当我们接入了微信、app、ldap等等登录验证的时候,我们如何去具体地了解到登录失败的原因呢?
举个例子,app无法登录有可能是密码错误,也有可能是密码正确但是该账号被限制登录。但是无论上面哪种情况,我们从登录接口拿到的返回信息都是同样的,甚至在app验证失败之后(用户名密码正确,但是用户过期了),在我们明知这个账号的确是app登录账号而不是其他验证方式的情况下,manager还会拿着用户名密码去ldap或者wx进行验证,最后我们连这个错误信息是哪个provider抛出的都不知道。
需求: 当app验证程序发现账号的确是app的账号,但是账号过期或者被锁而验证失败的情况下,忽略剩下的其他验证(比如wx),并且返回详细的验证失败提示信息
先看一下验证过程中的异常处理(可以直接略过A、B、C,解决方法在后面):
A:
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication); //调用验证方法
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result); //如果返回不为空,也没有抛出异常,则视为成功
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException e) { //该异常会打断验证
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) { //该异常会打断验证
prepareException(e, authentication);
throw e;
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) { //不会打断验证
lastException = e;
}
}循环的最外层,我们暂时叫它A层,往里就是B层、C层...
- 这里除了验证成功,抛出的AccountStatusException 和InternalAuthenticationServiceException 异常会直接打断循环验证,返回给调用者包含的错误信息。
- 最后面catch的AuthenticationException 是AccountStatusException 和InternalAuthenticationServiceException 的父类,它捕获了除这两者以外的该类异常,但是这个异常并不会打断验证,并且很重要的一点是,它会循环赋值给lastException ,最后返回给调用者的是最后一次捕获的AuthenticationException 。
其实spring对于AccountStatusException 已经有了很完备的处理,我们先往里层看。
B、
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); //1、调用下一层的验证方法
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException notFound) {
logger.debug("User '" + username + "' not found");
if (hideUserNotFoundExceptions) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials",
"Bad credentials"));
}
else {
throw notFound;
}
}
//2、这里很重要,如果返回的user为null,会抛出IllegalArgumentException,这个异常没有catch,直接返回给调用者,所以返回的user不能是null!
Assert.notNull(user,"retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract");
}
try {
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user); //3、这里的precheck很重要,如果用户被锁之类的,会抛出相应的AccountStatusException异常
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
catch (AuthenticationException exception) {
if (cacheWasUsed) {
// 重试一次
// 此处省略一大段。。。
}
else {
throw exception;
}
}
// 此处省略一大段。。。
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user); //4、如果前面没有异常,返回的肯定不会是null
B层没有拦截住验证方法抛出的任何异常,而是通过check方法,手动抛出了AccountStatusException,A层对这个异常是直接抛出的,所以我们主要依靠这个异常来打断验证、返回信息。虽然返回null也可以打断验证,但是没法细分情况和客户化异常信息。
另外,A层的验证循环只有在返回的result 为null,或者抛出了非AccountStatusException或InternalAuthenticationServiceException 的AuthenticationException 异常的情况下才能不打断循环继续验证,但是在B层中是不允许result 为null的,会抛IllegalArgumentException。所以要想继续循环验证的方式只有一个,那就是向A层抛出AuthenticationException 。
C、
UserDetails loadedUser;
try {
String repositoryProblem = (String)authentication.getCredentials();
loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username, repositoryProblem); //1、调用我们客户化的验证方法
} catch (UsernameNotFoundException var5) { //2、该异常虽然不会被B层拦截,但是A层也没有专门处理该异常
throw var5;
} catch (Exception var6) { //3、全部异常都抛成AuthenticationServiceException
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(var6.getMessage(), var6);
}
if(loadedUser == null) { //4、null也抛成AuthenticationServiceException
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
} else {
return loadedUser;
}C层只会抛出UsernameNotFoundException 和AuthenticationServiceException,这两者对A层的循环都没有影响,而且还会被后面抛出的该类型异常给覆盖
下面要请出我们的主角了:
CustomUserDetails userDetails1 = new CustomUserDetails(user.getUserId(), user.getUserName(), user.getPasswordEncrypted(), true, true, true, true, authorities);这就是我们实现验证逻辑的地方,这里构造方法里的的四个true都是啥呢?
public CustomUserDetails(Long userId, String userName, String password, boolean enabled, boolean accountNonExpired, boolean credentialsNonExpired, boolean accountNonLocked, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
this.userId = userId;
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
this.enabled = enabled;
this.accountNonExpired = accountNonExpired;
this.credentialsNonExpired = credentialsNonExpired;
this.accountNonLocked = accountNonLocked;
this.authorities = authorities;
}各自代表账户的有效、锁定、过期以及client是否过期。
如果我们将这四个属性其中一个设置为false,那么会在B层的preCheck中被检查出来,然后抛出与属性相应的AccountStatusException,打断循环并且返回异常信息,是不是很简单。
B层中调用的检查方法:
public void check(UserDetails user) {
if (!user.isAccountNonLocked()) {
throw new LockedException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.locked", "User account is locked"));
}
if (!user.isEnabled()) {
throw new DisabledException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.disabled", "User is disabled"));
}
if (!user.isAccountNonExpired()) {
throw new AccountExpiredException(
messages.getMessage("AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.expired",
"User account has expired"));
}
if (!user.isCredentialsNonExpired()) {
throw new CredentialsExpiredException(messages.getMessage(
"AccountStatusUserDetailsChecker.credentialsExpired",
"User credentials have expired"));
}
}检测下效果:
两个验证类:代表app和wx
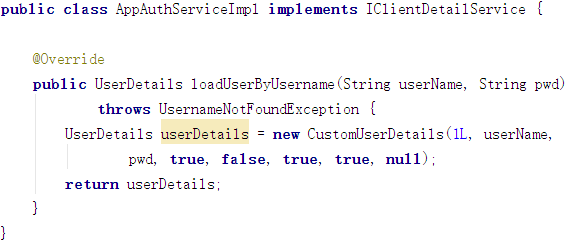
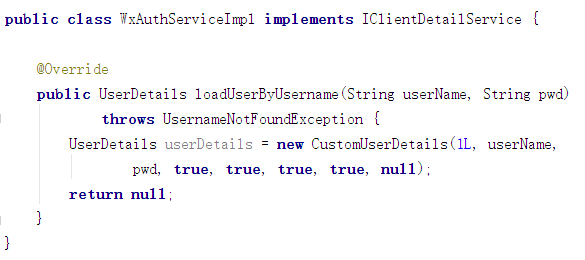
返回值:
{
"error": "invalid_grant",
"error_description": "expired"
}如果需要自定义返回信息,那就不能依靠AccountStatusException,需要重写LoginAuthenticationProvider即C层,在需要的情况下手动抛出InternalAuthenticationServiceException
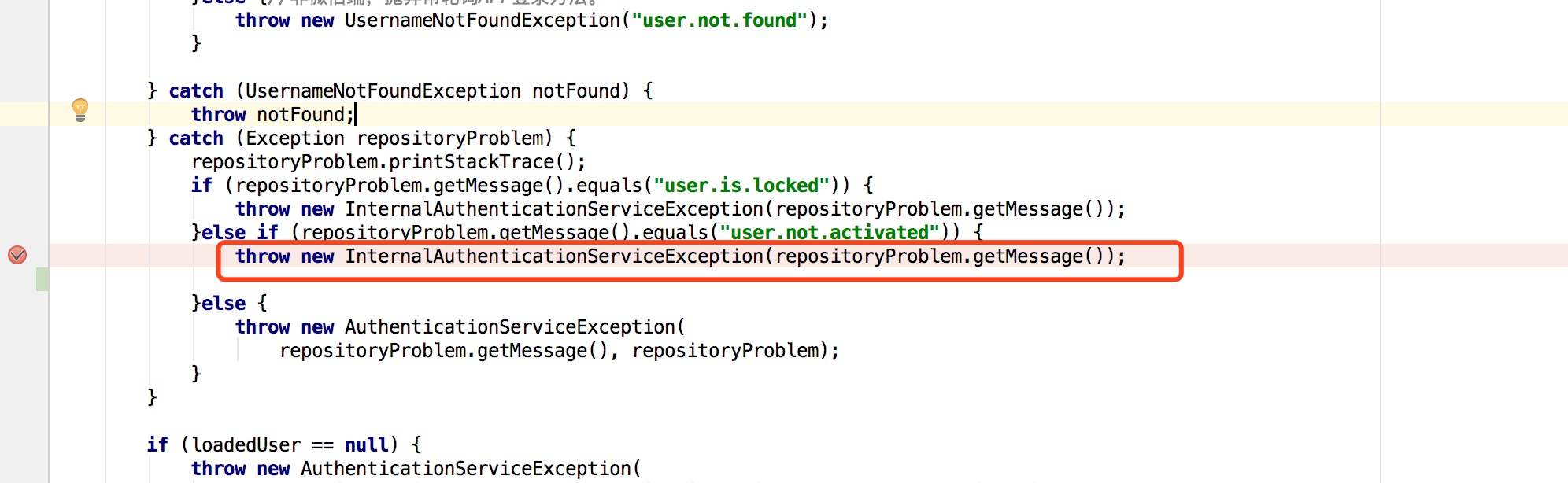
返回值:
{
"error": "invalid_grant",
"error_description": "user not activated"
}这样提示信息看起来会更友好
所以验证失败后不一定要返回null,可以有更多选择