浏览器解析import
初始化一个项目vite-mini,只有html.index和src/main.js,src/log.js
// html.index
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script src="/src/main.js"></script>
</body>
// main.js
import log from "./log.js"
log("this is main.js");
// log.js
export default function log(message) {
console.log("message:", message);
}
使用vscode自带的服务打开index.html
 提示不能在模块外部使用import,说明当前script不是一个模块,那么在script标签加上 type="module"
提示不能在模块外部使用import,说明当前script不是一个模块,那么在script标签加上 type="module"
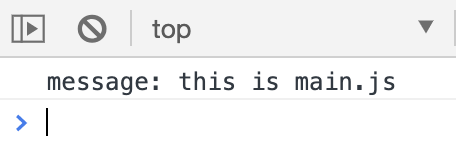
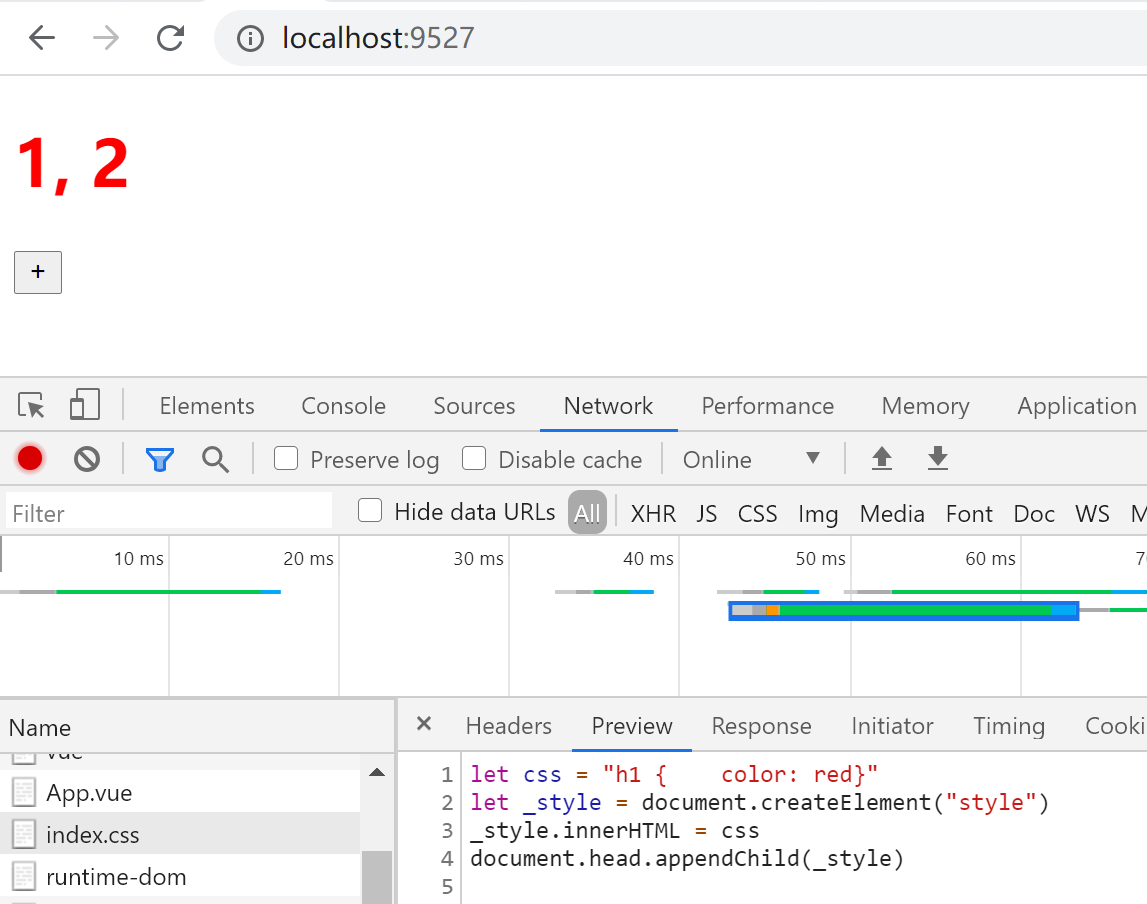
报错消失了,main.js的代码输出到了控制台。说明**type="module"**让script标签变成了一个模块,打开Network
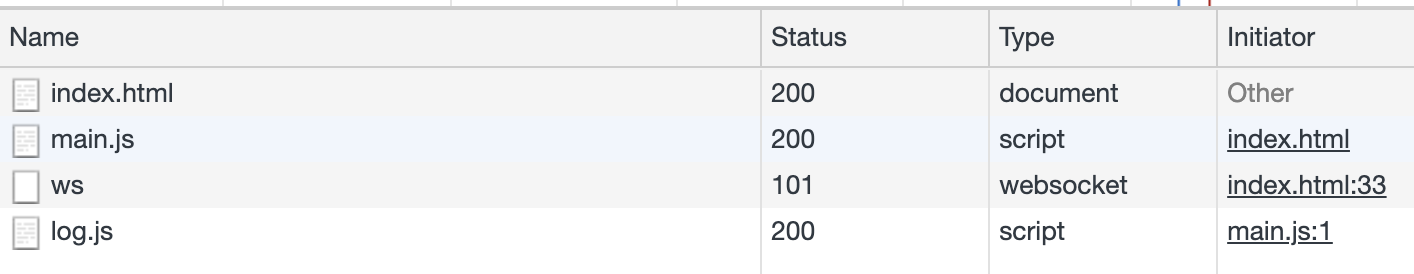
浏览器把import当做了一次网络请求,就像使用node读取一个js文件,把内容返回来。
用koa拦截浏览器请求
现在的页面访问是vscode服务,我们初始化一个koa的项目,启动koa的服务,前端访问koa的接口,让koa读取这个index.html
npm init -y && npm i koa
touch server.js
const Koa = require("koa")
const app = new Koa()
const fs = require("fs")
const path = require("path")
const js_type = "application/javascript"
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url}} = ctx
if (url === "/") {
let _path = path.resolve(__dirname, "index.html")
let _content = fs.readFileSync(_path, "utf-8")
ctx.body = _content
} else {
await next()
}
})
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url}} = ctx
if (url.endsWith(".js")) {
let _path = path.resolve(__dirname, url.slice(1))
let _content = fs.readFileSync(_path, "utf-8")
ctx.type = js_type
ctx.body = _content
} else {
await next()
}
})
app.listen(9527, () => {
console.log("koa.9527 ----> start")
})
现在就能正常加载main.js的内容了
实现目标
以上步骤:
- 浏览器是将import导入模块,解析成请求资源
- 我们可以用koa拦截浏览器的请求,读取资源,返回给前端
使用 vite 初始化一个demo,看下vite都做了什么。 将vite-demo/src/App.vue稍作修改
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{num}}, {{db}}</h1>
<button @click="fnAdd">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref, computed} from "vue"
export default {
setup() {
const num = ref(0)
function fnAdd() {
num.value ++
}
const db = computed(() => num.value * 2)
return {num, fnAdd, db}
}
}
</script>
// main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './index.css'
createApp(App).mount('#app')
这就是我们的实现目标,将这两段代码贴到vite-mini/src下,能正常运行,就ok了
运行npm run dev打开Network:
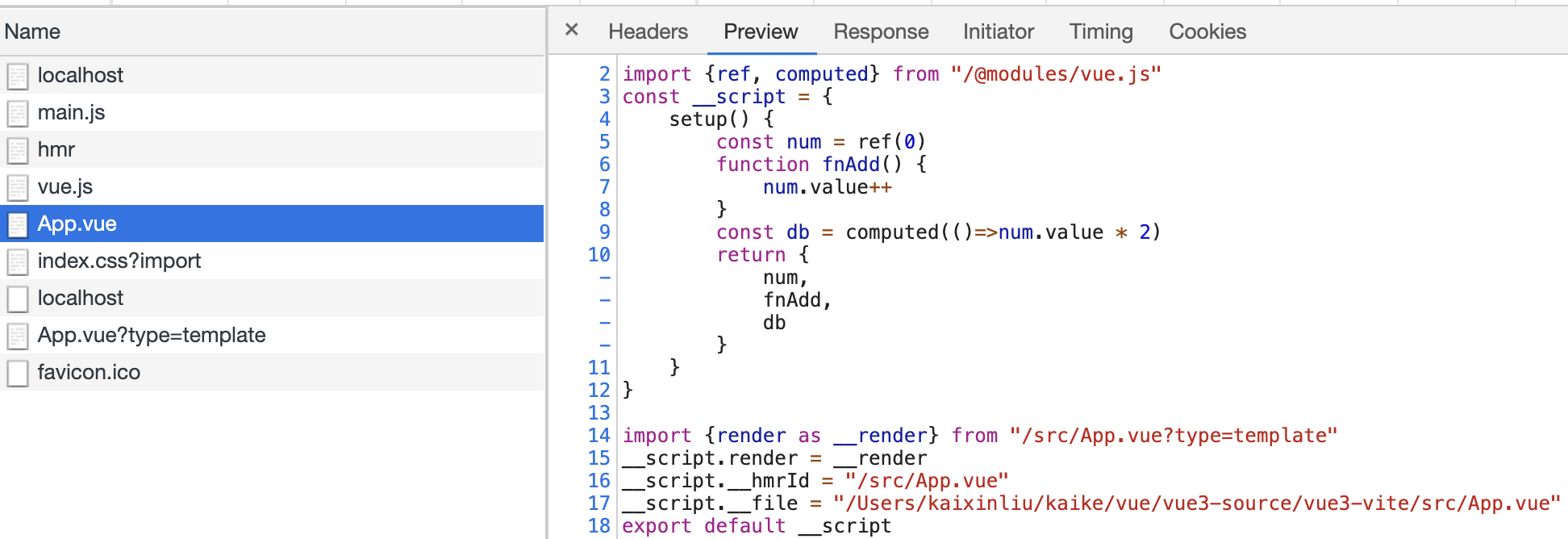 右边的代码块,就是使用 import vue from "vue" 时,koa拦截到浏览器对App.vue请求时,返回浏览器的结果
对我们来说,写代码的地方就是.js、.vue、.css、.scss等
右边的代码块,就是使用 import vue from "vue" 时,koa拦截到浏览器对App.vue请求时,返回浏览器的结果
对我们来说,写代码的地方就是.js、.vue、.css、.scss等
- 分析import包的来源,是node_modules,就解析成/@modules/
- 解析render
先把main.js、App.vue复制到vite-demo

解析node_modules包
在koa再加个中间件,解析vue包
import { createApp } from 'vue' => import { createApp } from '/@modules/vue.js'
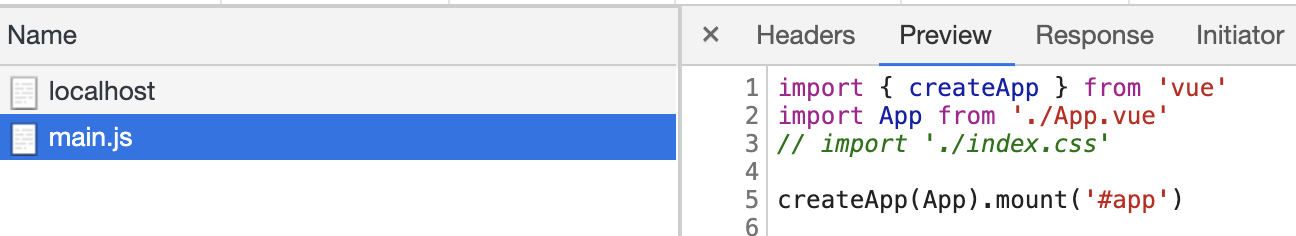 其实main.js解析并返回给前端了,只是前端解析不了,先写个辅助函数
其实main.js解析并返回给前端了,只是前端解析不了,先写个辅助函数
function fnReWriteImport(content) {
return content.replace(/from ['"]([^'"]+)['"]/g, function(s0, s1) {
// 只解析不带/的
if (s1[0] !== "." && s1[0] !== "/") {
return `from '/@modules/${s1}'`
}
return s0
})
}
在此推荐一个正则的可视化工具,挺适合我这种菜鸡用的。还有更多的工具,去大圣的bi站找吧 将解析的js包起来
ctx.body = fnReWriteImport(_content)
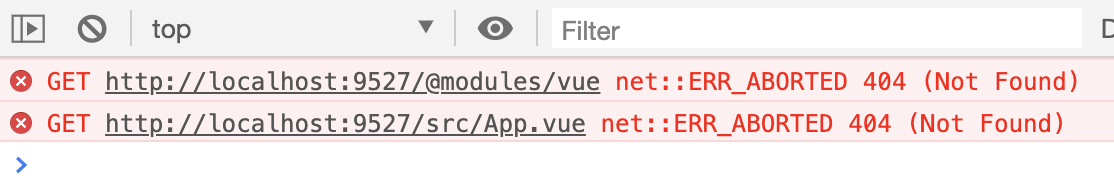 先下载vue
先下载vue
npm i vue && vue add vue-next
再加个中间件,将/@modules/指向包在node_modules实际位置
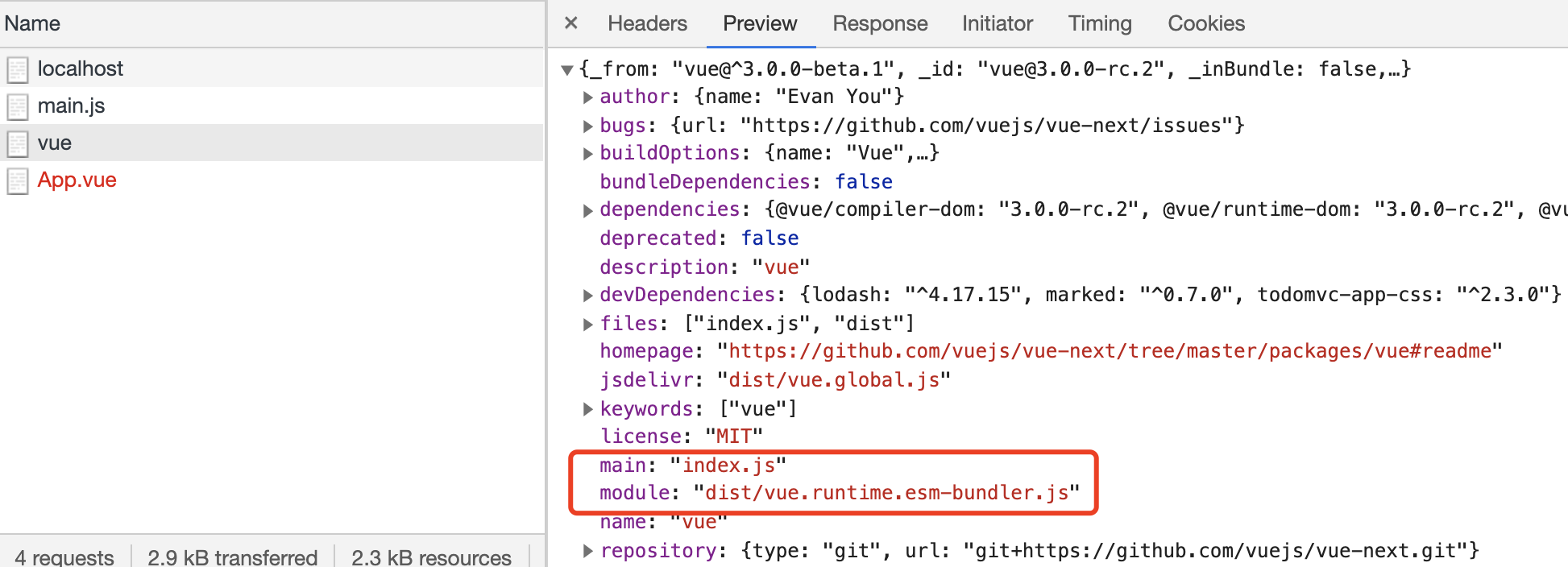
使用import指向的是module,require是main
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url}} = ctx
if (url.startsWith("/@modules/")) {
let _page = `node_modules/${url.replace("/@modules/", '')}`
// 读取包在node_modules的路径
let _path = path.resolve(__dirname, _page)
let _module = require(`${_path}/package.json`).module
// 读取包的打包文件在node_modules的路径
let _module_path = path.resolve(__dirname, _page, _module)
let _module_content = fs.readFileSync(_module_path, "utf-8")
ctx.type = js_type
ctx.body = fnReWriteImport(_module_content)
} else {
await next()
}
})
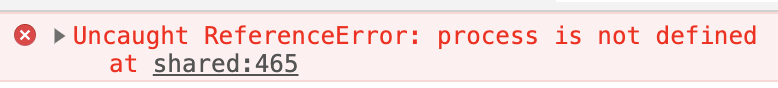
这个是没有设置node的环境变量,我们在第一个中间件加一段设置环境变量的脚本
_content = _content.replace("<script", `
<script>
window.process = {env: {NODE_ENV: 'DEV'}}
</script>
<script`)
ctx.body = _content
稍微修改下main.js,测试下node_modules的解析是否成功
import { createApp } from '/@modules/vue'
console.log("createApp", createApp)
node_modules解析成功了
解析.vue文件
添加解析vue单文件的中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url}} = ctx
console.log("url", url)
if (url.endsWith(".vue")) {
let _path = path.resolve(__dirname, url.slice(1))
let _content = fs.readFileSync(_path, "utf-8")
ctx.body = _content
} else {
await next()
}
})
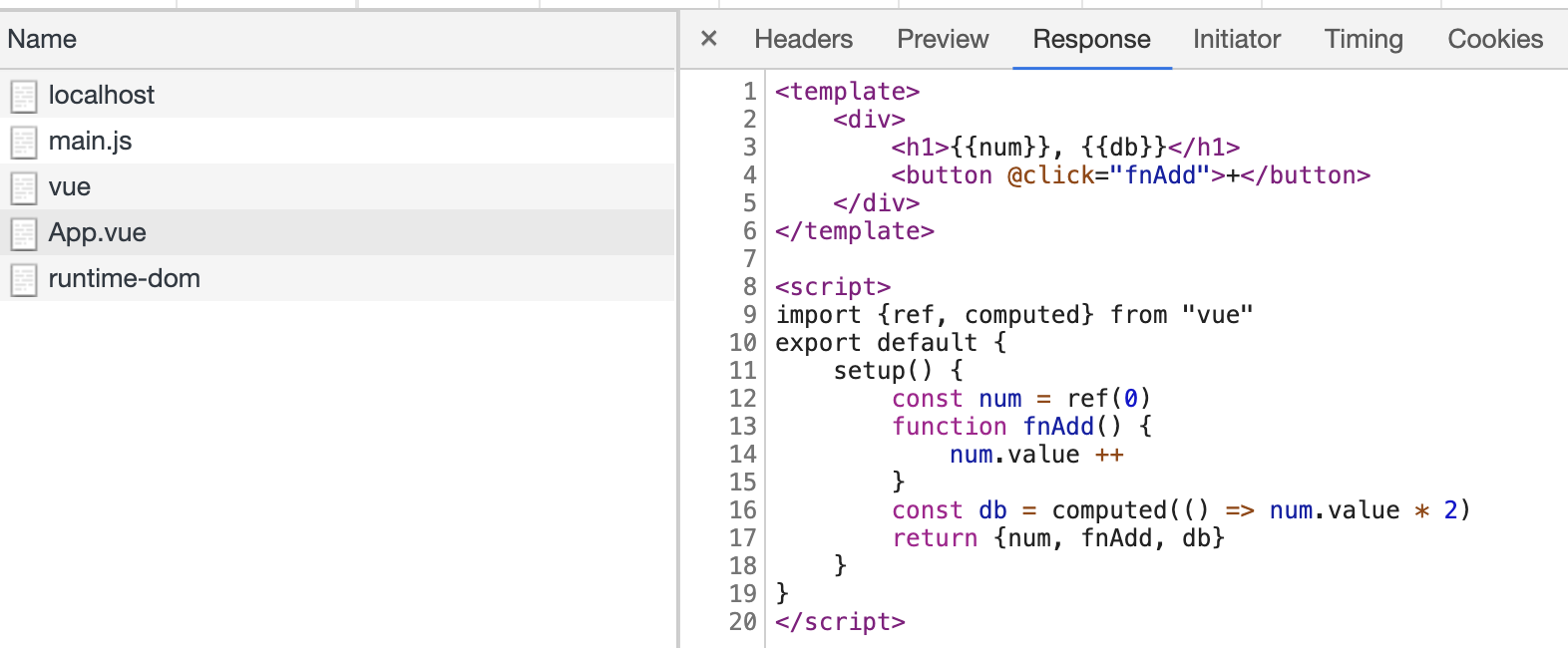
没有报错,但这并不是我们想要的,需要用到@vue/compiler-sfc帮我来解析这个.vue文件
ctx.body = _content => ctx.body = compilerSfc.parse(_content)
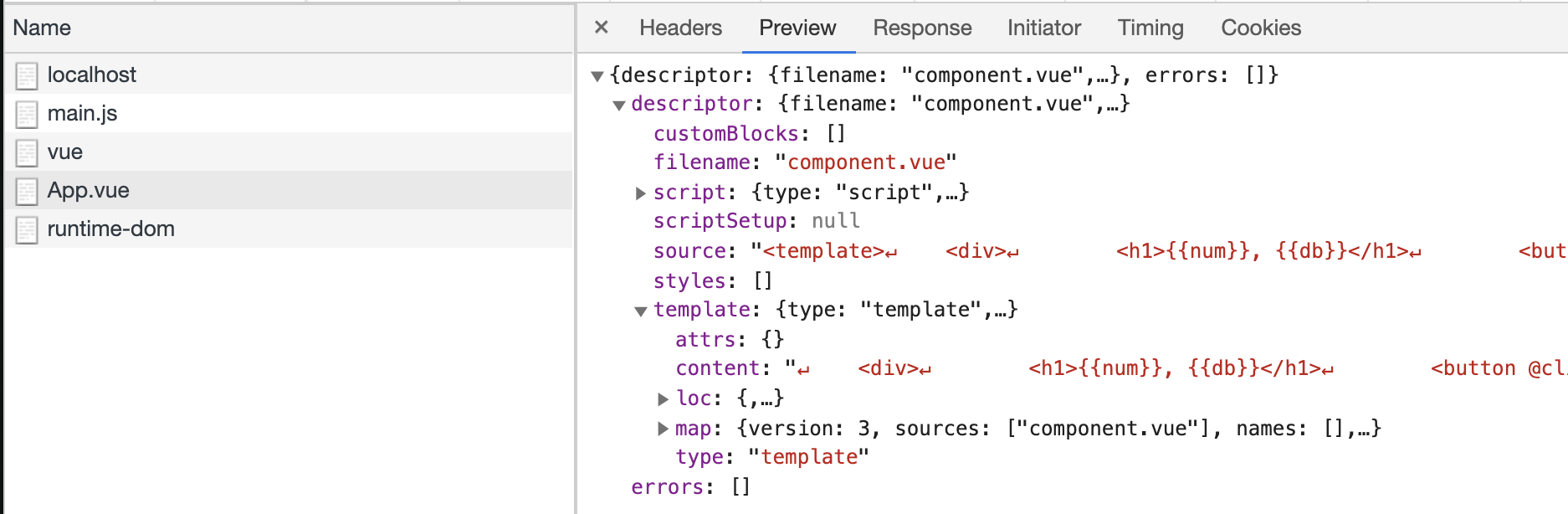
包含了我们平时看到的script、template、styles等,这就是最终要组合的内容,我们先看下 fnReWriteImport(descriptor.script.content) 先用的内容

__script.__hmrId = "/src/App.vue"是热更新,后面补充,接下来组合一下这个返回结果
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url}} = ctx
console.log("url", url)
if (url.endsWith(".vue")) {
let _path = path.resolve(__dirname, url.slice(1))
let _content = fs.readFileSync(_path, "utf-8")
let {descriptor} = compilerSfc.parse(_content)
let _parse_content = fnReWriteImport(descriptor.script.content).replace("export default", "const __script =")
ctx.type = js_type
ctx.body = `
${_parse_content}
import {render as __render} from "${url}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
} else {
await next()
}
})

因为我们处理的是.vue结尾的,所以上边要修改下,加上url?type=template的判断,报错的是这句:
import {render as __render} from "/src/App.vue?type=template"
import这个需要返回的是render函数,我们知道render函数式通过compiler编译来的,引入
npm i @vue/compiler-dom
使用@vue/compiler-dom来编译App.vue的内容
let _compiler_content = compilerDom.compile(descriptor.template.content, {mode: "module"})
ctx.type = js_type
ctx.body = fnReWriteImport(_compiler_content.code)
在前端看下输出:
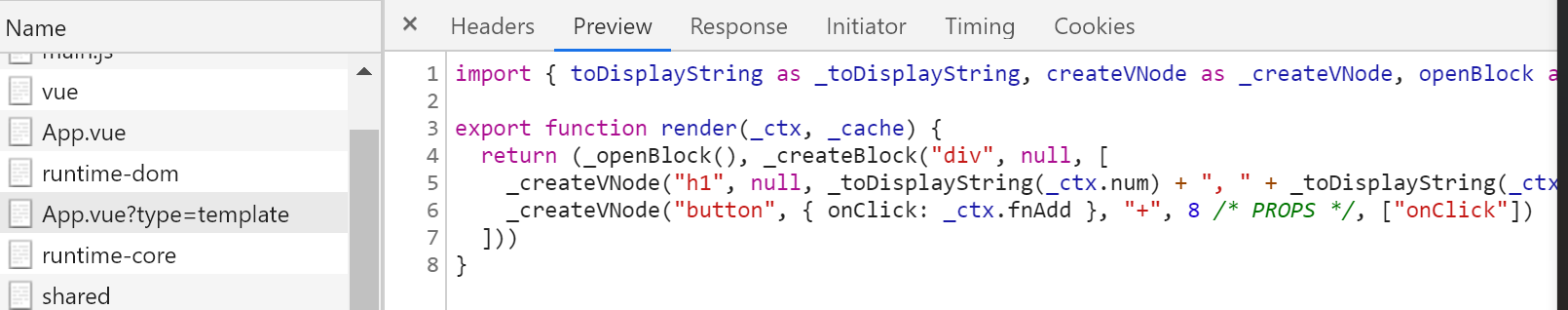
 可以正常使用了
可以正常使用了
解析.css
添加中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
const {request: {url, query}} = ctx
if (url.endsWith(".css")) {
const p = path.resolve(__dirname,url.slice(1))
let css = fs.readFileSync(p,'utf-8')
css = css.replace(/<\/?.+?>/g,"")
css = css.replace(/[\r\n]/g, "")
ctx.type = js_type
ctx.body = `let css = "${css}"
let _style = document.createElement("style")
_style.innerHTML = css
document.head.appendChild(_style)`
} else {
await next()
}
})