EXPRESSION = 17
}
function createRoot(children,loc){
return {
type: NodeTypes.ROOT,
children,
loc
}
}
export function baseParse(content) {
const context = createParserContext(content)
const start = getCursor(context)
let children = parseChildren(context)
let rootLoc = getSelection(context, start)
return createRoot(children, rootLoc)
}
function parseChildren(context) {
const nodes = []
while (!isEnd(context)) {
const s = context.source
let node
if (s[0] == '<') {
node = parseElement(context)
} else if (s.startsWith('{{')) {
node = parseInterpolation(context)
} else {
node = parseText(context)
}
nodes.push(node)
}
nodes.forEach((node, index) => {
if (node.type === NodeTypes.TEXT) {
if (!/[^ \t\r\n]/.test(node.content)) {
nodes[index] = null
} else {
node.content = node.content.replace(/[ \t\r\n]+/g,' ')
}
}
})
return nodes.filter(Boolean)
}
function parseElement(context) {
let ele:any = parseTag(context)
const children = parseChildren(context)
if(context.source.startsWith('</')){
parseTag(context)
}
ele.children = children
ele.loc = getSelection(context, ele.loc.start)
return ele
}
function parseInterpolation(context) {
const start = getCursor(context)
const closeIndex = context.source.indexOf('}}', '{{')
advanceBy(context, 2)
const innerStart = getCursor(context)
const innerEnd = getCursor(context)
const rawContentLength = closeIndex - 2
const preTrimContent = parseTextData(context, rawContentLength)
const content = preTrimContent.trim()
const startOffset = preTrimContent.indexOf(content)
if (startOffset > 0) {
advancePositionWithMutation(innerStart, preTrimContent, startOffset)
}
const endOffset = content.length + startOffset
advancePositionWithMutation(innerEnd,preTrimContent,endOffset)
advanceBy(context, 2)
return {
type: NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION,
content: {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION,
isStatic: false,
loc: getSelection(context, innerStart, innerEnd),
content
},
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
function parseText(context) {
const endTokens = ['<', '{{']
let endIndex = context.source.length
for (let i = 0; i < endTokens.length; i++) {
const index = context.source.indexOf(endTokens[i], 1)
if (index !== -1 && endIndex > index) {
endIndex = index
}
}
let start = getCursor(context)
const content = parseTextData(context, endIndex)
return {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT,
content,
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
function createParserContext(content) {
return {
column: 1,
line: 1,
offset: 0,
source: content,
originalSource: content,
}
}
function getCursor(context) {
let { line, column, offset } = context
return { line, column, offset }
}
function getSelection(context, start, end?) {
end = end || getCursor(context)
return {
start,
end,
source: context.originalSource.slice(start.offset, end.offset)
}
}
function isEnd(context) {
const source = context.source
if(source.startsWith('</')){ return true }
return !source
}
function advanceBy(context, endIndex) {
let s = context.source
advancePositionWithMutation(context, s, endIndex)
context.source = s.slice(endIndex)
}
function advancePositionWithMutation(context, s, endIndex) {
let linesCount = 0
let linePos = -1
for (let i = 0; i < endIndex; i++) {
if (s.charCodeAt(i) == 10) {
linesCount++;
linePos = i
}
}
context.offset += endIndex
context.line += linesCount
context.column = linePos == -1 ? context.column + endIndex : endIndex - linePos
}
function parseTextData(context, endIndex) {
const rawText = context.source.slice(0, endIndex)
advanceBy(context, endIndex)
return rawText
}
function parseTag(context){
const start = getCursor(context)
const match = /^<\/?([a-z][^ \t\r\n/>]*)/.exec(context.source)
const tag = match[1]
advanceBy(context, match[0].length)
advanceSpaces(context)
const isSelfClosing = context.source.startsWith('/>')
advanceBy(context, isSelfClosing ? 2 : 1)
return {
type: NodeTypes.ElEMENT,
tag,
isSelfClosing,
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
function advanceSpaces(context){
const match = /^[ \t\r\n]+/.exec(context.source)
if (match) {
advanceBy(context, match[0].length)
}
}
2.ast优化transfrom(transform.ts)
- 处理动态标记, 处理文本, 元素, 属性, 指令...
import { PatchFlags } from "@vue/shared/src"
import { NodeTypes } from "./parse"
export const CREATE_VNODE = Symbol('createVnode')
export const TO_DISPALY_STRING = Symbol('toDisplayString')
export const OPEN_BLOCK = Symbol('openBlock')
export const CREATE_BLOCK = Symbol('createBlock')
export const FRAGMENT = Symbol('Fragment')
export const CREATE_TEXT = Symbol('createTextVNode')
export function getBaseTransformPreset() {
return [
transformElement,
transformText
]
}
export function transform(root, nodeTransforms) {
const context = createTransformContext(root, nodeTransforms)
traverseNode(root, context)
createRootCodegen(root, context)
root.helpers = [...context.helpers]
}
function createVnodeCall(context, tag, props, children, patchFlag) {
context.helper(CREATE_VNODE);
return {
type: NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL,
tag,
props,
children,
patchFlag
}
}
function transformElement(node, context) {
if (node.type != NodeTypes.ElEMENT) { return }
return () => {
const { tag, children } = node
let vnodeTag = `'${tag}'`
let vnodeProps;
let vnodeChildren;
let vnodePatchFlag;
let patchFlag = 0;
if (children.length > 0) {
if (children.length == 1) {
const child = children[0]
const type = child.type
const hasDymanicTextChild = type === NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION || type === NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION;
if (hasDymanicTextChild) {
patchFlag |= PatchFlags.TEXT
}
vnodeChildren = child
} else {
vnodeChildren = children
}
}
if (patchFlag !== 0) {
vnodePatchFlag = patchFlag + ''
}
node.codegenNode = createVnodeCall(context, vnodeTag, vnodeProps, vnodeChildren, vnodePatchFlag);
}
}
function isText(node) {
return node.type === NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION || node.type == NodeTypes.TEXT
}
function createCallExpression(callee, args) {
return {
type: NodeTypes.JS_CALL_EXPRESSION,
callee,
arguments: args
}
}
function transformText(node, context) {
if (node.type == NodeTypes.ROOT || node.type == NodeTypes.ElEMENT) {
return () => {
let hasText = false;
let children = node.children;
let container = null;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const child = children[i];
if (isText(child)) {
hasText = true;
for (let j = i + 1; j < children.length; j++) {
const next = children[j];
if (isText(next)) {
if (!container) {
container = children[i] = {
type: NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION,
loc: child.loc,
children: [child]
}
container.children.push(`+`, next);
children.splice(j, 1);
j--;
}
} else {
container = null;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!hasText || children.length == 1) {
return;
}
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const child = children[i];
if (isText(child) || child.type == NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION) {
const callArgs = [];
callArgs.push(child);
if (child.type !== NodeTypes.TEXT) {
callArgs.push(PatchFlags.TEXT + '');
}
children[i] = {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT_CALL,
content: child,
loc: child.loc,
codegenNode: createCallExpression(
context.helper(CREATE_TEXT),
callArgs
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
export function createTransformContext(root, nodeTransforms) {
const context = {
root,
currentNode: root,
nodeTransforms,
helpers: new Set(),
helper(name) {
context.helpers.add(name);
return name;
}
};
return context
}
function traverseChildren(node, context) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++) {
const child = node.children[i];
traverseNode(child, context);
}
}
function traverseNode(node, context) {
const { nodeTransforms } = context;
context.currentNode = node;
const exits = [];
for (let i = 0; i < nodeTransforms.length; i++) {
const onExit = nodeTransforms[i](node, context);
if (onExit) exits.push(onExit)
}
switch (node.type) {
case NodeTypes.ROOT:
case NodeTypes.ElEMENT:
traverseChildren(node, context);
case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION:
context.helper(TO_DISPALY_STRING)
}
let i = exits.length;
context.currentNode = node;
while (i--) {
exits[i]();
}
}
function createRootCodegen(root, context) {
const { helper } = context;
const children = root.children;
helper(OPEN_BLOCK)
helper(CREATE_BLOCK)
if (children.length == 1) {
const child = children[0];
const codegen = child.codegenNode;
codegen.isBlock = true;
root.codegenNode = codegen
} else if (children.length > 1) {
root.codegenNode = createVnodeCall(
context, helper(FRAGMENT),
undefined,
children,
PatchFlags.STABLE_FRAGMENT)
root.codegenNode.isBlock= true;
}
}
3.拼接codegen(codegen.ts)
- 就是上面最终要的字符串
- 这里处理不完整 只是个思路
import { NodeTypes } from "./parse"
import { CREATE_BLOCK, CREATE_TEXT, CREATE_VNODE, FRAGMENT, OPEN_BLOCK, TO_DISPALY_STRING } from "./transform"
export const helperNameMap: any = {
[FRAGMENT]: `Fragment`,
[OPEN_BLOCK]: `openBlock`,
[CREATE_BLOCK]: `createBlock`,
[CREATE_VNODE]: `createVNode`,
[TO_DISPALY_STRING]: "toDisplayString",
[CREATE_TEXT]: "createTextVNode"
}
function createCodegenContext(ast) {
const newLine = (n) => {
context.push('\n' + ' '.repeat(n))
}
const context = {
code: ``,
push(c) {
context.code += c;
},
helper(key){
return `${helperNameMap[key]}`;
},
indentLevel: 0,
newLine() {
newLine(context.indentLevel);
},
indent() {
newLine(++context.indentLevel);
},
deindent() {
newLine(--context.indentLevel);
}
}
return context
}
function genVNodeCall(node,context){
const {push,helper} = context
const {tag,children,props,patchFlag,isBlock} = node
if (isBlock) {
push(`(${helper(OPEN_BLOCK)}(),`)
}
}
function genNode(node, context) {
switch (node.type) {
case NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL:
genVNodeCall(node, context)
break;
case NodeTypes.ElEMENT:
break;
case NodeTypes.TEXT:
break;
case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION:
break
case NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION:
break;
case NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION:
break;
case NodeTypes.TEXT_CALL:
break;
case NodeTypes.JS_CALL_EXPRESSION:
break;
}
}
export function generate(ast) {
const context = createCodegenContext(ast);
const { push, newLine, indent, deindent } = context;
push(`const _Vue = Vue`);
newLine();
push(`return function render(_ctx){`);
indent();
push(`with (_ctx) {`)
indent()
push(`const {${ast.helpers.map(s => `${helperNameMap[s]}`).join(',')}} = _Vue`);
newLine()
push(`return `)
genNode(ast.codegenNode, context);
deindent();
push(`}`)
deindent();
push(`}`);
return context.code
}
完