Background
基于hystrix版本
<dependency>
<groupId>com.netflix.hystrix</groupId>
<artifactId>hystrix-core</artifactId>
<version>1.5.12</version>
</dependency>
配置
hystrix.threadpool.default.coreSize=10
hystrix.threadpool.default.maximumSize=15
hystrix.threadpool.default.allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize=true
hystrix.threadpool.default.maxQueueSize=1000
hystrix.threadpool.default.queueSizeRejectionThreshold=1000
现象:在此配置之下,测试线程数始终不能达到最大线程数
Why
是什么样的逻辑,导致maximumSize配置失效?需要一步步深入源码探索
hytrixs使用的线程池是jdk的线程池吗?从相关类找答案
HystrixThreadPoolProperties:hytrix线程池的配置类HystrixThreadPool:是hytrix的线程池interface,其中有静态内部类Factory,一眼看到getInstance方法,追溯到另一个静态内部类HystrixThreadPoolDefault,再到HystrixConcurrencyStrategy,终于找到了线程池的创建方法getThreadPool
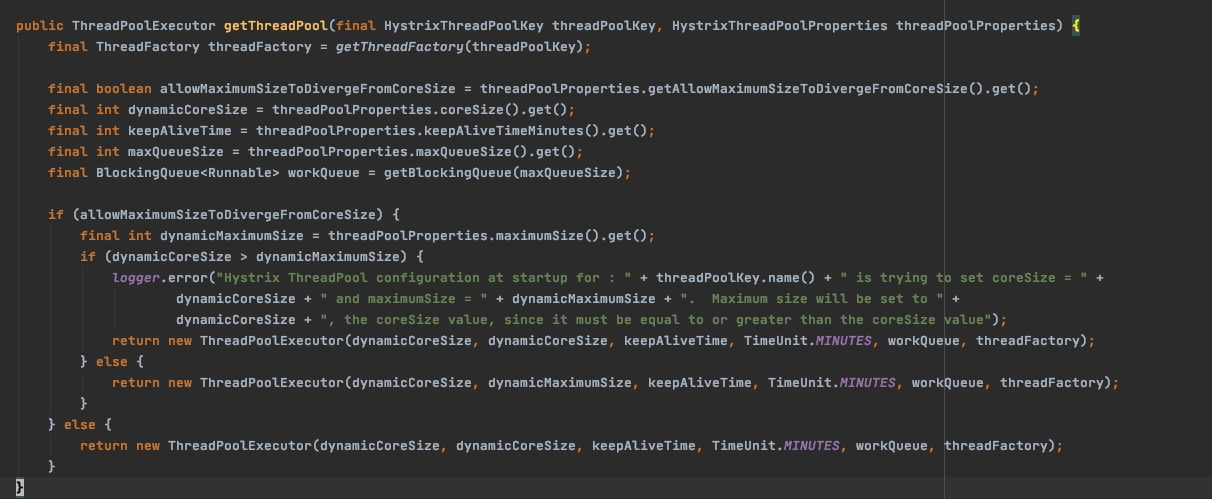
由此可以看出hytrix是使用jdk的线程池,所以线程池的运行规则应该都是一样的。
回顾java线程池的运行规则:
- 假设第一次运行线程池,当有任务来的时候,首先创建线程直到线程数达到核心线程数
- 核心线程数量的线程被占满,之后的任务加入到阻塞队列当中
- 当核心线程数和阻塞队列都被占满,之后的任务到达线程池,线程池则会创建更多的线程,直到存在的线程数量达到最大线程配置的数量
- 当最大线程数量的线程和队列都被占满,之后的任务到达线程池,那么线程池会根据拒绝策略执行相关逻辑
导致的失效的具体代码逻辑
HystrixContextScheduler,由于hytrix的源代码是使用RxJava框架来写的,不太理解,最终打断点找到了此类,进入了schedule方法。
@Override
public Subscription schedule(Action0 action) {
if (threadPool != null) {
// 线程池队列无可用空间时,直接拒绝任务
if (!threadPool.isQueueSpaceAvailable()) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Rejected command because thread-pool queueSize is at rejection threshold.");
}
}
return worker.schedule(new HystrixContexSchedulerAction(concurrencyStrategy, action));
}
可以看到,再添加action之前,会校验线程池的队列空间是否可用。具体逻辑如下:
public boolean isQueueSpaceAvailable() {
// 1. 配置的队列的数量小于等于0,直接返回true。那么继上一步任务会给到线程池,由它决定任务执行与否
if (queueSize <= 0) {
return true;
} else {
// 2. 线程池中已有任务队列的数量 vs queueSizeRejectionThreshold配置数量
return threadPool.getQueue().size() < properties.queueSizeRejectionThreshold().get();
}
}
根据此代码逻辑可以得出:
- 配置线程池队列大小参数为-1时,任务的执行与否交给java线程池决定,此时队列是同步队列,那么当并发任务数量大于核心线程数小于最大线程数的时候,是应该会创建新的线程来执行此任务。那么
maximumSize的配置是有效的 - 配置线程池队列的
maxQueueSize大于等于queueSizeRejectionThreshold配置时。若此时并发数达到了核心线程数和maxQueueSize配置之和,再有任务需要执行时,根据此逻辑,会返回false,拒绝任务的执行,并不会交给线程池处理。从而使得maximumSize的配置是无效的。
由此,我们追溯到了maximumSize配置无效的原因。
让maximumSize变得有效
- 不使用线程池的队列,直接将maxQueueSize配置设为 -1
queueSizeRejectionThreshold配置大于maxQueueSize也可以让线程池中线程的数量达到maximumSize数量,但是此时queueSizeRejectionThreshold配置并没有起到它应该承担的意义,因为线程池中队列的大小永远不可能达到queueSizeRejectionThreshold配置的数量
验证分析
# 核心线程数 默认值10
hystrix.threadpool.default.coreSize=10
# 最大线程数 默认值10 在1.5.9版本之前该值总是等于coreSize
hystrix.threadpool.default.maximumSize=10
# 阻塞队列大小 默认值-1表示使用同步队列
hystrix.threadpool.default.maxQueueSize=-1
# 阻塞队列大小拒绝阈值 默认值为5 当maxQueueSize=-1时,不起作用
hystrix.threadpool.default.queueSizeRejectionThreshold=5
# 释放线程时间 min为单位 默认为1min,当最大线程数大于核心线程数的时
hystrix.threadpool.default.keepAliveTimeMinutes=1
# 是否允许maximumSize配置生效,默认值为false
hystrix.threadpool.default.allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize=true
代码验证
public class HystrixThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 变量
final int coreSize = 5, maximumSize = 10, maxQueueSize = 5, rejThresholdSize = 6;
HystrixCommand.Setter commandConfig = generateCommandConfig(coreSize, maximumSize, maxQueueSize, rejThresholdSize);
// Run command once, so we can get metrics.
runOnce(commandConfig);
// 模拟并发
final CountDownLatch stopLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<Thread>();
for (int i = 0; i < coreSize + maximumSize + maxQueueSize + rejThresholdSize; i++) {
final int fi = i + 1;
String threadName = "TestThread-" + fi;
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
HystrixCommand<Void> command = new HystrixCommand<Void>(commandConfig) {
@Override
protected Void run() throws Exception {
stopLatch.await();
return null;
}
};
command.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Thread:" + threadName + " got rejected.");
System.out.println();
}
});
thread.setName(threadName);
threads.add(thread);
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.println("start:" + threadName);
printThreadPoolStatus();
}
// 线程执行释放
stopLatch.countDown();
for (Thread thread : threads) {
thread.join();
}
}
static void printThreadPoolStatus() {
for (HystrixThreadPoolMetrics threadPoolMetrics : HystrixThreadPoolMetrics.getInstances()) {
String name = threadPoolMetrics.getThreadPoolKey().name();
Number poolSize = threadPoolMetrics.getCurrentPoolSize();
Number queueSize = threadPoolMetrics.getCurrentQueueSize();
System.out.println("ThreadPoolKey: " + name + ", PoolSize: " + poolSize + ", QueueSize: " + queueSize);
}
}
static HystrixCommand.Setter generateCommandConfig(int coreSize, int maximumSize, int maxQueueSize, int rejThresholdSize) {
final String commandName = "TestThreadPoolCommand";
final HystrixCommand.Setter commandConfig = HystrixCommand.Setter
.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey(commandName))
.andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey(commandName))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
.withExecutionTimeoutEnabled(false))
.andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(
HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter()
.withCoreSize(coreSize)
.withMaximumSize(maximumSize)
.withAllowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize(true)
.withMaxQueueSize(maxQueueSize)
.withQueueSizeRejectionThreshold(rejThresholdSize));
return commandConfig;
}
static void runOnce(HystrixCommand.Setter commandConfig) throws InterruptedException {
HystrixCommand<Void> command = new HystrixCommand<Void>(commandConfig) {
@Override
protected Void run() {
return null;
}
};
command.execute();
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
测试数据:
coreSize=5,maxQueueSize=-1,maximumSize=10,queueSizeRejectionThreshold=100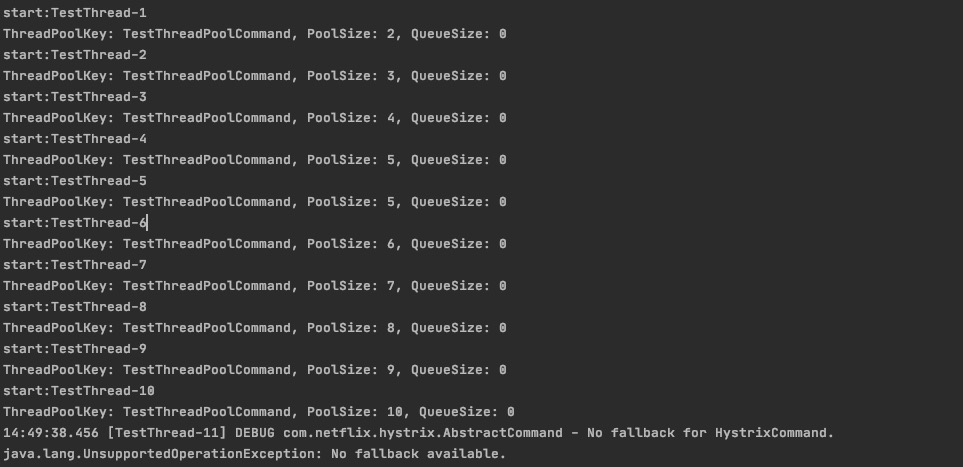
maxQueueSize=-1 结果显示:第11个任务并发的时候,hytrix拒绝执行任务,因此,
maxQueueSize为-1,maximumSize- 生效,queueSizeRejectionThreshold- 不生效测试数据
coreSize=5,maxQueueSize=5,maximumSize=10,queueSizeRejectionThreshold=5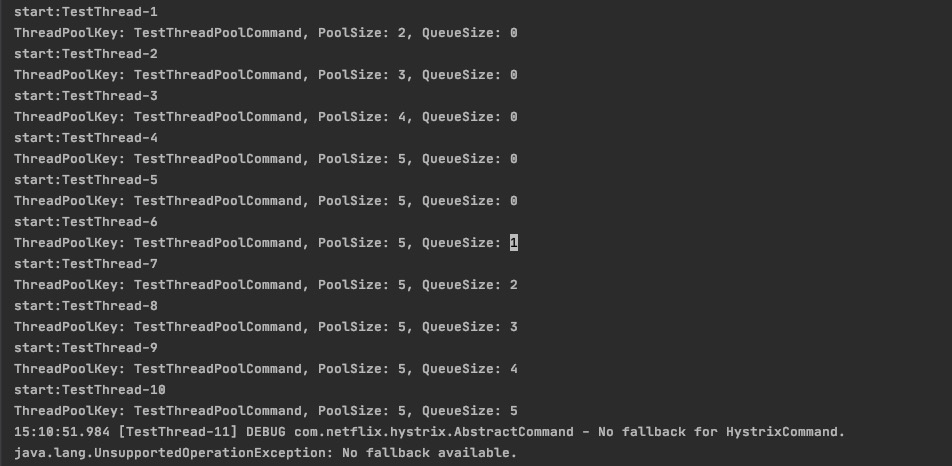
maxQueueSize=queueSizeRejectionThreshold 结果显示:在第11个任务并发的时候,hytrix会拒绝执行任务,因此
maxQueueSize> 0并且maxQueueSize=queueSizeRejectionThreshold时,maximumSize- 不生效,queueSizeRejectionThreshold- 生效测试数据
coreSize=5,maxQueueSize=5,maximumSize=10,queueSizeRejectionThreshold=3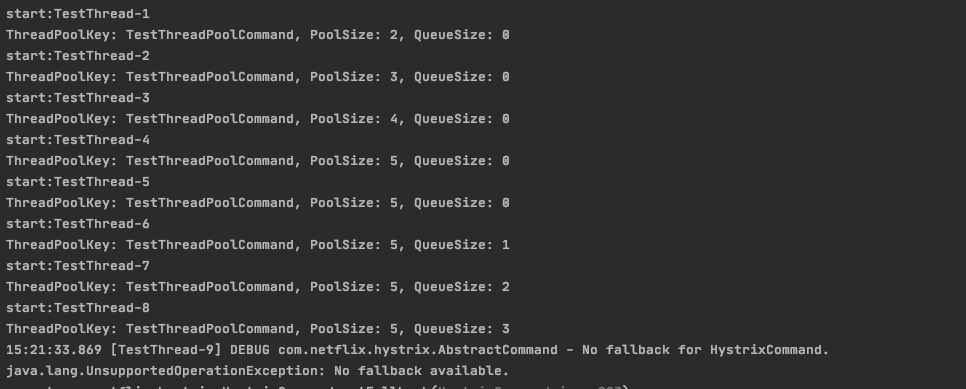
maxQueueSize>queueSizeRejectionThreshold 结果显示:在第9个任务并发的时候,hytrix会拒绝任务,因此,
maxQueueSize> 0并且maxQueueSize>queueSizeRejectionThreshold时,maximumSize- 不生效,queueSizeRejectionThreshold- 生效测试数据
coreSize=5,maxQueueSize=5,maximumSize=10,queueSizeRejectionThreshold=20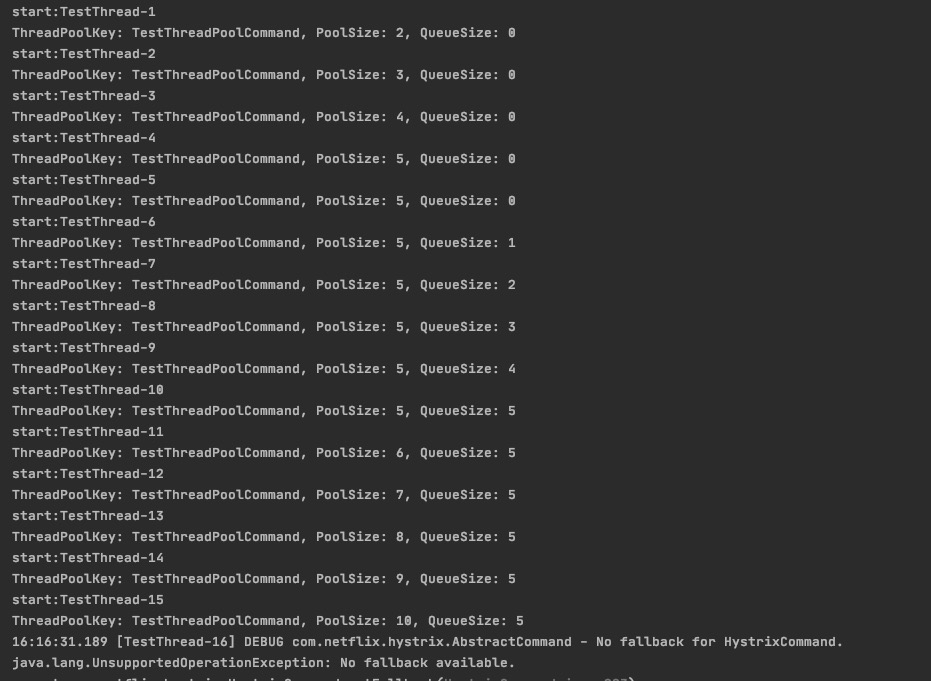
maxQueueSize<queueSizeRejectionThreshold 结果显示:在第16个任务并发的时候,hytrix会拒绝任务,因此,
maxQueueSize> 0并且maxQueueSize<queueSizeRejectionThreshold时,maximumSize- 生效,queueSizeRejectionThreshold- 生效(像摆设,它永远比maximumSize大)
结论
理解此hytrix的线程池配置的关键点,是在于搞清楚hytrix是否把任务交给线程池的逻辑部分,即HystrixThreadPool类中的isQueueSpaceAvailable方法,还有理清楚jdk的线程池的任务执行原理。基于提出的问题,做以下总结:
maximumSize 配置是否生效取决于 maxQueueSize 和 queueSizeRejectionThreshold 这两个配置:
maxQueueSize= -1, hytrix使用同步队列,从而queueSizeRejectionThreshold也没用,maximumSize是生效的maxQueueSize>=0maxQueueSize<queueSizeRejectionThreshold,maximumSize生效maxQueueSize>=queueSizeRejectionThreshold,maximumSize失效
Ref.