基础回顾
使用步骤:文件结构如下:
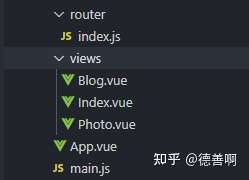
// router/index.js 配置
// 导入:
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Index from '../views/Index.vue'
// 1. 注册路由插件
// Vue.use 用来注册组件
// 接收一个参数,如果参数是函数直接调用来注册插件,
// 如果参数是对象,会调用传入对象的 install 方法注册插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 路由规则
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Index',
component: Index
},
{
path: '/blog',
name: 'Blog',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "blog" */ '../views/Blog.vue')
},
{
path: '/photo',
name: 'Photo',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "photo" */ '../views/Photo.vue')
}
]
// 2. 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
// main.js 配置
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
// 3. 注册 router 对象
router,
// 给 vue 实例注入 $route 与 $router 两个属性
// $route 路由规则
// $router 路由对象,VueRouter 实例,提供路由方法,路由模式,currentRoute当前路由规则
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
// App.vue 使用
<template>
<div id="app">
<div>
<img src="@/assets/logo.png" alt="">
</div>
<div id="nav">
<!-- 5. 创建链接 -->
<router-link to="/">Index</router-link> |
<router-link to="/blog">Blog</router-link> |
<router-link to="/photo">Photo</router-link>
</div>
<!-- 4. 创建路由组建的占位 -->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
动态路由:
文件结构: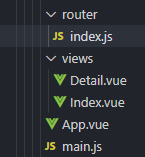
// router/index.js 配置
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Index from '../views/Index.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Index',
component: Index
},
{
// 根据id的值加载详情页面
path: '/detail/:id',
name: 'Detail',
// 开启 props,会把 URL 中的参数传递给组件
// 在组件中通过 props 来接收 URL 参数
props: true,
// 路由懒加载
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "detail" */ '../views/Detail.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
// views/Detail.vue
// 页面使用:两种方式,第一种方式依赖路由传参,推荐第二种方式
<template>
<div>
<!-- 方式1: 通过当前路由规则,获取数据 -->
通过当前路由规则获取:{{ $route.params.id }}
<br>
<!-- 方式2:路由规则中开启 props 传参 -->
通过开启 props 获取:{{ id }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Detail',
props: ['id']
}
</script>
嵌套路由:
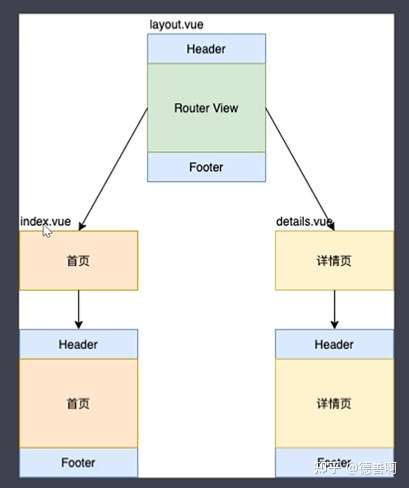
根据图示 index.vue 与 details.vue 页面均使用了layout的 Header 与 Footer,此时 index.vue 与 details.vue 页面保持不变,在 layout.vue 中,则需要使用 router-view 占位,用于获取即将插入的内容。
layout.vue 内容
<template>
<div>
<div>
<img width="25%" src="@/assets/logo.png">
</div>
<div>
<router-view></router-view> => 中间使用router-view 占位,用于存放其余组件内容
</div>
<div>
Footer
</div>
</div>
</template>
// router/index.js 配置
{
path: '/',
component: Layout,
children: [
{
name: 'index',
path: '',
component: Index
},
{
name: 'detail',
path: 'detail/:id',
props: true,
component: () => import('@/views/Detail.vue')
}
]
}
编程式导航:
根据 $router 的 replace() push() go() 方法,指定路由:
<template>
<div class="home">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/">Index</router-link>
</div>
<button @click="replace"> replace </button>
<button @click="goDetail"> Detail </button>
<button @click="go"> go(-2) </button>
</div>
</template>
export default {
name: 'Index',
methods: {
replace () {
this.$router.replace('/login') => 不保留访问历史
},
goDetail () {
// this.$router.push('/')
this.$router.push({ name: 'Detail', params: { id: 1 } }) => 保留访问历史且可以传递参数
},
go () {
this.$router.go(-2) => 回退页面到指定参数页面,回退两个页面
}
}
}
Hash 和 History 模式的区别:
以上两种形式都是客户端路由,不会向服务器发送请求:
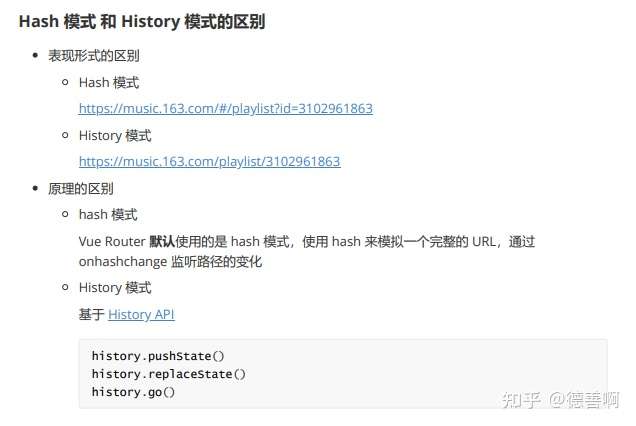


HTML5 History 模式的使用:
- History 需要服务器的支持
- 单页应用中,服务端不存在 www.testurl.com/login 这样的地址会返回找不到该页面
- 在服务端应该除了静态资源外都返回单页应用的index.html
node.js 服务器配置:
// node.js 配置
const path = require('path')
// 导入处理 history 模式的模块
const history = require('connect-history-api-fallback')
// 导入 express
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// 注册处理 history 模式的中间件
app.use(history()) => // 处理 History 模式
// 处理静态资源的中间件,网站根目录 ../web
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, '../web'))) // => 前端文件放置web文件夹下
// 开启服务器,端口是 3000
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('服务器开启,端口:3000')
})
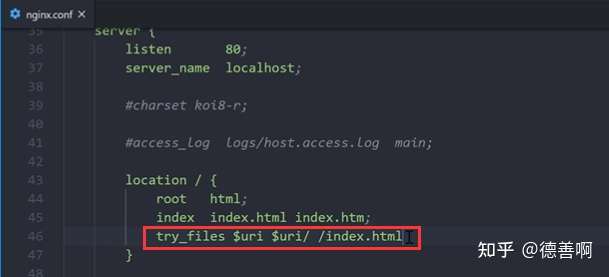
nginx服务器配置:
模拟实现自己的vue-router

回顾核心代码:
// 注册路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
new Vue({
// 创建 Vue实例,注册 router 对象
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
VueRouter 类图:
!
注:' + ' 代表对外公开的方法,' _ ' 代表静态方法
-
options:记录构造函数中传入的对象
-
data:对象,其中有一个属性current ,记录路由地址,设置data的目的是我们需要一个响应式的对象,路由地址发生变化,对应的组件自动更新,调用 Vue.observable() 实现data属性的响应式
-
routeMap:记录路由地址和组件的对应关系的对象,会将路由规则解析到 routeMap 中,键为路由地址,值为路由组件;
-
+constructor(option):VueRouter : 构造函数初始化 VueRouter 的属性
-
+init():void :调用下面三个方法,不同的代码分割到不同的方法中实现
-
+initEvent():void :注册popstate事件,监听浏览器历史的变化
-
+createRouteMap():void :初始化routeMap属性,将构造函数中传入的路由规则转换成键值对的形式,存放到routeMap中,在 router-view 组件中会使用到 routeMap。
-
+initComponents(Vue):void :用来创建 router-link 与 router-view 组件
-
_install(Vue):void :实现Vue的插件机制

// 模拟 VueRouter 响应式原理的 history 模式 || hash 模式
let _Vue = null
class VueRouter {
static install(Vue){
//1 判断当前插件是否被安装
if(VueRouter.install.installed) return;
VueRouter.install.installed = true
//2 把Vue的构造函数记录在全局
_Vue = Vue
//3 把创建Vue的实例传入的router对象注入到Vue实例
// _Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
// this.$options.router 在外部访问不到,使用mixin混入函数,当vue的钩子函数beforeCreat调用时
// 如果是vue实例不是vue组件,则将实例传入的router对象注入到_Vue实例
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
if(this.$options.router){
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
// 初始化插件的时候,调用 init
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
constructor(options){
this.options = options
this.routeMap = {}
// 使用observable方法,实现data的current的响应式
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current:"/"
})
}
// 调用 init 方法统一调用以下方法
init(){
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponent(_Vue)
this.initEvent()
}
createRouteMap(){
//遍历所有的路由规则 把路由规则解析成键值对的形式存储到routeMap中
this.options.routes.forEach(route => {
this.routeMap[route.path] = route.component
});
}
initComponent(Vue){
// 实现 router-link 组件 --- history
Vue.component("router-link",{
props:{ // 接受 router-link 传递的路由路径
to:String
},
render(h){ // 渲染dom
return h("a",{
attrs:{
href:this.to
},
on:{
click:this.clickhander
}
},[this.$slots.default])
},
methods:{
clickhander(e){
history.pushState({},"",this.to) // => 改变url地址
this.$router.data.current=this.to // => 更改路由地址,实现不刷新更改路由
e.preventDefault() // => 去除超链接默认点击事件
}
}
// template:"<a :href='to'><slot></slot><>" // 等同于上面的render函数,但是需要带编译器版本的vuejs支持template
})
// 实现 router-link 组件 --- hash
// Vue.component("router-link", {
// props: {
// to: String
// },
// render(h) {
// return h("a", {
// attrs: {
// href: "#" + this.to
// },
// }, [this.$slots.default])
// }
// })
const self = this
Vue.component("router-view",{
render(h){
// self.data.current => 当前路由地址
const cm = self.routeMap[self.data.current] // => h 函数可以渲染组件 self.data.current 为当前路由地址
return h(cm)
}
})
}
// 地址栏响应页面 --- history
initEvent(){
// 解决地址栏地址改变时(操作地址栏按钮),加载组件并渲染页面
// 历史发生变化
window.addEventListener("popstate",()=>{
this.data.current = window.location.pathname
})
}
// 地址栏响应页面 --- hash
// initEvent() {
// // 当路径变化之后,重新获取当前路径并记录到 current
// window.addEventListener('hashchange', this.onHashChange.bind(this))
// window.addEventListener('load', this.onHashChange.bind(this))
// }
// onHashChange() {
// // 初始化时路由的hash模式
// if (!window.location.hash) {
// window.location.hash = '#/'
// }
// this.data.current = window.location.hash.substr(1) || '/'
// }
}
注意:
1、关于 init() 事件也可以在构造函数 constructor 中执行,写在 beforeCreate () { } 是当 new Vue({ router }) 的时候更靠后执行;写在 constructor() { } 是当 new VueRouter() 的时候更靠前执行;二者只是调用时机不同。
2、# hash 又称为锚点, 浏览器会理解为页面上的某个具体的位置,不会刷新页面,所以hash模式下,并不需要注册点击事件。