objc_class 结构解析
1. 先回顾下内存偏移
int arr[4] = {1, 3, 5, 6};
int *p = arr;
for (int i=0; i<4; i++) {
printf("p[%d] == %d\n", i, p[i]);
}
// output
p[0] == 1
p[1] == 3
p[2] == 5
p[3] == 6
lldb调试
// 1. 打印p指针
p p
(int *) $0 = 0x00007ffeefbff4b0
// 2. 打印数组的地址
p &arr
(int (*)[4]) $10 = 0x00007ffeefbff4b0
// 3. p 指向 arr 的地址
p arr
(int [4]) $3 = ([0] = 1, [1] = 3, [2] = 5, [3] = 6)
// 4. 打印数组首元素的地址
p/x &arr[0] 等于 arr 的地址
(int *) $5 = 0x00007ffeefbff4b0
// 5. 打印数组首元素的值
p *arr
(int) $11 = 1
// 6. 打印数组后续元素的值, 最好带个括号,易读性强
(lldb) p * (arr + 1)
(int) $13 = 3
(lldb) p * (arr + 3)
(int) $14 = 6
通过数组的首地址,然后拿到偏移量就可以获取到其它的元素
2. objc_class & objc_object
根对象 objc_object
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
类 objc_class 继承于 objc_object
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA; // 8 字节
Class superclass; // 8 字节
cache_t cache; // 16 字节
class_data_bits_t bits;
class_rw_t *data() const {
return bits.data();
}
}
对象 + 类 + 元类 都有isa , objc_class 继承于 objc_object
Objective-C 中提供的 class 和 id 其实就是指向 objc_object 的指针, 都属于对象。
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
typedef struct objc_object *id;
只需要计算 cache_t cache 结构体的大小,就可以拿到存储类对象中的详细信息。
struct cache_t {
explicit_atomic<struct bucket_t *> _buckets;
// 结构体指针 8 字节
explicit_atomic<mask_t> _mask;
// typedef uint32_t mask_t; 4 字节
#if __LP64__
uint16_t _flags;
// typedef unsigned short uint16_t; 2 字节
#endif
uint16_t _occupied;
// typedef unsigned short uint16_t; 2 字节
}
计算总共有16字节,那么通过类对象的地址 + offset(8 + 8 + 16)就可以得到 class_data_bits_t bits; 的地址。
3. instance 对象 内存分布
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger age;
@end
@implementation Person
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Person *p1 = [Person alloc];
Person *p2 = [Person alloc];
NSLog(@"p1指向: %@ - p1 内存地址:%p", p1, &p1);
// p1指向: <Person: 0x100404ea0> - p1 内存地址:0x7ffeefbff4a8
NSLog(@"p2指向: %@ - p2 内存地址:%p", p2, &p2);
// p2指向: <Person: 0x100404590> - p2 内存地址:0x7ffeefbff4a0
NSLog(@"hello world");
}
return 0;
}
p1 和 p2 都是 Person 的实例对象,它们是不同的两个对象,分别指向两块不同的内存。
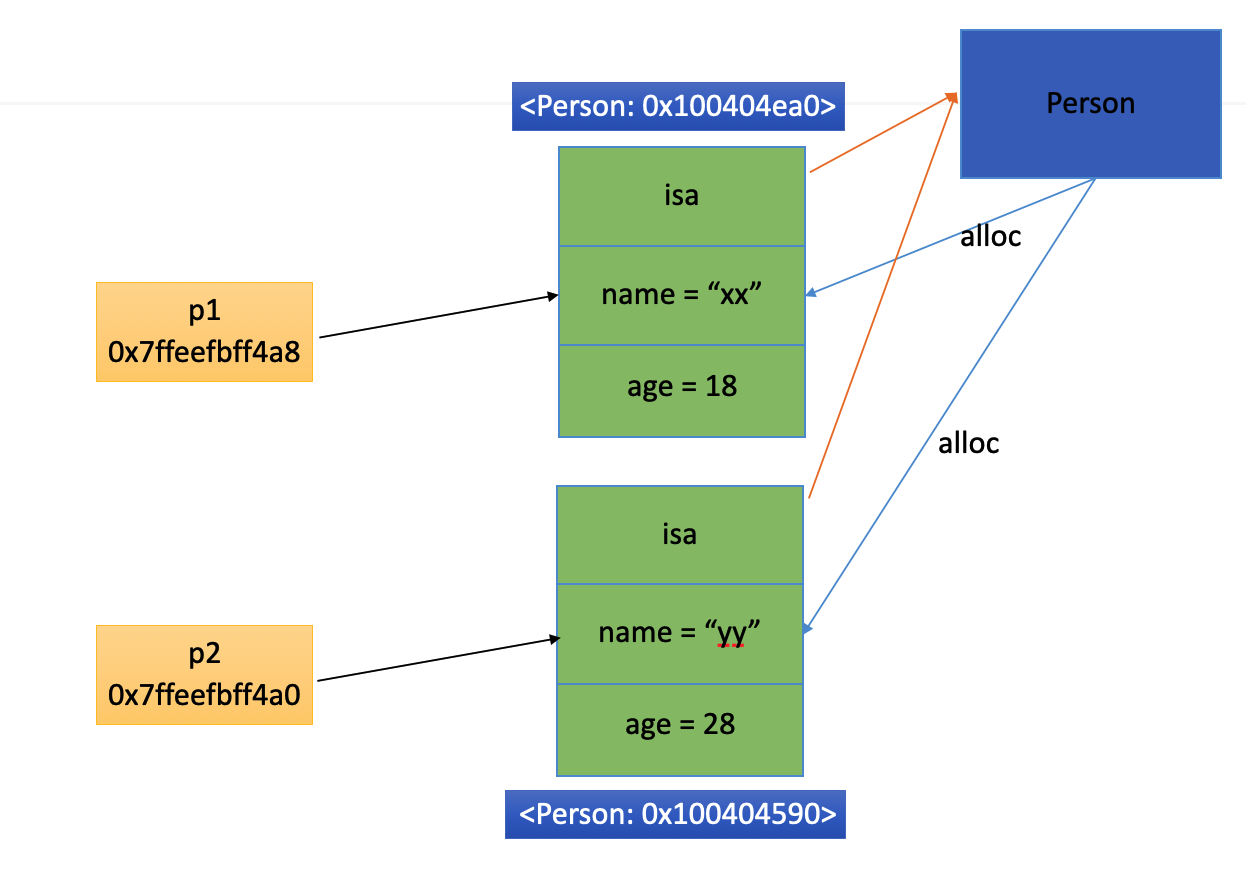
查看 p1 实例对象内存分布
p *p1
(Person) $1 = {
NSObject = {
isa = Person
}
_name = 0x0000000100001010 @"fenglin"
_age = 30
}
(lldb) x/4gx 0x100404ea0
0x100404ea0: 0x001d80010000221d 0x0000000100001010
0x100404eb0: 0x000000000000001e 0x0000000000000000
测试 通过 p *p1 和 x/4gx 0x100404ea0 都可以读到对应的内存分布,但倾向于使用第一种方法。
4. class 对象
Class cls1 = [p1 class];
Class cls2 = [p2 class];
Class cls3 = [Person class];
Class cls4 = object_getClass(p1);
Class cls5 = object_getClass(p2);
NSLog(@"cls1-> %p",cls1);
NSLog(@"cls2-> %p",cls2);
NSLog(@"cls3-> %p",cls3);
NSLog(@"cls4-> %p",cls4);
NSLog(@"cls5-> %p",cls5);
// output
cls1-> 0x100002218
cls2-> 0x100002218
cls3-> 0x100002218
cls4-> 0x100002218
cls5-> 0x100002218
cls1 -> cls5 都是 Person 的类对象,为同一个对象,每个类在内存中仅有一个** Class 对象**。
Class 对象在内存中存储的信息主要包括
-
打印实例对象的类对象
(lldb) p/x Person.class (Class) $0 = 0x00000001000020f0 Person -
查看类对象的内存分布
x/4gx 0x00000001000020f0
0x1000020f0: 0x00000001000020c8 0x0000000100334140 0x100002100: 0x000000010032e410 0x0000801000000000 ``` 3. 查看类对象的 isa 指针
```lldb
// 获取当前的isa
po 0x00000001000020c8
Person
// 通过其他方法获取到Person的元类
p/x object_getClass(Person.class)
(Class) $3 = 0x00000001000021f0
```
3. 查看Person的父类 ``` (lldb) po 0x0000000100334140 NSObject
p/x [objc2 superclass]
(Class) $4 = 0x0000000100334140 NSObject
```
-
获取
class_data_bits_t通过 isa + offset(32) 拿到bits 的地址,再取 * 获取到值0x00000001000020f0 + 0x20 = 0x100002110
(lldb) p/x (class_data_bits_t *)0x100002110 (class_data_bits_t *) $5 = 0x0000000100002110 // 打印class_rw_t (lldb) p $5->data() (class_rw_t *) $6 = 0x0000000100757480 // 打印methods (lldb) p $6.methods() (const method_array_t) $7 = { list_array_tt<method_t, method_list_t> = { = { list = 0x0000000000000000 arrayAndFlag = 0 } } } Fix-it applied, fixed expression was: $6->methods() // 打印properties (lldb) p $6.properties() (const property_array_t) $8 = { list_array_tt<property_t, property_list_t> = { = { list = 0x0000000000000000 arrayAndFlag = 0 } } } Fix-it applied, fixed expression was: $6->properties() // 打印protocols (lldb) p $6.protocols() (const protocol_array_t) $9 = { list_array_tt<unsigned long, protocol_list_t> = { = { list = 0x0000000000000000 arrayAndFlag = 0 } } } Fix-it applied, fixed expression was: $6->protocols()
每个类中有且只有一个 class对象。
5. meta-class 对象
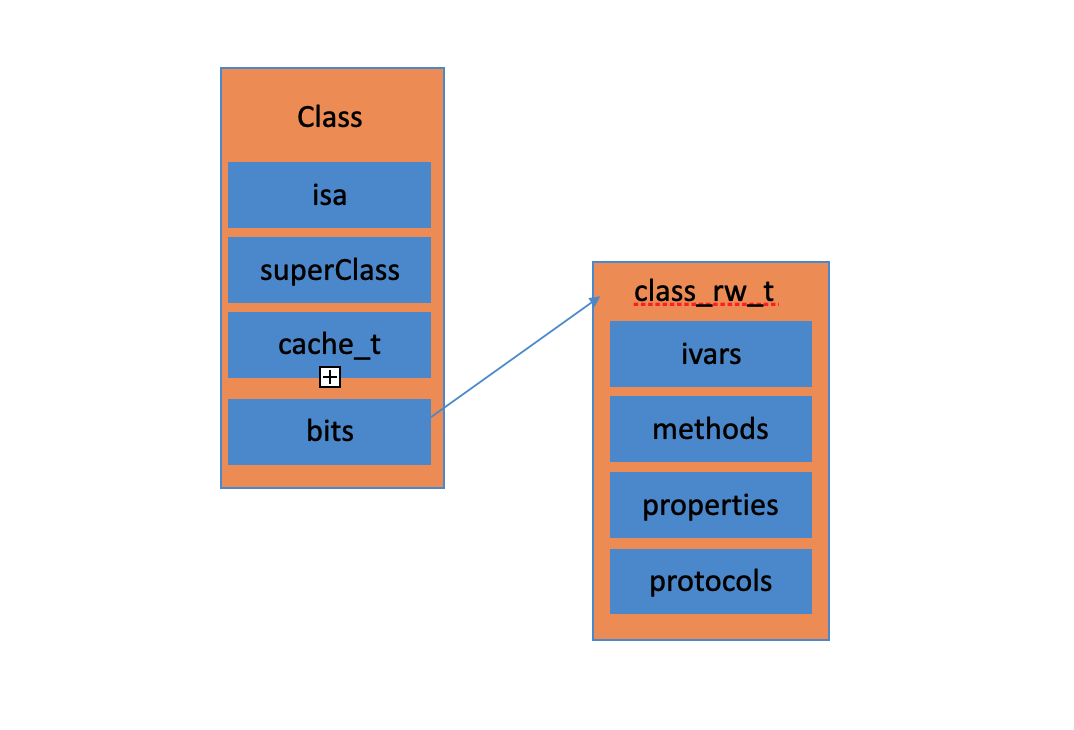
每个类中有且只有一个 meta-class对象。 类对象和元类 的内存结构是一致的,但是用途不一样。
下面通过lldb 来获取下 meta-class 的类方法
// 1. 获取类对象
(lldb) p/x Person.class
(Class) $0 = 0x0000000100002570 Person
// 2. 读取类对象的内存结构
(lldb) x/4gx 0x0000000100002570
0x100002570: 0x0000000100002548 0x0000000100334140
0x100002580: 0x000000010032e410 0x0000802400000000
// 3. 打印类对象的 isa 指针
(lldb) po 0x0000000100002548
Person
// 4. 通过runtime-api打印类对象的 isa 指针
(lldb) p/x object_getClass([Person class])
(Class) $3 = 0x0000000100002548
// 5. 测试结果获取到的Person meta-class 内存地址是一致的
// 6. 打印 Person meta-class 的内存结构
(lldb) x/4gx 0x0000000100002548
0x100002548: 0x00000001003340f0 0x00000001003340f0
0x100002558: 0x0000000100657ed0 0x0002e03500000007
// 7. 打印 Person meta-class 的isa ,返回的是 NSObject meta-class
(lldb) po 0x00000001003340f0
NSObject
// 8. 打印bits,通过Person meta-class 的地址 + offset(32)
(lldb) p/x 0x0000000100002568
(long) $6 = 0x0000000100002568
(lldb) p/x (class_data_bits_t *)0x0000000100002568
(class_data_bits_t *) $7 = 0x0000000100002568
// 9. 获取到 class_rw_t
(lldb) p $7.data()
(class_rw_t *) $8 = 0x00000001019043a0
// 10. 获取到Person 类方法
(lldb) p $8.methods()
(const method_array_t) $9 = {
list_array_tt<method_t, method_list_t> = {
= {
list = 0x0000000100002388
arrayAndFlag = 4294976392
}
}
}
// 11. 打印Person 类方法
(lldb) p $9.list.get(0)
(method_t) $11 = {
name = "class_eat"
types = 0x0000000100000e38 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100000b70 (KCObjc`+[Person class_eat])
}
6. 查看一个类是否是Meta-Class
通过class 方法获取到的都是类对象,不是元类对象
Class objCls = [NSObject class];
Class objCls2 = [[NSObject class] class];
NSLog(@"objCls->%p, objCls2->%p",objCls, objCls2);
// objCls->0x7fff97006118, objCls2->0x7fff97006118
怎么判断一个类是否为meta-class?
BOOL result = class_isMetaClass([NSObject class]);
NSLog(@"result1-> %d", result); // result1-> 0
result = class_isMetaClass(object_getClass([NSObject class]));
NSLog(@"result2-> %d", result); // result2-> 1
7. isa, superclass 总结
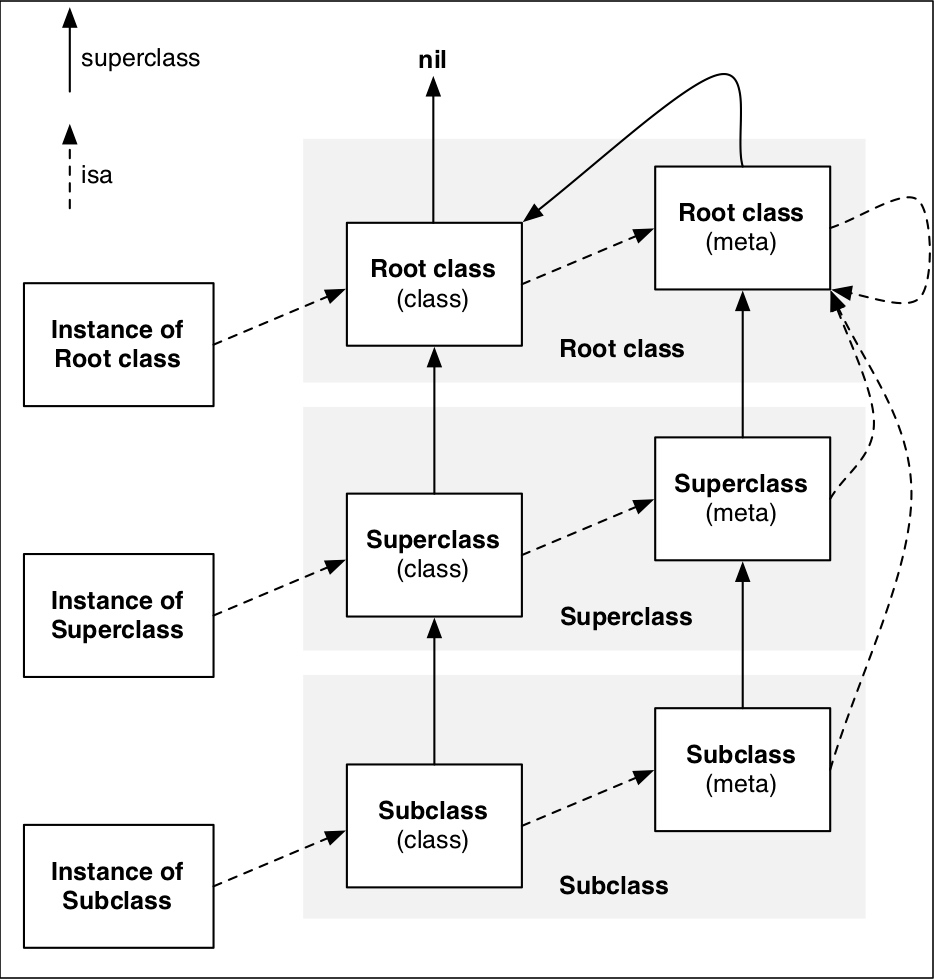 总结:
总结:
-
NSObject 类对象的 父类是什么? nil
-
instance 的 isa 指向 class
-
class 的 isa 指向 meta-class
-
meta-class 的 isa 指向 root-meta-class
-
root-meta-class 的 isa 指向 自身
-
class 的superclass 指向 父类的 class,如果没有父类,那么指向nil(比如NSObjective)
-
meta-class 的superclass 指向 父类的meta-class
-
基类的meta-class 的superclass 指向 基类
-
instance 调用对象方法的轨迹,先通过 isa 找到 class 对象,如果方法在class 对象中不存在,就通过super-class找到父类,只至找到NSObject 类对象
-
instance 调用类方法的轨迹,先通过 isa 找到 meta-class 对象,如果方法在 meta-class 对象中不存在,就通过super-class找到父类,只至找到NSObject 类对象