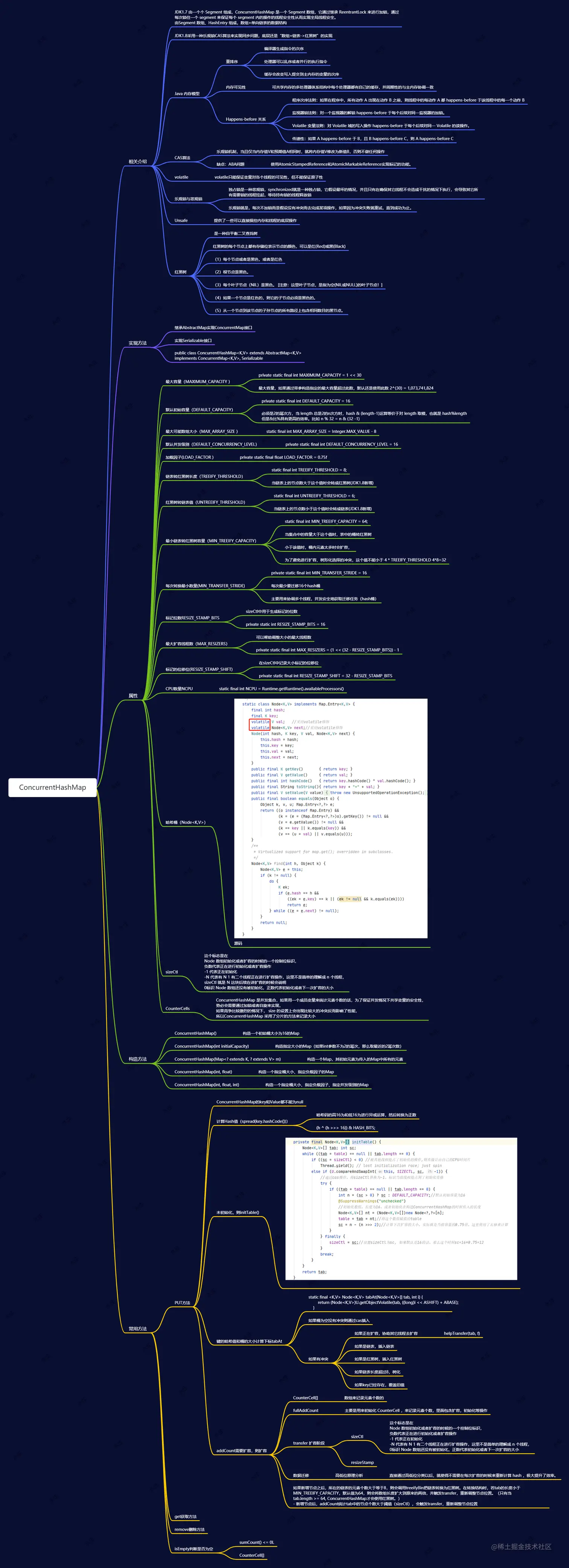
源码解析
put方法源码
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false)
}
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException()
int hash = spread(key.hashCode())
int binCount = 0
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table
Node<K,V> f
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)//如果数组为空,则进行数组初始化
tab = initTable()
// 通过hash值对应的数组下标得到第一个节点
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//如果该下标返回的节点为空,则直接通过cas将新的值封装成node插入即可;如果cas失败,说明存在竞争,则进入下一次循环
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f)
else {//进入到这个分支,说明f是当前nodes数组对应位置节点的头节点,并且不为空
V oldVal = null
synchronized (f) {//给对应的头结点加锁
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {//再次判断对应下标位置是否为f节点
if (fh >= 0) {//头结点的hash值大于0,说明是链表
binCount = 1
for (Node<K,V> e = f
K ek
//如果发现相同的key,则判断是否需要进行值的覆盖
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val
if (!onlyIfAbsent)//默认情况下,直接覆盖旧的值
e.val = value
break
}
//一直遍历到链表的最末端,直接把新的值加入到链表的最后面
Node<K,V> pred = e
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null)
break
}
}
}
//如果当前的f节点是一颗红黑树
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p
binCount = 2
//则调用红黑树的插入方法插入新的值
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {//说明上面在做链表操作
//如果链表长度已经达到临界值8 就需要把链表转换为树结构
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i)
if (oldVal != null)//如果val是被替换的,则返回替换之前的值
return oldVal
break
}
}
}
//将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量加1,有可能触发transfer操作(扩容)
addCount(1L, binCount)
return null
}
spread计算Hash值
static final int spread(int h) { return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;}
initTable初始化表格
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) //被其他线程抢占了初始化的操作,则直接让出自己的CPU时间片
Thread.yield()
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
//通过cas操作,将sizeCtl替换为-1,标识当前线程抢占到了初始化资格
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//初始化数组,长度为16,或者初始化在构造ConcurrentHashMap的时候传入的长度
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]
table = tab = nt
sc = n - (n >>> 2)
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc
}
break
}
}
return tab
}
tabAt计算下标
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
addCount计数
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt);
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
sumCount计数
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells
long sum = baseCount
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
sum += a.value
}
}
return sum
}
fullAddCount源码分析
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h
//获取当前线程的probe的值,如果值为0,则初始化当前线程的probe的值,probe就是随机数
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit()
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()
wasUncontended = true
}
boolean collide = false
for (
CounterCell[] as
//说明counterCells已经被初始化过了
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {//通过该值与当前线程probe求与,获得cells的下标元素,和hash 表获取索引是一样的
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell //cellsBusy=0表示counterCells不在初始化或者扩容状态下
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x)
if (cellsBusy == 0 && //通过cas设置cellsBusy标识,防止其他线程来对counterCells并发处理
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs
//将初始化的r对象的元素个数放在对应下标的位置
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r
created = true
}
} finally {//恢复标志位
cellsBusy = 0
}
if (created)//创建成功,退出循环
break
continue
}
}
collide = false
}
//说明在addCount方法中cas失败了,并且获取probe的值不为空
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))//由于指定下标位置的cell值不为空,则直接通过cas进行原子累加,如果成功,则直接退出
break
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)//如果已经有其他线程建立了新的counterCells或者CounterCells大于CPU核心数(很巧妙,线程的并发数不会超过cpu核心数)
collide = false
else if (!collide)//恢复collide状态,标识下次循环会进行扩容
collide = true
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&//进入这个步骤,说明CounterCell数组容量不够,线程竞争较大,所以先设置一个标识表示为正在扩容 else
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
//扩容一倍 2变成4,这个扩容比较简单
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1]
for (int i = 0
rs[i] = as[i]
counterCells = rs
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0
}
collide = false
continue
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h)
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as && //cellsBusy=0表示没有在做初始化,通过cas更新cellsbusy的值标注当前线程正在做初始化操作
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2]
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x)
counterCells = rs
init = true
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0
}
if (init)
break
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))//竞争激烈,其它线程占据cell 数组,直接累加在base变量中
break
}
}
transfer扩容
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride
//将 (n>>>3相当于 n/8) 然后除以 CPU核心数。如果得到的结果小于 16,那么就使用 16
// 这里的目的是让每个 CPU 处理的桶一样多,避免出现转移任务不均匀的现象,如果桶较少的话,默认一个 CPU(一个线程)处理 16 个桶,也就是长度为16的时候,扩容的时候只会有一个线程来扩容
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE
//nextTab未初始化,nextTab是用来扩容的node数组
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//新建一个n<<1原始table大小的nextTab,也就是32
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1]
nextTab = nt
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE
return
}
nextTable = nextTab
transferIndex = n
}
int nextn = nextTab.length
// 创建一个 fwd 节点,表示一个正在被迁移的Node,并且它的hash值为-1(MOVED),
// 也就是前面我们在讲putval方法的时候,会有一个判断MOVED的逻辑。
// 它的作用是用来占位,表示原数组中位置i处的节点完成迁移以后,
// 就会在i位置设置一个fwd来告诉其他线程这个位置已经处理过了,具体后续还会在讲
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab)
// 首次推进为 true,如果等于 true,说明需要再次推进一个下标(i--),反之,如果是 false,那么就不能推进下标,需要将当前的下标处理完毕才能继续推进
boolean advance = true
//判断是否已经扩容完成,完成就return,退出循环
boolean finishing = false
//通过for自循环处理每个槽位中的链表元素,默认advace为真,通过CAS设置transferIndex属性值,
// 并初始化i和bound值,i指当前处理的槽位序号,bound指需要处理的槽位边界,先处理槽位15的节点;
for (int i = 0, bound = 0
// 这个循环使用CAS不断尝试为当前线程分配任务
// 直到分配成功或任务队列已经被全部分配完毕
// 如果当前线程已经被分配过bucket区域
// 那么会通过--i指向下一个待处理bucket然后退出该循环
Node<K,V> f
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound
//--i表示下一个待处理的bucket,如果它>=bound,表示当前线程已经分配过bucket区域
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {//表示所有bucket已经被分配完毕
i = -1
advance = false
}
//通过cas来修改TRANSFERINDEX,为当前线程分配任务,处理的节点区间为(nextBound,nextIndex)->(0,15)
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound
i = nextIndex - 1
advance = false
}
}
//i<0说明已经遍历完旧的数组,也就是当前线程已经处理完所有负责的bucket
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc
if (finishing) {//如果完成了扩容
nextTable = null
table = nextTab
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1)
return
}
// sizeCtl 在迁移前会设置为 (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2
// 然后,每增加一个线程参与迁移就会将 sizeCtl 加 1, // 这里使用 CAS 操作对 sizeCtl 的低16位进行减 1,代表做完了属于自己的任务
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
//第一个扩容的线程,执行transfer方法之前,会设置 sizeCtl = (resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)
// 后续帮其扩容的线程,执行transfer方法之前,会设置 sizeCtl = sizeCtl+1 每一个退出transfer的方法的线程,退出之前,
// 会设置 sizeCtl = sizeCtl-1 那么最后一个线程退出时:必然有 sc == (resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2),
// 即 (sc - 2) == resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT // 如果 sc - 2 不等于标识符左移 16 位。如果他们相等了,
// 说明没有线程在帮助他们扩容了。也就是说,扩容结束了。
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return
// 如果相等,扩容结束了,更新 finising 变量
finishing = advance = true
// 再次循环检查一下整张表
i = n
}
}
// 如果位置 i 处是空的,没有任何节点,那么放入刚刚初始化的 ForwardingNode ”空节点“
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd)
//表示该位置已经完成了迁移,也就是如果线程A已经处理过这个节点,那么线程B处理这个节点时,hash值一定为MOVED
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true
else {
synchronized (f) {//对数组该节点位置加锁,开始处理数组该位置的迁移工作
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n
Node<K,V> lastRun = f
//遍历当前bucket的链表,目的是尽量重用Node链表尾部的一部分
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next
int b = p.hash & n
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b
lastRun = p
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {//如果最后更新的runBit是0,设置低位节点
ln = lastRun
hn = null
}
else {//否则,设置高位节点
hn = lastRun
ln = null
}
//构造高位以及低位的链表
for (Node<K,V> p = f
int ph = p.hash
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln)
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn)
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln)
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn)
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd)
advance = true
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { //红黑 树的扩容部分
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null
int lc = 0, hc = 0
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first
int h = e.hash
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null)
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p
else
loTail.next = p
loTail = p
++lc
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p
else
hiTail.next = p
hiTail = p
++hc
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln)
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn)
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd)
advance = true
}
}
}
}
}
}
resizeStamp
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
helpTransfer
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab
// 判断此时是否仍然在执行扩容,nextTab=null的时候说明扩容已经结束了
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length)
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {//说明扩容还未完成的情况下不断循环来尝试将当前线程加入到扩容操作中
//下面部分的整个代码表示扩容结束,直接退出循环
// transferIndex<=0表示所有的Node都已经分配了线程
// sc=rs+MAX_RESIZERS 表示扩容线程数达到最大扩容线程数
// sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT !=rs, 如果在同一轮扩容中,那么sc无符号右移比较高位和rs的值,那么应该是相等的。如果不相等,说明扩容结束了
// sc==rs+1 表示扩容结束
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {//在低16位上增加扩容线程数
transfer(tab, nextTab)
break
}
}
return nextTab
}
return table
}
tryPresize
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
//对size进行修复,主要目的是防止传入的值不是一个2次幂的整数,然后通过tableSizeFor来讲入参转化为离该整数最近的2次幂
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1)
int sc
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table
//下面这段代码和initTable是一样的,如果table没有初始化,则开始初始化
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]
table = nt
sc = n - (n >>> 2)
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc
}
}
}
else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break
else if (tab == table) { //这段代码和addCount后部分代码是一样的,做辅助扩容操作
int rs = resizeStamp(n)
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt)
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null)
}
}
}
treeifyBin
private final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int index) {
Node<K,V> b
if (tab != null) {
if ((n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)//tab的长度是不是小于64,如果是,则执行扩容
tryPresize(n << 1)
else if ((b = tabAt(tab, index)) != null && b.hash >= 0) {//否则,将当前链表转化为红黑树结构存储
synchronized (b) { // 将链表转换成红黑树
if (tabAt(tab, index) == b) {
TreeNode<K,V> hd = null, tl = null
for (Node<K,V> e = b
TreeNode<K,V> p =
new TreeNode<K,V>(e.hash, e.key, e.val,
null, null)
if ((p.prev = tl) == null)
hd = p
else
tl.next = p
tl = p
}
setTabAt(tab, index, new TreeBin<K,V>(hd))
}
}
}
}
}
tryPresize
private final void tryPresize(int size) {
//对size进行修复,主要目的是防止传入的值不是一个2次幂的整数,然后通过tableSizeFor来讲入参转化为离该整数最近的2次幂
int c = (size >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(size + (size >>> 1) + 1)
int sc
while ((sc = sizeCtl) >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab = table
//下面这段代码和initTable是一样的,如果table没有初始化,则开始初始化
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (sc > c) ? sc : c
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if (table == tab) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]
table = nt
sc = n - (n >>> 2)
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc
}
}
}
else if (c <= sc || n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
break
else if (tab == table) { //这段代码和addCount后部分代码是一样的,做辅助扩容操作
int rs = resizeStamp(n)
if (sc < 0) {
Node<K,V>[] nt
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
transfer(tab, nt)
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
transfer(tab, null)
}
}
}