方法及简单代码详解
- 线程停止
package com.Thread;
public class ThreadStop implements Runnable{
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(flag){
System.out.println("线程正在进行"+i++);
}
}
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadStop threadStop = new ThreadStop();
new Thread(threadStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main线程"+i);
if (i==800){
threadStop.stop();
System.out.println("线程停止");
}
}
}
}
- 线程休眠(每一个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁)
package com.Thread;
public class threadTest3 implements Runnable{
private int tickerNumber = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (tickerNumber>=1){
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->得到第"+tickerNumber+"张票");
tickerNumber--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
threadTest3 threadTest3 = new threadTest3();
new Thread(threadTest3,"小盆友").start();
new Thread(threadTest3,"黄牛").start();
new Thread(threadTest3,"农民工").start();
}
}
- 线程礼让
package com.Thread;
public class ThreadYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程结束");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadYield threadYield = new ThreadYield();
new Thread(threadYield,"a").start();
new Thread(threadYield,"b").start();
}
}
- 线程强制执行
package com.Thread;
public class ThreadJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
System.out.println("vip来了"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadJoin threadJoin = new ThreadJoin();
Thread thread= new Thread(threadJoin);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i==100){
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("主线程正在执行"+i);
}
}
}
- 线程状态
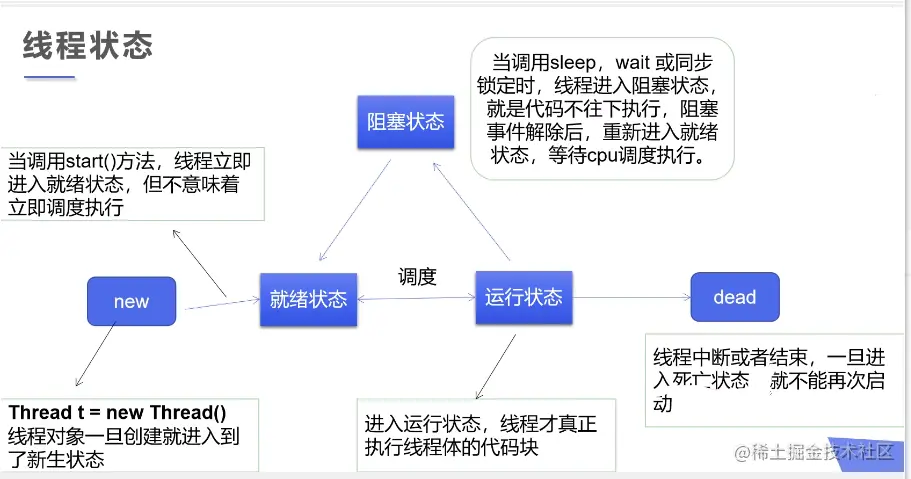
package com.Thread;
import org.omg.PortableServer.THREAD_POLICY_ID;
public class ThreadTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("------");
});
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
while(state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}