SecurityContextHolder大家都脸熟,比如我们获取登录用户id就可以这么做:

开始我们的请求中携带的是token,在经过了过滤器验证及处理之后,我们的SecurityContextHolder中就携带了我们登录时生成的Authentication。具体过程如下:
这个过滤器是OAuth2AuthenticationProcessingFilter.java 位于org.springframework.security.oauth2.provider.authentication包下
首先从request的请求头或者参数中获取到tokenValue
try {
Authentication authentication = tokenExtractor.extract(request);此时的authentication只携带TokenValue信息,其他均为空
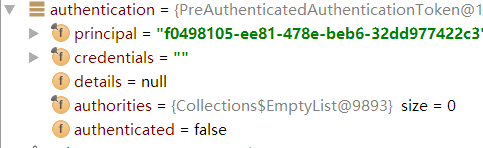
然后调用了authenticate方法来验证这个tokenvalue:
Authentication authResult = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);这里调用的是OAuth2AuthenticationManager的方法
1.验证token的有效性
String token = (String) authentication.getPrincipal();
OAuth2Authentication auth = tokenServices.loadAuthentication(token);2.验证资源访问的权限
Collection<String> resourceIds = auth.getOAuth2Request().getResourceIds();
if (resourceId != null && resourceIds != null && !resourceIds.isEmpty() && !resourceIds.contains(resourceId)) {
throw new OAuth2AccessDeniedException("Invalid token does not contain resource id (" + resourceId + ")");
}3.验证client对资源的读写权限
checkClientDetails(auth);检验完成之后,再把从数据库读出来的、结合当前请求的Authentication返回。
在过滤器的最后,调用
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
将Authentication放入到context中,供其他地方调用