Python是一种越来越流行的编程语言,特别是在科学界,因为它有丰富的数字和统计包。因此,能够从Java应用程序中调用Python代码的需求并不少见。
在本教程中,我们将了解从Java调用Python代码的一些最常见方法。
运行环境
java version "1.8.0_191"Python 3.8.3
准备工作
一个非常简单的python脚本,命名为hello.py
print("hello python")
运行该脚本效果如下:
$ python hello.pyhello python
hello.py放在java项目的resources目录下。
实战部分
使用ProcessBuilder
public class ProcessBuilderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder("python", resolvePythonScriptPath("hello.py")); processBuilder.redirectErrorStream(true); Process process = processBuilder.start(); List<String> results = readProcessOutput(process.getInputStream()); System.out.println("results = " + results); } private static String resolvePythonScriptPath(String filename) { File file = new File("src/main/resources/" + filename); return file.getAbsolutePath(); } private static List<String> readProcessOutput(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException { try (BufferedReader output = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream))) { return output.lines() .collect(Collectors.toList()); } }}
其中需要注意的是redirectErrorStream(true)这个属性,如果出现任何错误,错误输出将与标准输出合并。如果我们没有将这个属性设置为true,那么我们将需要使用getInputStream()和getErrorStream()方法从两个单独的流读取输出。
程序执行结果
我们修改以下代码看看实际输出效果:
//python脚本名修改为不存在的脚本名ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder("python", resolvePythonScriptPath("hello2.py"));processBuilder.redirectErrorStream(true);
运行结果执行不成功会打印出错误结果:
去掉redirectErrorStream(true)这行代码再运行控制台不会打印我们预期的结果,错误信息也不会输出。
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder("python", resolvePythonScriptPath("hello2.py"));//processBuilder.redirectErrorStream(true);
这种情况下要想获取错误信息需要修改代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder("python", resolvePythonScriptPath("hello2.py"));// processBuilder.redirectErrorStream(true); Process process = processBuilder.start(); List<String> results = readProcessOutput(process.getInputStream()); List<String> errMsg = readProcessOutput(process.getErrorStream()); System.out.println("results = " + results); System.out.println("errMsg = " + errMsg); }
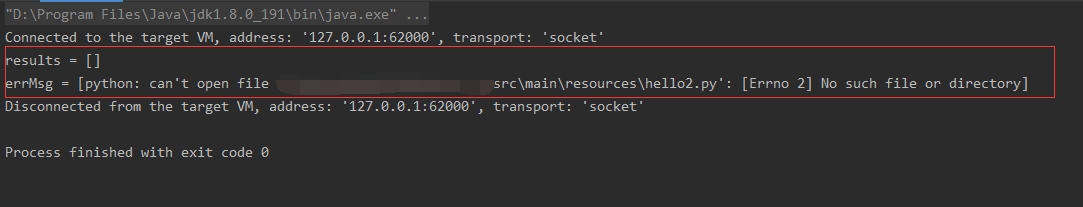
这样写是不是很繁琐,所以直接设置redirectErrorStream(true),世界瞬间清爽了。
使用Jython
Jython官网:www.jython.org
JSR-223脚本引擎
Java 6中首次引入的JSR-223定义了一组提供基本脚本功能的脚本API。这些方法提供了用于执行脚本以及在Java和脚本语言之间共享值的机制。该标准的主要目的是试图使Java与不同脚本语言具有互操性。
当然,我们可以为任何具有JVM实现的动态语言使用可插入脚本引擎架构。Jython是运行在JVM上的Python的Java平台实现。
在pom.xml中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.python</groupId> <artifactId>jython</artifactId> <version>2.7.2</version></dependency>
使用下面的代码可以列出所有可用的脚本引擎:
public static void listEngines() { ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager(); List<ScriptEngineFactory> engines = manager.getEngineFactories(); for (ScriptEngineFactory engine : engines) { System.out.println("Engine name:" + engine.getEngineName()); System.out.println("Version: " + engine.getEngineVersion()); System.out.println("Language: " + engine.getLanguageName()); System.out.println("Short Names:"); for (String names : engine.getNames()) { System.out.println(names); } }}
如果我们看到控制台打印了下面相应的脚本引擎,则可以使用Jython
使用Jython脚本引擎的代码逻辑如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ScriptException { StringWriter writer = new StringWriter(); ScriptContext context = new SimpleScriptContext(); context.setWriter(writer); ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager(); ScriptEngine engine = manager.getEngineByName("python"); engine.eval(new FileReader(resolvePythonScriptPath("hello.py")), context); System.out.println("执行结果: " + writer.toString());}
我们使用ScriptEngineManager类的getEngineByName方法为给定的短名称查找和创建ScriptEngine。在我们的例子中,我们可以传递python或jython,它们是与此引擎关联的两个短名称。、
执行结果
程序执行manager.getEngineByName("python")这句为null,解决方案有两种:
1、在调用getEngineByName之前,设置Options.importSite = false
简化代码如下:
import org.python.core.Options;ScriptEngineManager manager = new ScriptEngineManager();Options.importSite = false;ScriptEngine engine = manager.getEngineByName("python");
2、使用官方提供的独立jar
<!--<dependency> <groupId>org.python</groupId> <artifactId>jython</artifactId> <version>2.7.2</version></dependency>--><dependency> <groupId>org.python</groupId> <artifactId>jython-standalone</artifactId> <version>2.7.2</version></dependency>
执行成功
Python代码直接嵌入到Java代码
使用PythonInterpretor类可以将Python代码直接嵌入到Java代码中。
public static void main(String[] args) { try (PythonInterpreter pyInterp = new PythonInterpreter()) { StringWriter output = new StringWriter(); pyInterp.setOut(output); pyInterp.exec("print('Hello jython')"); System.out.println("执行结果: " + output.toString()); }}
又遇到错误了。。。
两种解决方案:
1、错误信息最后一句给出了解决方案 ,设置 python.import.site=false
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("python.import.site", "false"); PythonInterpreter.initialize(System.getProperties(), props, null); try (PythonInterpreter pyInterp = new PythonInterpreter()) { StringWriter output = new StringWriter(); pyInterp.setOut(output); pyInterp.exec("print('Hello jython')"); System.out.println("执行结果: " + output.toString()); }}
2、使用官方提供的独立jar
<!--<dependency> <groupId>org.python</groupId> <artifactId>jython</artifactId> <version>2.7.2</version></dependency>--><dependency> <groupId>org.python</groupId> <artifactId>jython-standalone</artifactId> <version>2.7.2</version></dependency>
运行成功
再看一个将两个数字加在一起的示例,使用_get_方法访问变量的值。
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("python.import.site", "false"); PythonInterpreter.initialize(System.getProperties(), props, null); try (PythonInterpreter pyInterp = new PythonInterpreter()) { pyInterp.exec("x = 10 + 10"); PyObject x = pyInterp.get("x"); System.out.println("执行结果: " + x.asInt()); }}
运行结果
Apache Commons Exec
我们还可以使用的另一个第三方库是Apache Common Exec,它试图克服Java Process API的一些缺陷。
在pom.xml中引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-exec</artifactId> <version>1.3</version></dependency>
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String line = "python " + resolvePythonScriptPath("hello.py"); CommandLine cmdLine = CommandLine.parse(line); ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); PumpStreamHandler streamHandler = new PumpStreamHandler(outputStream); DefaultExecutor executor = new DefaultExecutor(); executor.setStreamHandler(streamHandler); int exitCode = executor.execute(cmdLine); System.out.println("执行状态, 成功为0 , 非0为失败,结果为 = " + exitCode); System.out.println("执行结果: " + outputStream.toString());}
执行结果
使用HTTP进行操作
让我们回顾一下,与其尝试直接调用Python,不如考虑使用一个完善的协议(如HTTP)作为两种不同语言之间的抽象层。
实际上,Python附带了一个简单的内置HTTP服务器,我们可以使用共享内容或文件通过HTTP:
python -m http.server 9000
如果现在转到http://localhost:9000,我们将看到前面命令启动时所在目录的内容。
我们可以考虑使用其他一些流行的框架来创建更健壮的基于python的web服务或应用程序,它们是Flask和Django。
一旦我们有了可以访问的端点,我们就可以使用几个Java HTTP库中的任何一个来调用我们的Python web服务/应用程序实现。