算法
复杂度、稳定性
O的概念,来描述算法的复杂度,简而言之,就是算法执行所需要的的执行次数,和数据量的关系(时间复杂度),占用额外空间和数据量的关系(空间复杂度)
O(1):常数复杂度(和数据量无关)
从数组中取出第i个元素
O(log n):对数复杂度(每次二分)
O(n):线性时间复杂度(对数组遍历一次)
O(n*log n):线性对数(遍历+二分)
O(n^2):平方方 两层遍历
O(n^3):立立方方
O(log n):对数复杂度(每次二分)
稳定性
数组中[{name:'',age:'xx1'},{name:'',age:'xx2'}]如果按照age排序,排序后,xx1和xx2相对位置不变,我们称为稳定的算法,否则不稳定
排序
搜索和排序,是计算机中几个基本问题
数组的操作就是对比,交换位置比大小
冒泡
最经典和简单粗暴的排序算法,简而言之,就是挨个对比,如果右边的数字大,就交换位置 遍历一次,最大的在最右边
javascript const arr = [10,9,8,7,6] function sort(arr){ let len = arr.length for(let o=arr.length;o>=2;o--){ for(let i=0;i>= len - 1;i++){ if(arr[i] > arr[i + 1]){ [arr[i], arr[i+1]] = [arr[i+1],arr[i]] } } } } sort(arr)
稳定性:复杂度 On^2。稳定(只有在大于时才交换位置)
插入
插入排序逻辑和冒泡类似,只不过没采用挨个交换的逻辑,而是在一个已经拍好序的数组里,插入一个元素,让它依然是有序的
function insertSort(arr){
for(let i = 1;i< arr.length;i++){
for(let j=i;j>0;j--){
if(arr[j] < arr[j - 1]){
[arr[j], arr[j-1]] = [arr[j-1],arr[j]]
}else{
break;
}
}
}
return arr
}
insertSort([11,2,3,32,543,656,2])
快速排序
使用二分思想,可以算是最重要的排序算法,找一个标志位,先遍历一次,所有个头比他矮的放左边,高的放右边,遍历一次就把数组分成两部分,然后遍历两遍数组,递归执行相同的逻辑
let arr = [8, 1, 23, 234, 2, 345, 4564, 56]
function quickSort1(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) {
return arr
}
let left = [];
let right = [];
let flag = arr.shift()
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < flag) {
left.push(arr[i])
} else {
right.push(arr[i])
}
}
return quickSort1(left).concat(flag, quickSort1(right))
}
console.log(quickSort1(arr))
// 原地快排
function quickSort2(arr, low = 0, high = arr.length - 1) {
if (low >= high) {
return
}
let left = low
let right = high
let flag = arr[left]
while (left < right) {
// 从右边尝试找出比flag小的,比flag大,right左移
if (left < right && flag <= arr[right]) {
right--
}
arr[left] = arr[right]
if (left < right && flag >= arr[left]) {
left++
}
arr[right] = arr[left]
}
arr[left] = flag
quickSort2(arr, low, left - 1)
quickSort2(arr, left + 1, high)
return arr
}
console.log(quickSort2(arr))
// 快速排序复杂度是多少()
快速排序啥时候复杂度最差,如果一个数字已经排好序的
复杂度是O(n*2)取第一个
递归
自己调用自己,形成一个调用栈,逐渐缩小目标,达到截止条件返回执行的逻辑
let arr = [1, 2, 3, [4, 5, [6, 7]], 8, 9]
Array.prototype.flat = function(){
let arr = []
this.forEach(item => {
if(Array.isArray(item)){
arr = arr.concat(item)
}else{
arr.push(item)
}
})
return arr
}
二分查找
查找比较简单,我们先来看一个景点的二分查找,有点类似幸运52的猜价格,比如在1和1000之间猜个数字,要先猜500,如果大了,那就是0-500,每次减半很快能查到(已经拍好序的)
// 循环(修改游标)
function binarySearch(arr, target) {
let low = 0;
let high = arr.length - 1
let mid
while (low <= high) {
mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
console.log(mid, arr[mid], target)
if (target === arr[mid]) {
return `找到了${target},在第${mid}个`
}
if (target > arr[mid]) {
low = mid + 1
} else if (target < arr[mid]) {
high = mid - 1
}
}
return -1
}
// 递归
function binarySearch(arr, target,low=0,high=arr.length -1 ){
let n = Math.floor((low + high) / 2)
let mid = arr[n]
if(target === mid){
return `找到了${target},在第${n+1}个`
}else if(target > mid){
return binarySearch(arr, target,n+1, high)
}else if(target < mid){
return binarySearch(arr, target, 0, n-1)
}
}
console.log(binarySearch([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15], 7))
数据结构
队列
先入先出,有点像排队,通过数组push和shift模拟,通常用作任务管理
栈
先入后出,羽毛球筒,先进入的后拿出(匹配括号,函数调用)
class stack {
constructor(){
this.items = []
}
push(item){
this.items.push(item)
}
pop(){
return this.items.pop()
}
}
// 匹配字符'((){}}}{{}}'是否是完整
// html规范校验,jsx解析,表达式计算
function isBlance(symbol){
const stack = new Stack()
const let = '({'
const right = '})'
let popValue
let blance = true
for(let i=0;i< symbol.length;i++){
let s = symbol[i]
if(left.indexOf(symbol[i])){
stack.push(s)
}else if(right.includes(s)){
let popValue = stack.pop()
match(popValue,s)
}
}
function match(popValue, current){
if(left.indexOf(popValue) !== right.indexOf(current)){
blance = false
}
}
return blance
}
console.log(isBlance(''))
链表
有点像火车,车厢和车厢之间链接,有点是可以随时替换车厢,react最新架构的fiber,就是从树变成了链表,能够让diff任务随时中断。
链表不像数组那样式连续的,数组删除插入时需要整体操作,链表只需要记住下一位是哪个就可以
class Node{
constructor(ele){
this.element = ele
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = null
this.current
this.length = 0
}
append(ele){
const node = new Node(ele)
if(this.header === null){
this.heade = node
}else{
this.current = this.head
while(this.current.next){
this.current = this.current.next
}
this.current.next = node
}
this.length ++
}
}
//{head:Node{ele,next:{Node{ele,}}}}
集合
其实就是es6的set,特点就是没有重复数据,也可以用数组模拟
class Set{
constructor(){
this.items = {}
}
match(val){
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(val)
}
add(val){
if(!this.match(val)){
this.items[val] = val
return true
}
return false
}
remove(val){
if(this.has(val)){
delete this.items[val]
}
}
}
哈希表
其实就是js里的对象,它在实际的键值和存入的哈希值之间存在一层映射
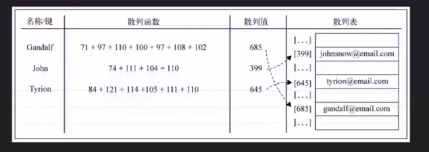
class HashTable{
constructor(){
this.items = []
}
keyToHash(key){
let hash = 0
for(leti=0;i<key.length;i++){
hash += key[i].charCodeAt()
}
hash = hash % 13
return hash
}
get(key){
const hash = this.keyToHash(key)
return this.items[hash]
}
set(key,val){
const hash = this.keyToHash(key)
this.items[hash] = val
}
remove(key){
const hash = this.keyToHash(key)
delete this.items[hash]
}
}
let ht = new HashTable()
ht.set('name','hi')
哈希的问题也很明显,比如两个数的hash值一样的时候,会发生碰撞,(可以扩容)或者可以用存储链表的方式来解决,这些v8引擎帮我们处理的很好了
树
浏览器的DOM就是经典的树结构
* 根节点: 一棵树最顶部的节点
* 内部节点: 在它上面还有其他内部节点或者叶节点的节点
* 叶节点:处于一棵树根部的节点
* 子树: 由树种的内部节点和叶节点组成,
function walk(node, func=() => {}){
_walk(node, func)
}
function _walk(node, func){
node = node.firstChild
while(node){
_walk(node, func)
node = node.nextSibling
}
}
wa
暴力递归
function fb(n){
if(n==1 || n== 2){
return 1
}
return fb(n-1) + fb(n-2)
}
fb(10)
动态规划
动态规划是一种常见的[算法设计技巧],并没有什么高深莫测,至于各种高大上的术语,那是吓唬别人的,
动态规划遵循一套固定的流程,递归的暴力揭发->带备忘录的递归解法->非递归的动态规划解法,这个过程是层层递进的解决问题的过程
// 动态规划找零
class Change{
constructor(changeType){
this.changeType = changeType
this.cache = {}
}
makeChange(amount){
let min = []
if(!amount){
return []
}
if(this.cache[amount]){
return this.cache[amount]
}
for(let i=0;i<this.changeType.length;i++){
//先找一张试试
const leftAmount = amount - this.changeType[i]
let newMin
// 剩余金钱继续找
if(leftAmount >= 0){
newMin = this.makeChange(leftAmount)
}
if(leftAmount >= 0 && (newMin.length < min.length - 1 || !min.length)){
min = [this.changeType[i]].concat(newMin)
}
}
return this.cache[amount] = min
}
}
贪心算法
是一种求近似解的意思,当能满足大部分最优解时就认为符合逻辑
class Change {
constructor(changeType){
this.changeType = changeType.sort((r1-r2) => r2-r1)
}
makeChange(amount){
const arr = []
for(let i=0;i< this.changeType.length;i++){
while(amount - this.changeType[i] > 0){
arr.push(this.changeType[i])
amount = amount - this.changeType[i]
}
}
return arr
}
}
const change = new Change([1,5,10,20,100])