JDK7源码解析
引入
jdk7版本下的HashMap是以数组和链表作为底层结构的,其核心方法是put和get。这会让人联想到ArrayLsit(数组)和LinedList(链表),并思考其实现原理是否是一样的。
这里简单的分析一下ArrayList的get和add方法
package setlearn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* @author Enoch
*/
public class ArrayListLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("Name");
arrayList.add(0,"Enoch");
System.out.println(arrayList.get(0));
System.out.println(arrayList.get(1));
}
}
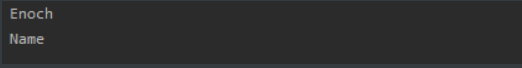
ArrayList有两个add方法,一个是add(element),另一个是add(index,element)。
思考:如果不指定其下标时,如何确定元素添加的元素?
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
//判断index是否合法
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
可见ArrayList中有一个size属性,当指定下标时,将元素添加到下标位置,当没有指定下标时,则默认在下标大小为size处添加元素。
再来看看ArrayList的get方法
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
即根据传入的index获得数组中的值。
思考:HashMap是否也采用这样的方法呢?
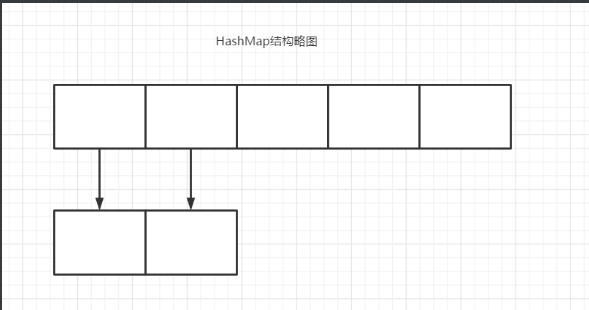
HashMap的put方法为put(K,V),而get方法为get(key)。由结构略图可知,如果HashMap也采用ArrayList类似的方法的话,那么put方法将会有一个size,由(size++)依次从数组的第一个位置添加到数组的最后一个位置,当数组充满时,则会在数组的第一个位置下添加一个链表,再依次添加,这种方式的效率似乎不错,那么真是如此吗?这里需要考虑get方法,他需要根据key的值,一个个遍历过去。显而易见这种get的效率是及其低下的,其get效率远低于put,这是不被允许的。那么HashMap的put和get是如何实现的呢?
put方法的简单分析
既然ArrayList的类似方式是不合适的,那么put该如何实现呢?
猜想:
put(key,value);
key-->key.hashCode()-->10234512-->10234512-->
index-->index%table.length
不同的key其hashcode值是不同的,但经过取余后,其在数组的位置可能是相同的(冲突),这时就用到了链表结构。
public class Node{
private Object content;
private Node next;
public Node(Object content,Node next){
this.content=content;
this.next=next;
}
}
链表是如何插入的呢?这里从效率的角度出发,应该是采用头插法,即在某一数组下标有值的情况下,新值作为链表头,这样能减少遍历链表的时间。
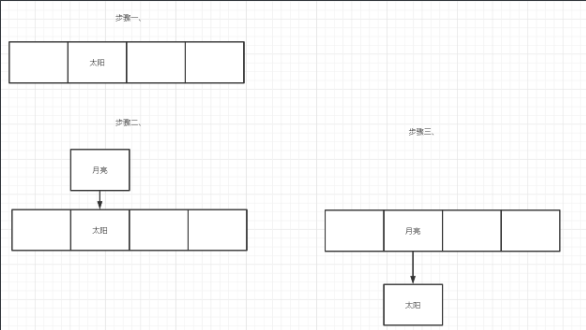
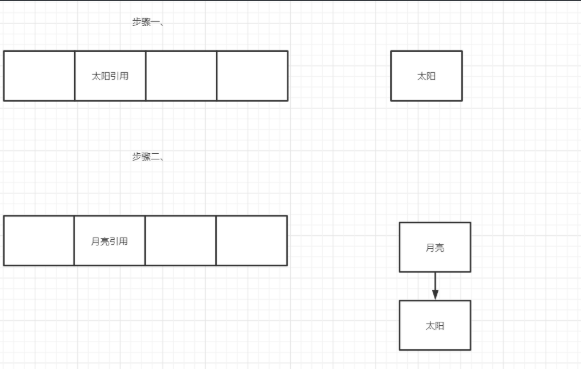
对应代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node header=new Node(new Object(),null);
header.next=new Node(new Object,null);
new Node(new Object(),header);
}
综上所述,其put方法的大致流程用伪代码表示为
put(key,value){
int hashcode=key.hashCode();
//下标为index的第一个元素
//table[index]=new Entry(key,value,null);
//头插法的大致实现形式
table[index]=new Entry(key,value,table[index]);
}
以上是对put方法的简单的分析,现在从源码角度入手,了解其大致执行方式
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
当table为空时,会执行inflateTable(threshold)方法(会在下文详细分析该方法),初始化table大小。然后获取一个hash值。根据该hash值和table大小,形成数组下标。然后进入for循环,该循环是遍历该数组下标下的链表,如果put的key和链表下的key相同,则会将原先key的value值返回。
public class HashMapLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("a","a");
System.out.println(map.put("a","b"));
}
}
输出:a.
若没有key的值相同,则返回null。
然后进入addEntry方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//扩容那一块再讲
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
if语句是扩容操作(下面会详细讲)。
然后进入createEntry()方法
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
即上述分析的简单的put方法实现。
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
HashMap初始化数组详解
HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>(10,0.75F);
HashMap在创建对象时,可以设置其数组容量(用于扩容)和加载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
threshold默认大小为16,loadFactor默认大小为0.75.
由于table为空,所以在put时要进行初始化操作
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
//下面会结合扩容简单分析
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
table默认为empty,进入inflateTable(threshold)方法,即真正初始化数组,确定其数组大小。
要想得到capacity,需要进入roundUpToPowerOf2()方法。
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
}
着重考察Integer.highestOneBit()方法
public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
//传入的是int类型,长度为32位
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
以17为例:
17 -----> 0001 0001
右移1位 : 0000 1000
或运算 0001 1001
右移2位 : 0000 0110
或运算 0001 1111
右移4位 : 0000 0001
或运算 0001 1111
右移8位 : ------
右移16位 : ------
return (0001 1111-0000 1111)=(0001 0000)
16是小于17的二的幂次最大值
分析:是个例还是整体?
以001* ****为例,依据上例,结果应该是0001 0000
输入值 001* ****
右移1位 0001 ****
或运算 0011 ****
右移2位 0000 11**
或运算 0011 11**
右移4位 0000 0011
或运算 0011 1111
右移8位 (以下结果均不变)
或运算
右移16位
或运算
return (0011 1111-0001 1111)==>0010 0000
总结,这个方法返回的是小于传入值的二的幂次最大值。
回过头来看roundUpToPowerOf2()方法,当传入的toSize(threshold),大于MAXIMUM_CAPACITY取该值,当其小于1时取1(2^0),否则执行Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1),由上述分析可知Integer.highestOneBit获得的是小于当前值的2的幂次方最大值。
设num为 0010 **** *号中可能有1,也可能全为0,
当全为0时(num-1)<<1 --> 0001 1111 -->0011 1110
highestOneBit() --->0010 0000
当不全为0时-1后,则最高位仍为1 0010 ****(可能有1)
010* ***0--->highestOneBit -->0100 0000
可知输出的是大于当前值的2的幂次最小值。
故可知,初始化数组时传入的threshold不是其最后生成的数组长度。
思考:为什么要求容量是2的幂次方呢?
put方法数组下标生成
由put方法的简要分析可知,其key存放的位置,并不是按照顺序存放的,而是以一种随机的方式存放的,但该方式需要尽可能满足两个要求
- 生成的index不能越界
- 尽可能平均的存放在各个位置上。
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
h是返回的任意hash值,由初始化数组可知,length的值一定为2的幂次方。
假设h为 0110 0001
length 为 0001 0000,则其存放的位置为0-15
h&(length-1)---> 0110 0001 & 0000 1111 --> 0000 0001
即根据任意的hash值,生成在任意的index处,由此也可理解数组初始化容量为2的幂次方的好处
思考:为什么不用%来计算呢?
答:在计算机中,位运算的速度是最快的,这种方法能很好的提高效率。
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
h是默认为0的,所以h的赋值结果仍为k的hash值,h异或和移位运算主要是为了使h的各个位上的值在indexfor方法中充分利用,提高散列性。
putForNullKey方法
以上,put的方法中,仅剩putForNullKey方法还没讲了。正所谓人如其名,该方法口头翻译就是对于put进的key为null值进行处理。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//该变量会在扩容那一块讲
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
循环table[0]处的Entry<K,V>对象,查找e==null的情况,当e.key==null时,读取其旧值,并赋上新值,最终将旧值返回
扩容操作
进入addEntry()方法中
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
当数组中的个数超过阈值时就会扩容,同时要求当前添加的位置不为null。(在jdk8中没有后者这个条件)
此时就会执行resize()方法,并设置新的容量为旧容量的两倍。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
先获取oldtable数组,然后判断其大小是否等于Integer.MAX_VALUE,如果是则直接返回,反之,由新容量生成新的Entry对象。
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
//默认为false
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
上面已经提过indexFor方法是求数组下标,但需要注意的是,在新的容量的table中,其元素下标并不一定和旧元素下标一样,也可能向右平移table.oldlength的长度。
假设h为0101 0101
oldlength 为 0001 0000
-1 ---> 0000 1111
& ---> 0000 0101
newlength 为 0010 0000
-1 ---> 0001 1111
& ---> 0001 0101
可知与原结果相比,向右移动了oldlength个位置,这与hash值相关。
transfer运行流程图(容量大小应该为2的幂次,画图时没注意)
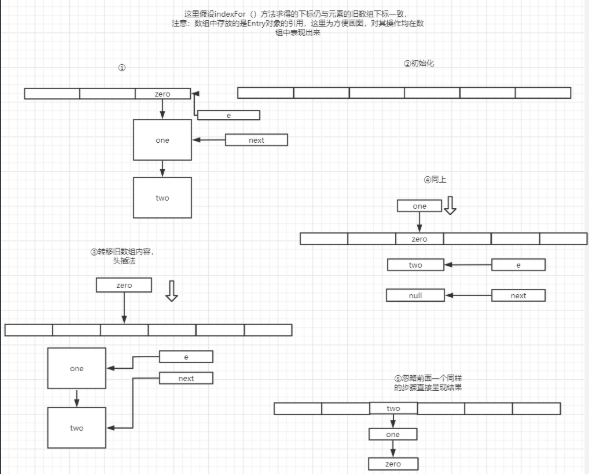
由此可知,transfer时会将链表倒序呈现,这会导致一个问题,
假设有两个线程同时进入了transfer方法,第一个线程按正常顺序执行,而第二个线程执行到Entry<K,V> next = e.next;就停止了。
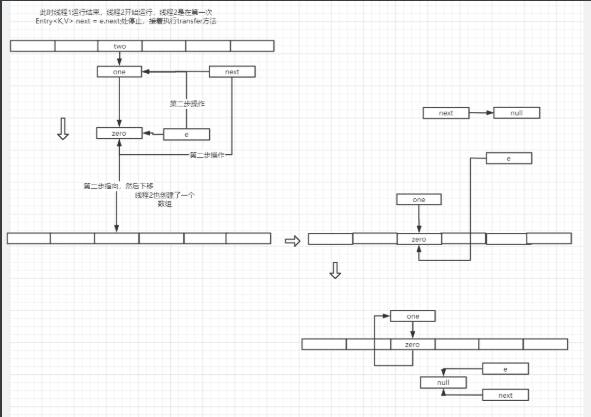
由此可见,当多线程时,可能会出现循环链表的情况,当然这只是其中一种情况。
思考:既然会出现这样的情况,为什么不选择直接将旧数组的Entry引用,直接复制到新数组中呢?这样不仅效率快,且能避免出现这种循环链表的情况。
这里需要思考的是扩容的最终目的是什么,他不仅仅是为了扩大数组容量,进行将旧数组的值原封不动的放在新数组中,其根本目的是为了缩短链表的长度,实现更好的散列性能。
initHashSeedAsNeeded()方法
回到transfer中,他有一个rehash的判断,rehash的值是由initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)获得的。
final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) {
//hashSeed默认为0,故第一次进入currentAltHashing肯定为false
boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0;
boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
//只有switching为true,hashSeed值才能改变,即要求useAltHashing为true
if (switching) {
hashSeed = useAltHashing
? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this)
: 0;
}
return switching;
}
private static class Holder {
/**
* Table capacity above which to switch to use alternative hashing.
*/
static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD;
static {
String altThreshold = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction(
"jdk.map.althashing.threshold"));
int threshold;
try {
threshold = (null != altThreshold)
? Integer.parseInt(altThreshold)
: ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT;
// disable alternative hashing if -1
if (threshold == -1) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if (threshold < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("value must be positive integer.");
}
} catch(IllegalArgumentException failed) {
throw new Error("Illegal value for 'jdk.map.althashing.threshold'", failed);
}
ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD = threshold;
}
}
在Holder类中,判断是否有设置jdk.map.althashing.threshold的环境变量,如果有就给threshold赋值,并将该值赋给ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD
故该方法的思路是,判断有无设置环境变量,如果有,则数组容量若大于jdk.map.althashing.threshold的值,就会生成一个HashSeed,HashSeed的目的是为了hash算法返回的hash值更散列一些。
在有新的HashSeed生成时,rehash为true,即重新生成hash值。
modCount分析
public class HashMapLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("1","1");
// hashMap.put("2","2");
for (String key:hashMap.keySet()){
if (key.equals("1")){
hashMap.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
无异常
public class HashMapLearn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("1","1");
hashMap.put("2","2");
for (String key:hashMap.keySet()){
if (key.equals("2")){
hashMap.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
报错
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.HashMap$HashIterator.nextEntry(HashMap.java:922)
at java.util.HashMap$KeyIterator.next(HashMap.java:956)
at setlearn.HashMapLearn.main(HashMapLearn.java:14)
观察其反编译文件
public class HashMapLearn {
public HashMapLearn() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("1", "1");
hashMap.put("2", "2");
//返回的是KeyIterator
Iterator i$ = hashMap.keySet().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
String key = (String)i$.next();
if (key.equals("2")) {
hashMap.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
KeyIterator继承自HashIterator
HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
if (size > 0) { // advance to first entry
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
}
modCount是HashMap的属性,回到put方法中,发现其每put一次modCount++,所以expectedModCount:2 modCount:2
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
private final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator<K> {
public K next() {
return nextEntry().getKey();
}
}
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
//出现异常的位置
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = e.next) == null) {
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
current = e;
return e;
}
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev;
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return e;
}
可见remove方法也会导致modCount的改变,所以modCount的含义即修改的次数。所以第一次循环结束时modCount的值为1,而expectedModCount值为2 ,第二次循环时,进入next方法中的nextEntry方法,由于modCount与expectedModCount的值不同从而导致异常。
修改方案:采用Iterator的remove方法
public void remove() {
if (current == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Object k = current.key;
current = null;
HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
//每次remove,重新赋值expectedModCount
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
思考:modCount的作用是什么?
modCount是一个快速失败的容错机制。
重新审视报错的代码,就好像是有两个线程,一个在遍历,一个在修改,这时会出现并发问题,此时HashMap认为会出现这个问题,就抛出异常。
think more,read more,learn more