在使用Spring开发时,我们都知道,所有bean都交给Spring容器来统一管理,如果我们想在容器本身的生命周期(比如容器启动、停止)事件上做一些工作怎么办呢?Spring提供了以下接口:Lifecycle接口
1.SmartLifecycle接口概览
我们先来看看SmartLifecycle接口的类图:
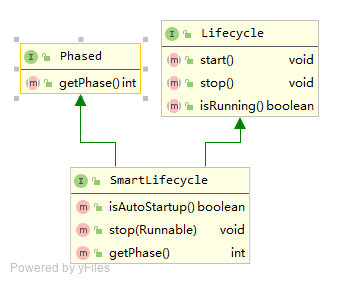
如上所示,SmartLifecycle继承自Lifecycle和Phased两个接口,一共定义了六个方法,简要说明如下:
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| start() | bean初始化完毕后,该方法会被执行 |
| stop() | 容器关闭后: spring容器发现当前对象实现了SmartLifecycle,就调用stop(Runnable), 如果只是实现了Lifecycle,就调用stop() |
| isRunning() | 当前状态,用来判你的断组件是否在运行。 |
| getPhase() | 控制多个SmartLifecycle的回调顺序的,返回值越小越靠前执行start()方法,越靠后执行stop()方法 |
| isAutoStartup() | start方法被执行前先看此方法返回值,返回false就不执行start方法了 |
| stop(Runnable) | 容器关闭后: spring容器发现当前对象实现了SmartLifecycle,就调用stop(Runnable), 如果只是实现了Lifecycle,就调用stop() |
可以看到,Lifecycle接口的方法感知容器变化,而SmartLifecycle只是Lifecycle的增强版,可以自定义优先级(getPhase),自主决定是否随容器启动(isAutoStartup),以及停止时能接受一个runnable对象(stop(Runnable))。
2.Spring容器启动与SmartLifecycle的关系
与之前的切入点一样,我们再来看AbstractApplicationContext类。在AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh方法中,在bean的实例化和初始化操作完毕后,会调用finishRefresh方法:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
...
try {
...
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
...
}
}
finishRefresh方法内容如下,功能注释较清晰
/**
* Finish the refresh of this context, invoking the LifecycleProcessor's
* onRefresh() method and publishing the
* {@link org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent}.
*/
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
可以看到,initLifecycleProcessor()和getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh()这两个方法和本节的主题有关,先从从initLifecycleProcessor开始看起。
initLifecycleProcessor方法的作用是为applicationContext的成员变量lifecycleProcessor赋值,如果名称为lifecycleProcessor的bean对象,则lifecycleProcessor就等于这个bean,否则就实例化一个DefaultLifecycleProcessor对象,再让lifecycleProcessor等于这个对象,并且把这个对象作注册到spring上下文中。
public static final String LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME = "lifecycleProcessor";
...
/**
* Initialize the LifecycleProcessor.
* Uses DefaultLifecycleProcessor if none defined in the context.
* @see org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor
*/
protected void initLifecycleProcessor() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.lifecycleProcessor =
beanFactory.getBean(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, LifecycleProcessor.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using LifecycleProcessor [" + this.lifecycleProcessor + "]");
}
}
else {
DefaultLifecycleProcessor defaultProcessor = new DefaultLifecycleProcessor();
defaultProcessor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.lifecycleProcessor = defaultProcessor;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME, this.lifecycleProcessor);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + LIFECYCLE_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.lifecycleProcessor.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
接着看getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh()的执行。根据上面的分析,如果没有自定义的LifecycleProcessor对象,就会创建一个DefaultLifecycleProcessor对象,因此执行的就是DefaultLifecycleProcessor的onRefresh方法
@Override
public void onRefresh() {
startBeans(true);
this.running = true;
}
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
//取得所有Lifecycle接口的实例,此map的key是实例的名称,value是实例
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<>();
lifecycleBeans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
//autoStartupOnly等于true时,bean必须实现SmartLifecycle接口,并且isAutoStartup()返回true,才会被放入LifecycleGroup中(后续会从LifecycleGroup中取出来执行start())
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle && ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
int phase = getPhase(bean);
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(phase);
if (group == null) {
group = new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly);
//phases是个map,key是Lifecycle实例的phase值,value是Lifecycle实例
phases.put(phase, group);
}
//当前实例加入LifecycleGroup中,该LifecycleGroup内的所有实例的phase都相等
group.add(beanName, bean);
}
});
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<>(phases.keySet());
//按照所有的phase值排序,然后依次执行bean的start方法,每次都是一批phase相同的
Collections.sort(keys);
for (Integer key : keys) {
//对所有Lifecycle实例逐个调用start方法
phases.get(key).start();
}
}
}
SmartLifecycle的实例的start()被调用的地方是在LifecycleGroup内部,对应的方法是doStart(),如下所示:
/**
* Start the specified bean as part of the given set of Lifecycle beans,
* making sure that any beans that it depends on are started first.
* @param lifecycleBeans a Map with bean name as key and Lifecycle instance as value
* @param beanName the name of the bean to start
*/
private void doStart(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, String beanName, boolean autoStartupOnly) {
Lifecycle bean = lifecycleBeans.remove(beanName);
if (bean != null && bean != this) {
String[] dependenciesForBean = getBeanFactory().getDependenciesForBean(beanName);
for (String dependency : dependenciesForBean) {
//如果有依赖类,迭代调用依赖类的start方法
doStart(lifecycleBeans, dependency, autoStartupOnly);
}
if (!bean.isRunning() &&
(!autoStartupOnly || !(bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) || ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Starting bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" + bean.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
try {
bean.start();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to start bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully started bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
}
}
小结如下:
Lifecycle的处理都是委托给LifecycleProcessor执行的,先准备好此实例;- 将所有的
Lifecycle实例按照phase分组; - 从
phase值最小的分组开始,依次执行其中每个Lifecycle对象的start()方法;
3.Spring容器关闭与SmartLifecycle的关系
在上述容器启动时的分析中,我们知道Lifecycle的处理都是委托给LifecycleProcessor执行的,再看一下LifecycleProcessor接口,除了与启动相关的onRefresh()方法,还有与容器关闭相关的onClose()方法。
public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle {
/**
* Notification of context refresh, e.g. for auto-starting components.
*/
void onRefresh();
/**
* Notification of context close phase, e.g. for auto-stopping components.
*/
void onClose();
}
去看看该方法的调用处,LifecycleProcessor的onClose()方法是在AbstractApplicationContext的doClose()方法中被调用的:
protected void doClose() {
// Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary...
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing " + this);
}
...
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
...
}
}
继续去看DefaultLifecycleProcessor中是如何实现的,DefaultLifecycleProcessor的onClose()方法中先调用stopBeans()方法,再将成员变量running设置为false,表示状态已不是运行中:
@Override
public void onClose() {
stopBeans();
this.running = false;
}
startBeans方法和启动时执行start的逻辑基本相似,不同的是执行顺序正好相反;
private void stopBeans() {
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<>();
lifecycleBeans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
int shutdownPhase = getPhase(bean);
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(shutdownPhase);
if (group == null) {
group = new LifecycleGroup(shutdownPhase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, false);
phases.put(shutdownPhase, group);
}
group.add(beanName, bean);
});
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<>(phases.keySet());
keys.sort(Collections.reverseOrder());
for (Integer key : keys) {
phases.get(key).stop();
}
}
}
继续看stop()方法:
public void stop() {
if (this.members.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Stopping beans in phase " + this.phase);
}
this.members.sort(Collections.reverseOrder());
//这里有个同步逻辑,CounDownLatch中计数器的数量为当前LifecycleGroup中Lifecycle实例数量
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(this.smartMemberCount);
Set<String> countDownBeanNames = Collections.synchronizedSet(new LinkedHashSet<>());
Set<String> lifecycleBeanNames = new HashSet<>(this.lifecycleBeans.keySet());
for (LifecycleGroupMember member : this.members) {
//这个containsKey判断很重要,在doStop方法中,SmartLifecycle的stop方法可能会在新线程中执行,执行时如果发现了bean的依赖bean,会先去执行依赖bean的stop方法,
//因此有可能此处的Lifecycle实例是某个实例A的依赖bean,已经在执行A实例的stop时执行过stop方法了,执行stop方法完成的时候会将自己从this.lifecycleBeans中remove掉,所以在this.lifecycleBeans就不存在了
if (lifecycleBeanNames.contains(member.name)) {
doStop(this.lifecycleBeans, member.name, latch, countDownBeanNames);
}
else if (member.bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) {
// Already removed: must have been a dependent bean from another phase
latch.countDown();
}
}
try {
//等到所有Lifecycle实例都执行完毕,当前线程才会执行下去
latch.await(this.timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (latch.getCount() > 0 && !countDownBeanNames.isEmpty() && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Failed to shut down " + countDownBeanNames.size() + " bean" +
(countDownBeanNames.size() > 1 ? "s" : "") + " with phase value " +
this.phase + " within timeout of " + this.timeout + ": " + countDownBeanNames);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
PS:SmartLifecycle实例有个stop(Runnable)方法,实现的时候可以在另一个线程中执行stop()的逻辑,这样就可以多个SmartLifecycle实例并行执行,可以提高执行速度,当前线程为了等待所有执行stop()的线程,用了CountDownLatch来等待,为了避免无限期等待还设置了超时时间;
最后来看看doStop()方法,这里面才会真正的调用到Lifecycle实例的stop()方法,还有上面我们分析的多线程逻辑:
private void doStop(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, final String beanName,
final CountDownLatch latch, final Set<String> countDownBeanNames) {
//从成员变量lifecycleBeans中remove当前bean,表示已经执行过stop方法
Lifecycle bean = lifecycleBeans.remove(beanName);
if (bean != null) {
//找出依赖bean,通过迭代调用来保证依赖bean先执行stop方法
String[] dependentBeans = getBeanFactory().getDependentBeans(beanName);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
doStop(lifecycleBeans, dependentBean, latch, countDownBeanNames);
}
try {
if (bean.isRunning()) {
if (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Asking bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" +
bean.getClass().getName() + "] to stop");
}
countDownBeanNames.add(beanName);
//传入CountDownLatch减一的逻辑,这样SmartLifecycle的stop方法中就可以使用新线程来执行相关逻辑了
((SmartLifecycle) bean).stop(() -> {
latch.countDown();
countDownBeanNames.remove(beanName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean '" + beanName + "' completed its stop procedure");
}
});
}
else {
//如果不是SmartLifecycle实例,就调用stop,在当前线程中执行
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Stopping bean '" + beanName + "' of type [" +
bean.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
bean.stop();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Successfully stopped bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
}
else if (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle) {
// Don't wait for beans that aren't running...
// CountDownLatch中计数器的数量是按照SmartLifecycle实例的数量来算的,如果不在runing状态,实例的stop方法就不会调用,主线程就不用等待这次stop,latch直接减一
latch.countDown();
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failed to stop bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
}
从以上代码可以看出,SmartLifecycle实现类的stop(Runnable)被调用时,LifecycleGroup已经将stop调用完毕后要做的工作通过Runnable传递给实现类了,因此实现类中要记得执行Runnable的run()方法,否则会导致外部调用逻辑的参数不准备,影响调用线程的执行。
小结如下:
AbstractApplicationContext的doClose()方法在容器关闭时会被执行,此处调用LifecycleProcessor的onClose()方法,由LifecycleProcessor负责所有Lifecycle实例的关闭操作;- 将所有的
Lifecycle实例按照phase分组; - 从
phase值最大的分组开始,依次执行其中每个Lifecycle对象的stop()方法; - 对每个
SmartLifecycle实例,若想并行执行以加快stop()执行速度,可以在stop()方法中用新的线程来执行stop()业务逻辑,但是最后不要忘记调用Runnable入参的run()方法,以完成主线程的计数和统计; - 主线程使用了
CountDownLatch,在调用了SmartLifecycle实例的stop()方法后就会等待,等到计数达到SmartLifecycle总数或者等待超时,再继续向后执行;
4.Lifecycle VS SmartLifecycle
经过上面的分析,我们对Lifecycle和SmartLifecycle有了更全面的认知,如果对执行顺序没有要求,在关闭的时候也没有性能或者时间要求,那么就用Lifecycle吧,因为更简单,如果在乎顺序,也期望关闭时多个Lifecycle实例能并行执行,快速结束,SmartLifecycle无疑更适合。
5.实战SmartLifecycle接口扩展
@Component
public class CustomizeLifeCycleLinstener implements SmartLifecycle {
public boolean isRunningFlag() {
return runningFlag;
}
public void setRunningFlag(boolean runningFlag) {
this.runningFlag = runningFlag;
}
private boolean runningFlag = false;
/**
* SmartLifecycle子类的才有的方法,当isRunning方法返回true时,该方法才会被调用。
*/
@Override
public void stop(Runnable callback) {
System.out.println("stop(Runnable)");
/**
* 如果你让isRunning返回true,需要执行stop这个方法,那么就不要忘记调用callback.run()。
* 否则在你程序退出时,Spring的DefaultLifecycleProcessor会认为你这个TestSmartLifecycle没有stop完成,程序会一直卡着结束不了,等待一定时间(默认超时时间30秒)后才会自动结束。
*/
callback.run();
setRunningFlag(false);
}
/**
* 1. 我们主要在该方法中启动任务或者其他异步服务,比如开启MQ接收消息<br/>
* 2. 当上下文被刷新(所有对象已被实例化和初始化之后)时,将调用该方法,默认生命周期处理器将检查每个SmartLifecycle对象的isAutoStartup()方法返回的布尔值。
* 如果为“true”,则该方法会被调用,而不是等待显式调用自己的start()方法。
*/
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("start");
// 执行完其他业务后,可以修改 isRunning = true
setRunningFlag(true);
}
/**
* 接口Lifecycle的子类的方法,只有非SmartLifecycle的子类才会执行该方法。<br/>
* 1. 该方法只对直接实现接口Lifecycle的类才起作用,对实现SmartLifecycle接口的类无效。<br/>
* 2. 方法stop()和方法stop(Runnable callback)的区别只在于,后者是SmartLifecycle子类的专属。
*/
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("stop");
setRunningFlag(false);
}
/**
* 如果工程中有多个实现接口SmartLifecycle的类,则这些类的start的执行顺序按getPhase方法返回值从小到大执行。<br/>
* 例如:1比2先执行,-1比0先执行。 stop方法的执行顺序则相反,getPhase返回值较大类的stop方法先被调用,小的后被调用。
*/
@Override
public int getPhase() {
// 默认为0
return 0;
}
/**
* 1. 只有该方法返回false时,start方法才会被执行。<br/>
* 2. 只有该方法返回true时,stop(Runnable callback)或stop()方法才会被执行。
*/
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
// 默认返回false
return isRunningFlag();
}
/**
* 根据该方法的返回值决定是否执行start方法。<br/>
* 返回true时start方法会被自动执行,返回false则不会。
*/
@Override
public boolean isAutoStartup() {
// 默认为false
return true;
}
}
启动程序,然后停止,控制台可以看到如下输出
2020-08-06 23:12:24.005 INFO 19200 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'
2020-08-06 23:12:24.145 INFO 19200 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.d.a.OptionalLiveReloadServer : LiveReload server is running on port 35729
start
2020-08-06 23:12:24.180 INFO 19200 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 (http) with context path ''
2020-08-06 23:12:24.183 INFO 19200 --- [ restartedMain] com.wyf.spring.Application : Started Application in 1.675 seconds (JVM running for 2.908)
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:27538', transport: 'socket'
stop(Runnable)
2020-08-06 23:12:29.172 INFO 19200 --- [extShutdownHook] o.s.s.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Shutting down ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor'