须知
- 源码部分去除了无关紧要的方法。例如:get相关方法
- 源码依赖:spring-data-commons-1.13.11.RELEASE
简介
- PartTree是spring-data抽象出的用于表示自定义方法名的类。一个自定义方法对应一个PartTree对象,可以用于基于其API来构建查询,而不必为每次查询执行解析方法名称
整体结构图
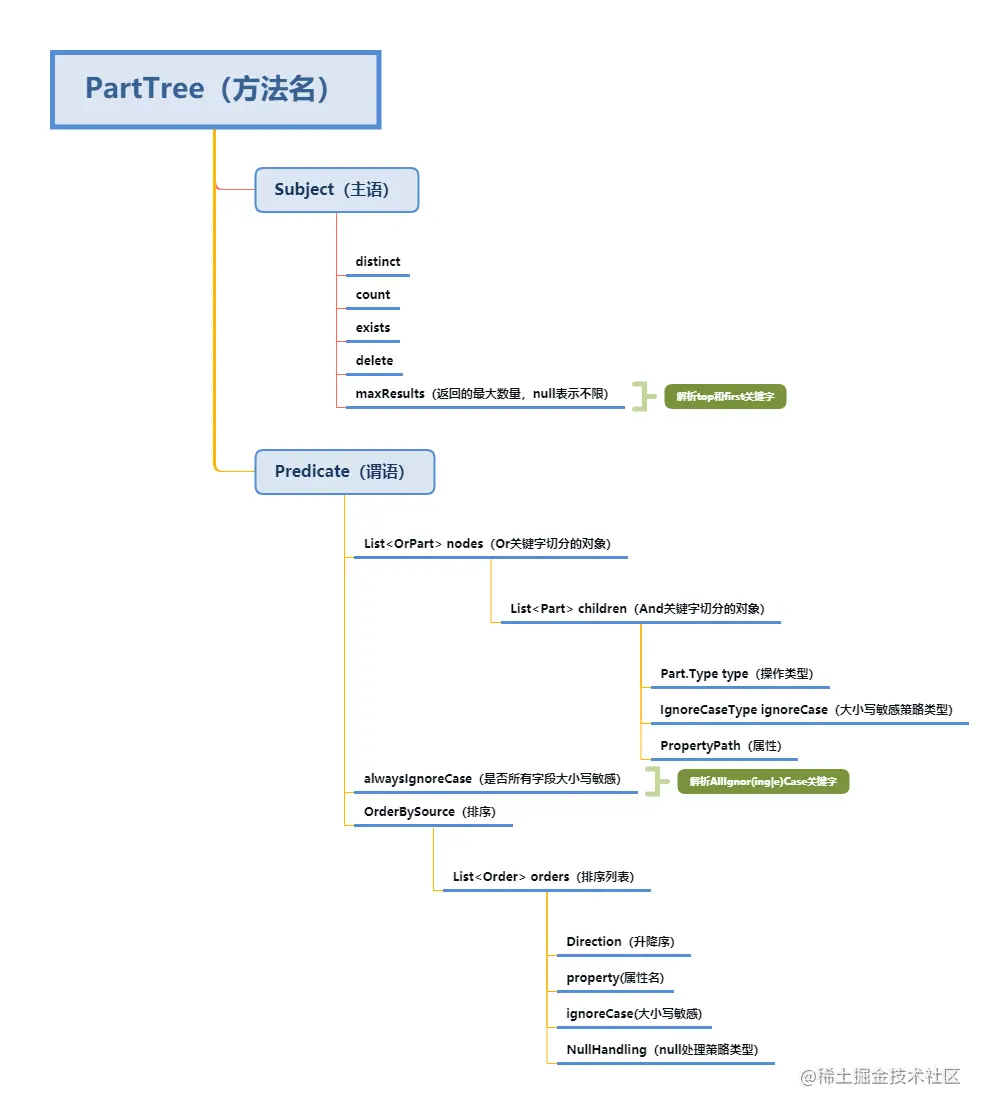
源码
**
* PartTree将repository方法命名字符串解析成对象。使用domain class来校验Part(属性节点)都引用合法的属性。
* PartTree 可以用于基于其API来构建查询,而不必为每次查询执行解析方法名称
*/
public class PartTree implements Iterable<OrPart> {
private static final String KEYWORD_TEMPLATE = "(%s)(?=(\\p{Lu}|\\P{InBASIC_LATIN}))";
private static final String QUERY_PATTERN = "find|read|get|query|stream";
private static final String COUNT_PATTERN = "count";
private static final String EXISTS_PATTERN = "exists";
private static final String DELETE_PATTERN = "delete|remove";
private static final Pattern PREFIX_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile(
"^(" + QUERY_PATTERN + "|" + COUNT_PATTERN + "|" + EXISTS_PATTERN + "|" + DELETE_PATTERN + ")((\\p{Lu}.*?))??By");
private final Subject subject;
private final Predicate predicate;
public PartTree(String source, Class<?> domainClass) {
Matcher matcher = PREFIX_TEMPLATE.matcher(source);
if (!matcher.find()) {
this.subject = new Subject(null);
this.predicate = new Predicate(source, domainClass);
} else {
this.subject = new Subject(matcher.group(0));
this.predicate = new Predicate(source.substring(matcher.group().length()), domainClass);
}
}
public Iterator<OrPart> iterator() {
return predicate.iterator();
}
public Sort getSort() {
OrderBySource orderBySource = predicate.getOrderBySource();
return orderBySource == null ? null : orderBySource.toSort();
}
public boolean isDistinct() {
return subject.isDistinct();
}
public Boolean isCountProjection() {
return subject.isCountProjection();
}
public Boolean isExistsProjection() {
return subject.isExistsProjection();
}
public Boolean isDelete() {
return subject.isDelete();
}
public boolean isLimiting() {
return getMaxResults() != null;
}
public Integer getMaxResults() {
return subject.getMaxResults();
}
public Iterable<Part> getParts() {
List<Part> result = new ArrayList<Part>();
for (OrPart orPart : this) {
for (Part part : orPart) {
result.add(part);
}
}
return result;
}
public Iterable<Part> getParts(Type type) {
List<Part> result = new ArrayList<Part>();
for (Part part : getParts()) {
if (part.getType().equals(type)) {
result.add(part);
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
OrderBySource orderBySource = predicate.getOrderBySource();
return String.format("%s%s", StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(predicate.nodes, " or "),
orderBySource == null ? "" : " " + orderBySource);
}
private static String[] split(String text, String keyword) {
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(String.format(KEYWORD_TEMPLATE, keyword));
return pattern.split(text);
}
private static class Subject {
private static final String DISTINCT = "Distinct";
private static final Pattern COUNT_BY_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile("^count(\\p{Lu}.*?)??By");
private static final Pattern EXISTS_BY_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile("^(" + EXISTS_PATTERN + ")(\\p{Lu}.*?)??By");
private static final Pattern DELETE_BY_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile("^(" + DELETE_PATTERN + ")(\\p{Lu}.*?)??By");
private static final String LIMITING_QUERY_PATTERN = "(First|Top)(\\d*)?";
private static final Pattern LIMITED_QUERY_TEMPLATE = Pattern.compile("^(" + QUERY_PATTERN + ")(" + DISTINCT + ")?"
+ LIMITING_QUERY_PATTERN + "(\\p{Lu}.*?)??By");
private final boolean distinct;
private final boolean count;
private final boolean exists;
private final boolean delete;
private final Integer maxResults;
public Subject(String subject) {
this.distinct = subject == null ? false : subject.contains(DISTINCT);
this.count = matches(subject, COUNT_BY_TEMPLATE);
this.exists = matches(subject, EXISTS_BY_TEMPLATE);
this.delete = matches(subject, DELETE_BY_TEMPLATE);
this.maxResults = returnMaxResultsIfFirstKSubjectOrNull(subject);
}
private Integer returnMaxResultsIfFirstKSubjectOrNull(String subject) {
if (subject == null) {
return null;
}
Matcher grp = LIMITED_QUERY_TEMPLATE.matcher(subject);
if (!grp.find()) {
return null;
}
return StringUtils.hasText(grp.group(4)) ? Integer.valueOf(grp.group(4)) : 1;
}
private final boolean matches(String subject, Pattern pattern) {
return subject == null ? false : pattern.matcher(subject).find();
}
}
private static class Predicate {
private static final Pattern ALL_IGNORE_CASE = Pattern.compile("AllIgnor(ing|e)Case");
private static final String ORDER_BY = "OrderBy";
private final List<OrPart> nodes = new ArrayList<OrPart>();
private final OrderBySource orderBySource;
private boolean alwaysIgnoreCase;
public Predicate(String predicate, Class<?> domainClass) {
String[] parts = split(detectAndSetAllIgnoreCase(predicate), ORDER_BY);
if (parts.length > 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("OrderBy must not be used more than once in a method name!");
}
buildTree(parts[0], domainClass);
this.orderBySource = parts.length == 2 ? new OrderBySource(parts[1], domainClass) : null;
}
private String detectAndSetAllIgnoreCase(String predicate) {
Matcher matcher = ALL_IGNORE_CASE.matcher(predicate);
if (matcher.find()) {
alwaysIgnoreCase = true;
predicate = predicate.substring(0, matcher.start()) + predicate.substring(matcher.end(), predicate.length());
}
return predicate;
}
private void buildTree(String source, Class<?> domainClass) {
String[] split = split(source, "Or");
for (String part : split) {
nodes.add(new OrPart(part, domainClass, alwaysIgnoreCase));
}
}
public Iterator<OrPart> iterator() {
return nodes.iterator();
}
public OrderBySource getOrderBySource() {
return orderBySource;
}
}
public static class OrPart implements Iterable<Part> {
private final List<Part> children = new ArrayList<Part>();
OrPart(String source, Class<?> domainClass, boolean alwaysIgnoreCase) {
String[] split = split(source, "And");
for (String part : split) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(part)) {
children.add(new Part(part, domainClass, alwaysIgnoreCase));
}
}
}
public Iterator<Part> iterator() {
return children.iterator();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(children, " and ");
}
}
}
相关类
Part
源码
public class Part {
private static final Pattern IGNORE_CASE = Pattern.compile("Ignor(ing|e)Case");
private final PropertyPath propertyPath;
private final Part.Type type;
private IgnoreCaseType ignoreCase = IgnoreCaseType.NEVER;
public Part(String source, Class<?> clazz) {
this(source, clazz, false);
}
public Part(String source, Class<?> clazz, boolean alwaysIgnoreCase) {
String partToUse = detectAndSetIgnoreCase(source);
if (alwaysIgnoreCase && ignoreCase != IgnoreCaseType.ALWAYS) {
this.ignoreCase = IgnoreCaseType.WHEN_POSSIBLE;
}
this.type = Type.fromProperty(partToUse);
this.propertyPath = PropertyPath.from(type.extractProperty(partToUse), clazz);
}
private String detectAndSetIgnoreCase(String part) {
Matcher matcher = IGNORE_CASE.matcher(part);
String result = part;
if (matcher.find()) {
ignoreCase = IgnoreCaseType.ALWAYS;
result = part.substring(0, matcher.start()) + part.substring(matcher.end(), part.length());
}
return result;
}
public static enum Type {
BETWEEN(2, "IsBetween", "Between"), IS_NOT_NULL(0, "IsNotNull", "NotNull"), IS_NULL(0, "IsNull", "Null"), LESS_THAN(
"IsLessThan", "LessThan"), LESS_THAN_EQUAL("IsLessThanEqual", "LessThanEqual"), GREATER_THAN("IsGreaterThan",
"GreaterThan"), GREATER_THAN_EQUAL("IsGreaterThanEqual", "GreaterThanEqual"), BEFORE("IsBefore", "Before"), AFTER(
"IsAfter", "After"), NOT_LIKE("IsNotLike", "NotLike"), LIKE("IsLike", "Like"), STARTING_WITH("IsStartingWith",
"StartingWith", "StartsWith"), ENDING_WITH("IsEndingWith", "EndingWith", "EndsWith"), NOT_CONTAINING(
"IsNotContaining", "NotContaining", "NotContains"), CONTAINING("IsContaining", "Containing", "Contains"), NOT_IN(
"IsNotIn", "NotIn"), IN("IsIn", "In"), NEAR("IsNear", "Near"), WITHIN("IsWithin", "Within"), REGEX(
"MatchesRegex", "Matches", "Regex"), EXISTS(0, "Exists"), TRUE(0, "IsTrue", "True"), FALSE(0, "IsFalse",
"False"), NEGATING_SIMPLE_PROPERTY("IsNot", "Not"), SIMPLE_PROPERTY("Is", "Equals");
private static final List<Part.Type> ALL = Arrays.asList(IS_NOT_NULL, IS_NULL, BETWEEN, LESS_THAN, LESS_THAN_EQUAL,
GREATER_THAN, GREATER_THAN_EQUAL, BEFORE, AFTER, NOT_LIKE, LIKE, STARTING_WITH, ENDING_WITH, NOT_CONTAINING,
CONTAINING, NOT_IN, IN, NEAR, WITHIN, REGEX, EXISTS, TRUE, FALSE, NEGATING_SIMPLE_PROPERTY, SIMPLE_PROPERTY);
public static final Collection<String> ALL_KEYWORDS;
static {
List<String> allKeywords = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Type type : ALL) {
allKeywords.addAll(type.keywords);
}
ALL_KEYWORDS = Collections.unmodifiableList(allKeywords);
}
private final List<String> keywords;
private final int numberOfArguments;
private Type(int numberOfArguments, String... keywords) {
this.numberOfArguments = numberOfArguments;
this.keywords = Arrays.asList(keywords);
}
private Type(String... keywords) {
this(1, keywords);
}
public static Part.Type fromProperty(String rawProperty) {
for (Part.Type type : ALL) {
if (type.supports(rawProperty)) {
return type;
}
}
return SIMPLE_PROPERTY;
}
protected boolean supports(String property) {
if (keywords == null) {
return true;
}
for (String keyword : keywords) {
if (property.endsWith(keyword)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public String extractProperty(String part) {
String candidate = StringUtils.uncapitalize(part);
for (String keyword : keywords) {
if (candidate.endsWith(keyword)) {
return candidate.substring(0, candidate.length() - keyword.length());
}
}
return candidate;
}
}
public enum IgnoreCaseType {
NEVER,
ALWAYS,
WHEN_POSSIBLE
}
}
PropertyPath
源码
public class PropertyPath implements Iterable<PropertyPath> {
private static final String PARSE_DEPTH_EXCEEDED = "Trying to parse a path with depth greater than 1000! This has been disabled for security reasons to prevent parsing overflows.";
private static final String DELIMITERS = "_\\.";
private static final String ALL_UPPERCASE = "[A-Z0-9._$]+";
private static final Pattern SPLITTER = Pattern.compile("(?:[%s]?([%s]*?[^%s]+))".replaceAll("%s", DELIMITERS));
private final TypeInformation<?> owningType;
private final String name;
private final TypeInformation<?> type;
private final boolean isCollection;
private PropertyPath next;
PropertyPath(String name, Class<?> owningType) {
this(name, ClassTypeInformation.from(owningType), Collections.<PropertyPath> emptyList());
}
PropertyPath(String name, TypeInformation<?> owningType, List<PropertyPath> base) {
String propertyName = name.matches(ALL_UPPERCASE) ? name : StringUtils.uncapitalize(name);
TypeInformation<?> propertyType = owningType.getProperty(propertyName);
if (propertyType == null) {
throw new PropertyReferenceException(propertyName, owningType, base);
}
this.owningType = owningType;
this.isCollection = propertyType.isCollectionLike();
this.type = propertyType.getActualType();
this.name = propertyName;
}
public static PropertyPath from(String source, Class<?> type) {
return from(source, ClassTypeInformation.from(type));
}
public static PropertyPath from(String source, TypeInformation<?> type) {
List<String> iteratorSource = new ArrayList<String>();
Matcher matcher = SPLITTER.matcher("_" + source);
while (matcher.find()) {
iteratorSource.add(matcher.group(1));
}
Iterator<String> parts = iteratorSource.iterator();
PropertyPath result = null;
Stack<PropertyPath> current = new Stack<PropertyPath>();
while (parts.hasNext()) {
if (result == null) {
result = create(parts.next(), type, current);
current.push(result);
} else {
current.push(create(parts.next(), current));
}
}
return result;
}
private static PropertyPath create(String source, Stack<PropertyPath> base) {
PropertyPath previous = base.peek();
PropertyPath propertyPath = create(source, previous.type, base);
previous.next = propertyPath;
return propertyPath;
}
private static PropertyPath create(String source, TypeInformation<?> type, List<PropertyPath> base) {
return create(source, type, "", base);
}
private static PropertyPath create(String source, TypeInformation<?> type, String addTail, List<PropertyPath> base) {
if (base.size() > 1000) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(PARSE_DEPTH_EXCEEDED);
}
PropertyReferenceException exception = null;
PropertyPath current = null;
try {
current = new PropertyPath(source, type, base);
if (!base.isEmpty()) {
base.get(base.size() - 1).next = current;
}
List<PropertyPath> newBase = new ArrayList<PropertyPath>(base);
newBase.add(current);
if (StringUtils.hasText(addTail)) {
current.next = create(addTail, current.type, newBase);
}
return current;
} catch (PropertyReferenceException e) {
if (current != null) {
throw e;
}
exception = e;
}
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\p{Lu}+\\p{Ll}*$");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(source);
if (matcher.find() && matcher.start() != 0) {
int position = matcher.start();
String head = source.substring(0, position);
String tail = source.substring(position);
try {
return create(head, type, tail + addTail, base);
} catch (PropertyReferenceException e) {
throw e.hasDeeperResolutionDepthThan(exception) ? e : exception;
}
}
throw exception;
}
}
总结
属性名解析算法
- 假设: 一个Person实体对象里面有一个Address属性里面包含一个ZipCode属性。在这种情况下,方法名为:
List<Person> findByAddressZipCode(ZipCode zipCode);
- 解析算法: 首先将整个part(AddressZipCode)解释为属性,并使用该名称(首字符小写)检查域类的属性。如果算法成功,就使用该属性。如果不是,就拆分右侧驼峰部分的信号源到头部和尾部,并试图找出相应的属性,在我们的例子中是AddressZip和Code。如果算法找到一个具有头部的属性,那么它需要尾部,并从那里继续构建树,然后按照刚刚描述的方式将尾部分割。如果第一个分割不匹配,就将分割点移动到左边(Address、ZipCode),然后继续。
- 算法的缺点:可能会选择错误的属性。假设Person该类也具有一个addressZip属性。该算法将在第一个拆分回合中匹配,选择错误的属性,然后失败(因为addressZip可能的类型没有code属性)
- 解决方案:使用下划线"_" 手动指定遍历点。例如:findByAddress_ZipCode。
- 注意:官方文档强烈建议遵循以下标准Java命名约定(即,在属性名称中不使用下划线,而使用驼峰大小写)。所以非特殊情况,建议还是使用驼峰命名法即可
自定义方法名解析成PartTree的简单流程
参考