本章描述子集。
Subsets (easy)
求子集最初题目,Leetcode链接:子集
Educative 原题


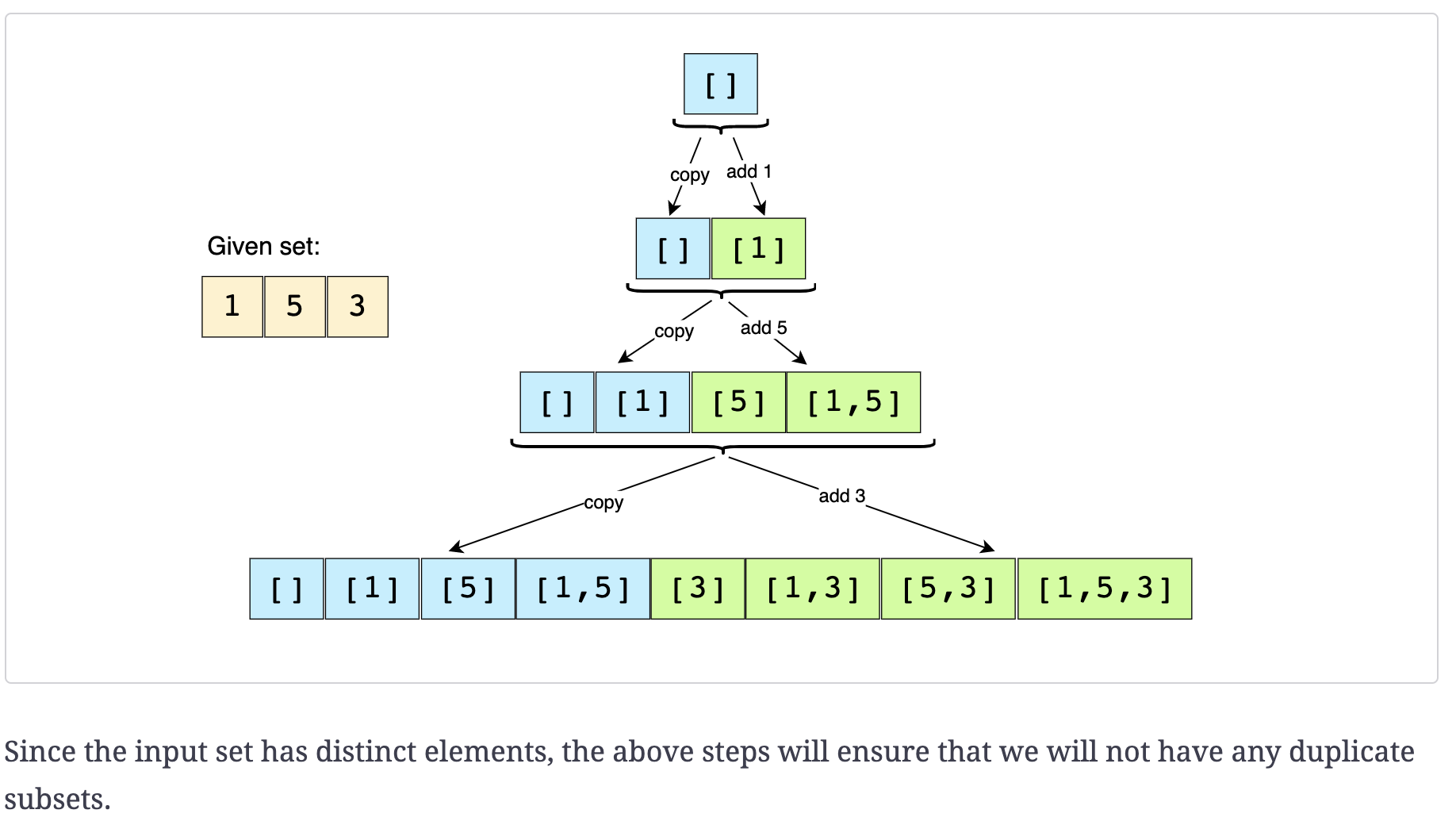

自身理解
当时思考的路径和这边文章差不多:www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p… 最后还是选择add和copy的方法,需要注意的是拷贝,而不是直接复用。
解法
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
subsets.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int num : nums) {
int size = subsets.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
List<Integer> subset = new ArrayList<>(subsets.get(i));a
subset.add(num);
subsets.add(subset);
}
}
return subsets;
}
小结
这个就是一个知不知道的事,需要用这些add+copy的方式去想,就很好解。
Subsets With Duplicates (easy)
有重复元素的求子集,Leetcode链接:子集 II
Educative 原题



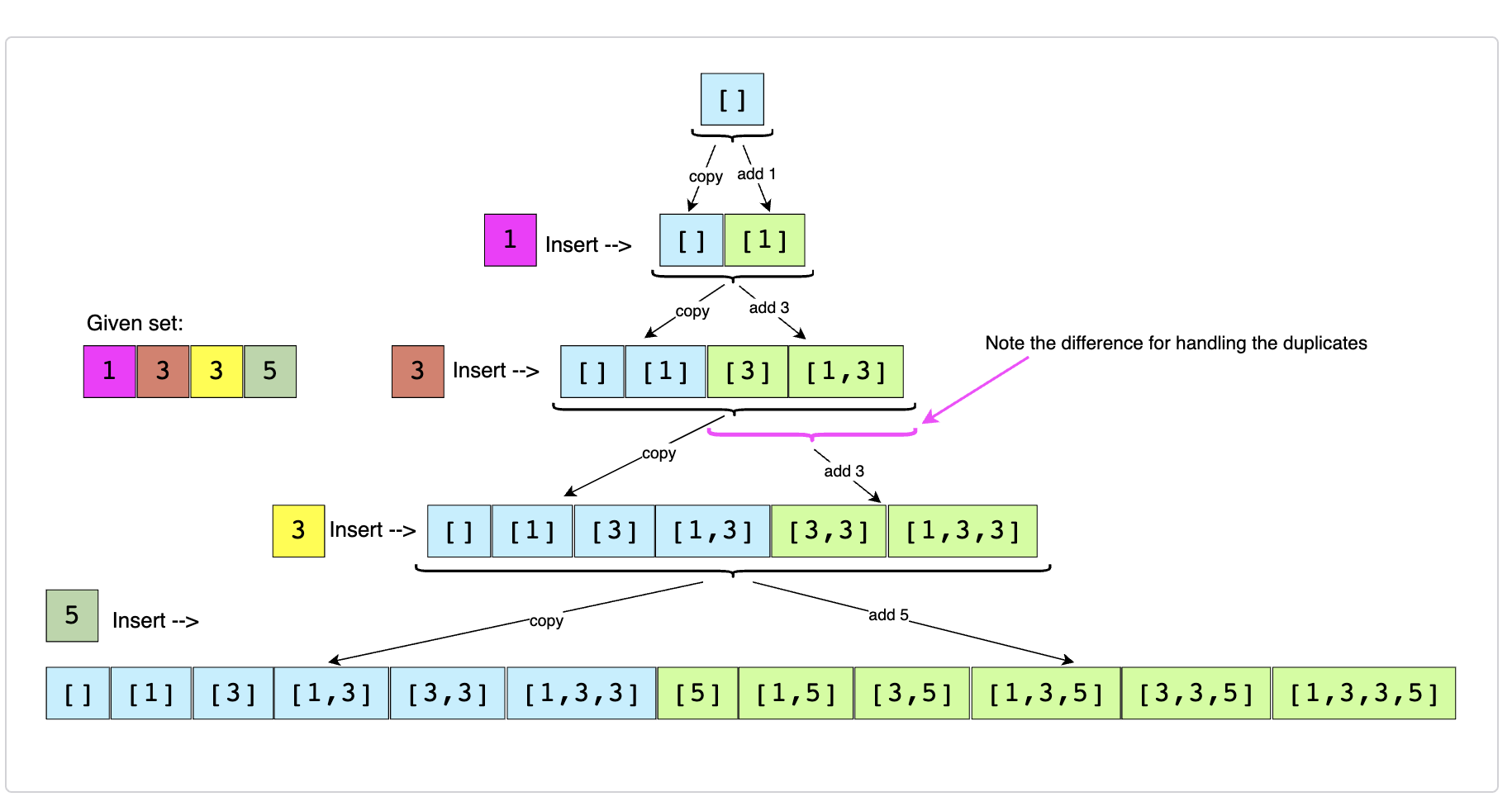

自身理解
相比Subsets (easy)多了一个需要去重的操作, 原算法可以理解成:集合 = 集合 + 集合的copy里面扩充num(新增),现在如果出现重复的num,第二次集合的原来部分便不需要再扩充了(第一次已扩),所以只需要扩充新增部分,即:集合 = 集合 +(上次的新增的copy扩充num)。
整理如下:
解法
方法一:我自己实现的解法
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>());
int lastNum = 0;
List<List<Integer>> lastNewSubsets = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
List<List<Integer>> tempLastNewSubsets = new ArrayList<>();
int size;
if (lastNum != nums[i] || i == 0) {
size = subsets.size();
for (int subsetIndex = 0; subsetIndex < size; subsetIndex++) {
List<Integer> subset = new ArrayList<>(subsets.get(subsetIndex));
subset.add(nums[i]);
subsets.add(subset);
tempLastNewSubsets.add(subset);
}
} else {
size = lastNewSubsets.size();
for (int subsetIndex = 0; subsetIndex < size; subsetIndex++) {
List<Integer> subset = new ArrayList<>(lastNewSubsets.get(subsetIndex));
subset.add(nums[i]);
subsets.add(subset);
tempLastNewSubsets.add(subset);
}
}
lastNum = nums[i];
lastNewSubsets = tempLastNewSubsets;
}
return subsets;
}
方法二:Educative的解法
public static List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
// sort the numbers to handle duplicates
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> subsets = new ArrayList<>();
subsets.add(new ArrayList<>());
int startIndex = 0, endIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
startIndex = 0;
// if current and the previous elements are same, create new subsets only from the subsets
// added in the previous step
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
startIndex = endIndex + 1;
}
endIndex = subsets.size() - 1;
for (int j = startIndex; j <= endIndex; j++) {
// create a new subset from the existing subset and add the current element to it
List<Integer> set = new ArrayList<>(subsets.get(j));
set.add(nums[i]);
subsets.add(set);
}
}
return subsets;
}
小结
上面两个方法,本质逻辑是一样的,但我更喜欢我自己的,看着更清晰。
Permutations (medium)
Leetcode链接:全排列
Educative 原题


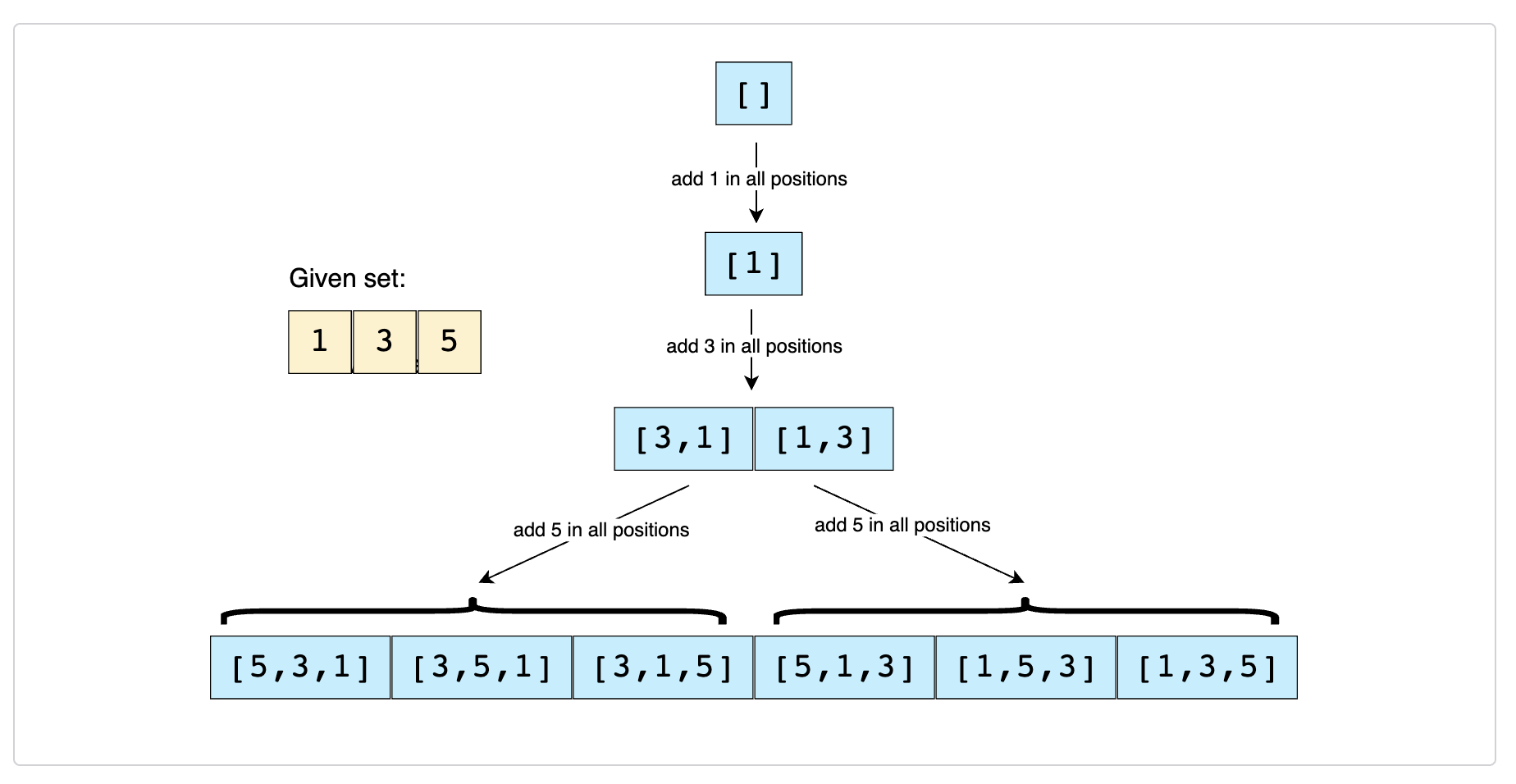

自身理解
全排列,可以采用和Subsets (easy)一样的思路,第一次是空集,第二次有一个地方可插入新值,第三次有2个地方,第三次有3个地方,依次迭代。
解法
方法一:我实现的解法,按全排的思路,迭代的解法。
public static List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
for (int num : nums) {
List<List<Integer>> tempResult = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> list : result) {
for (int i = 0; i <= list.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>(list);
tempList.add(i, num);
tempResult.add(tempList);
}
}
result = tempResult;
}
return result;
}
方法二:递归的思路
public static List<List<Integer>> permute2(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(new ArrayList<>());
generatePermutationsRecursive(nums, 0, result);
return result;
}
private static void generatePermutationsRecursive(int[] nums, int index, List<List<Integer>> result) {
List<List<Integer>> tempResult = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || index >= nums.length) {
return;
}
//LOG("input 1:",JsonUtil.toJson(result),System.identityHashCode(result));
for (List<Integer> list : result) {
for (int i = 0; i <= list.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>(list);
tempList.add(i, nums[index]);
tempResult.add(tempList);
}
}
//LOG("input 2:",JsonUtil.toJson(tempResult),System.identityHashCode(tempResult));
result.clear();
result.addAll(tempResult);
//LOG("input 3:",JsonUtil.toJson(result),System.identityHashCode(result));
generatePermutationsRecursive(nums, ++index, result);
}
方法二实现时碰到点小问题,递归时将generatePermutationsRecursive(nums, ++index, result);中result传错成tempResult,导致没有正确结果,从内容上看两者似乎相同,但2次递归后,result的原始对象将无法再被使用到,所以无法指向最终的正确的值。
小结
还是沿用Subsets (easy)一贯的从小扩充到大的思路。到是在定位方法二的问题时,有个点值得拿来说一下,Object.hashCode() 和 System.identityHashCode() 的区别。stackoverflow有个专门的问题:How do hashCode() and identityHashCode() work at the back end?,这里做一下总结:
- identityHashCode()和对象的生命周期绑定,对象生成后就不再改变,可以对应的理解成C中的指针(具体实现和jvm实现有关)。
- identityHashCode()是static的方法,无法被重写,而hashCode()是可以被重写的,且很多hashCode()的实现与对象具体内容有关,所以hashCode()是可变的。
String Permutations by changing case (medium)
Educative 原题


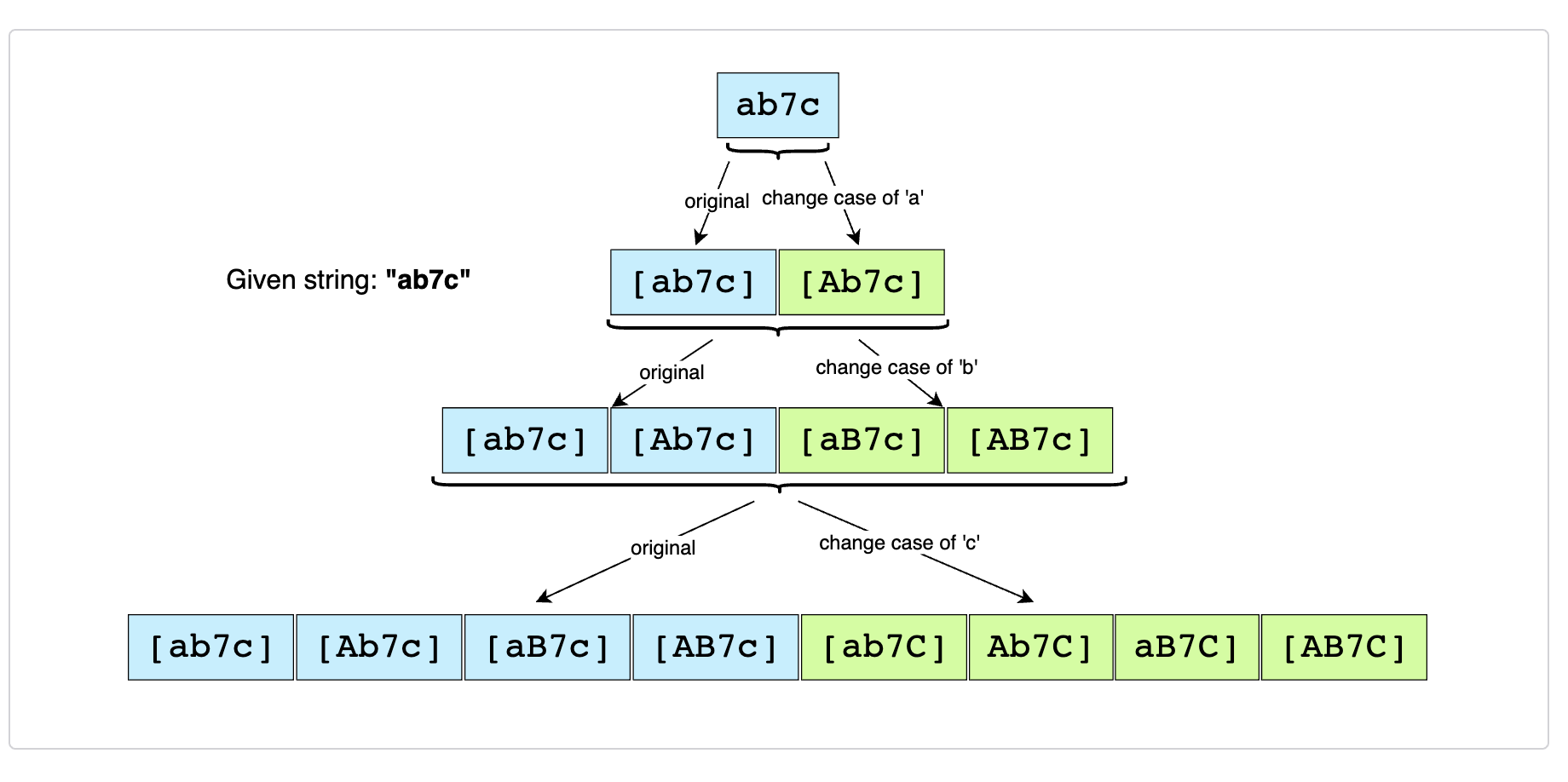

自身理解
解法
方法一:我的解法,和Subsets (easy)类似,从小变到大
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String S) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add("");
for(int i = 0;i<S.length();i++){
char value = S.charAt(i);
List<String> tempResult = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j=0;j<result.size();j++){
String temp;
if(value>='0'&&value<='9'){
temp = result.get(j) + Character.toLowerCase(value);
tempResult.add(temp);
}else{
temp = result.get(j) + Character.toUpperCase(value);
tempResult.add(temp);
temp = result.get(j) + Character.toLowerCase(value);
tempResult.add(temp);
}
}
result = tempResult;
}
return result;
}
但无论是内存暂用还是时间复杂读都不太好,里面有太多的字符串相加。
方法二:Educative的解法
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String str) {
List<String> permutations = new ArrayList<>();
if (str == null) return permutations;
permutations.add(str);
// process every character of the string one by one
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (Character.isLetter(str.charAt(i))) { // only process characters, skip digits
// we will take all existing permutations and change the letter case appropriately
int n = permutations.size();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
char[] chs = permutations.get(j).toCharArray();
// if the current character is in upper case change it to lower case or vice versa
if (Character.isUpperCase(chs[i]))
chs[i] = Character.toLowerCase(chs[i]);
else
chs[i] = Character.toUpperCase(chs[i]);
permutations.add(String.valueOf(chs));
}
}
}
return permutations;
}
一开始就对整个字符串本身进行操作,这个思路是合理的,因为结果的长度肯定都是一样的。
小结
算是一类新题型,需要注意下细节。
Balanced Parentheses (hard)
Educative 原题



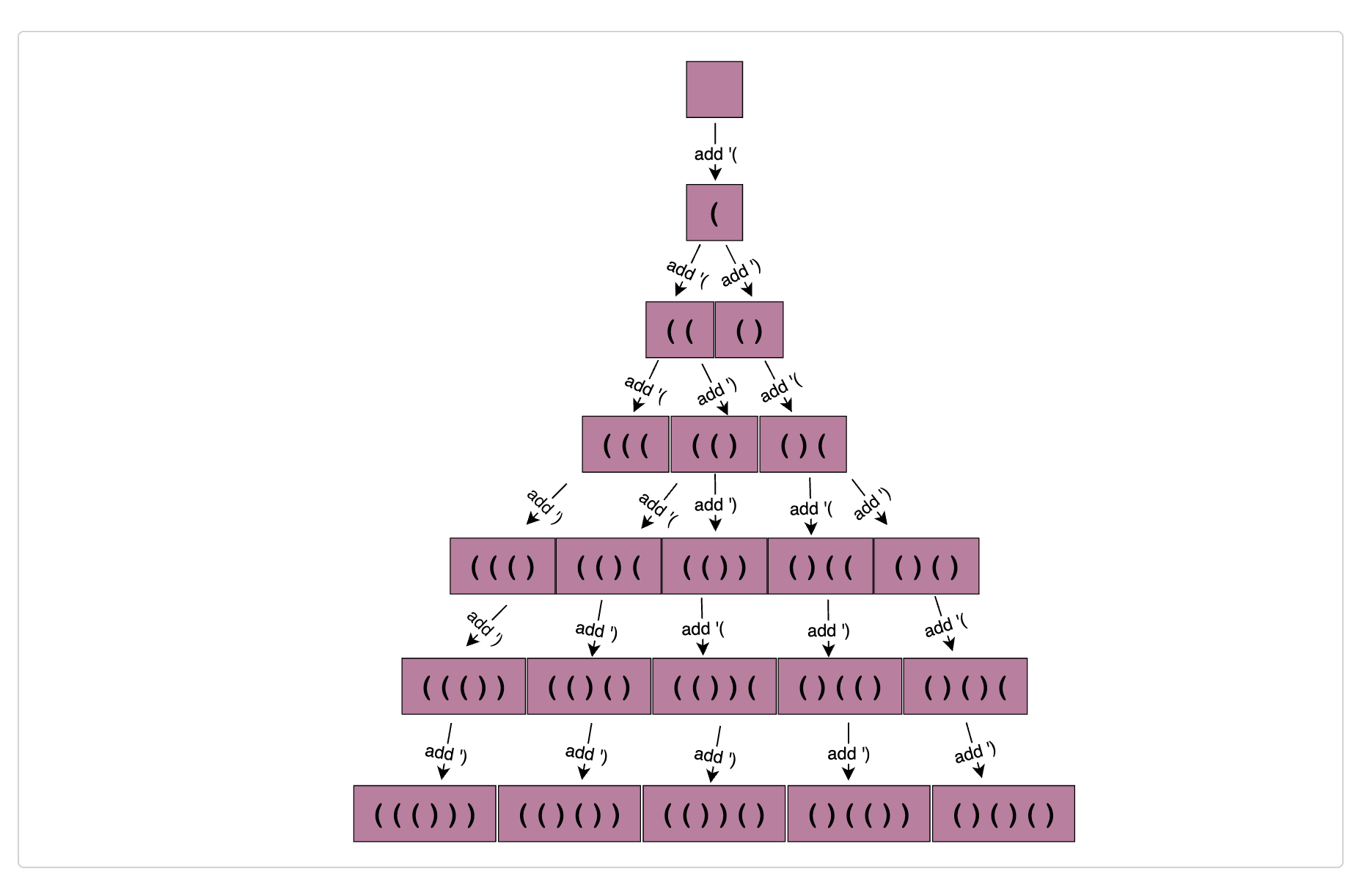
自身理解
重点在于要整理出一套添加括号的规则。
我的思路:
- openCount大于closeCount,可以加open(open < n),可以加close。
- openCount等于closeCount,只能加open(open < n)。
- openCount小于closeCount,不存在。
Educative思路:
- 判断当前状态,能加什么就加什么。
- openCount<n,加open。
- openCount>closeCount,加close。
解法
方法一:我的解法
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<ParenthesisStr> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(0, 0, ""));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ParenthesisStr pr = queue.poll();
if (pr.openCount == n && pr.closeCount == n) {
result.add(pr.str);
}
if (pr.closeCount == n) {
continue;
}
if (pr.openCount > pr.closeCount) {
if (pr.openCount < n) {
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(pr.openCount + 1, pr.closeCount, pr.str + "("));
}
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(pr.openCount, pr.closeCount + 1, pr.str + ")"));
} else if (pr.openCount == pr.closeCount && pr.openCount < n) {
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(pr.openCount + 1, pr.closeCount, pr.str + "("));
}
}
return result;
}
public static class ParenthesisStr {
int openCount = 0;
int closeCount = 0;
String str;
public ParenthesisStr(int openCount, int closeCount, String str) {
this.openCount = openCount;
this.closeCount = closeCount;
this.str = str;
}
}
方法二:Educative解法
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
Queue<ParenthesisStr> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(0, 0, ""));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ParenthesisStr ps = queue.poll();
// if we've reached the maximum number of open and close parentheses, add to the result
if (ps.openCount == n && ps.closeCount == n) {
result.add(ps.str);
} else {
if (ps.openCount < num) // if we can add an open parentheses, add it
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(ps.openCount + 1, ps.closeCount, ps.str + "("));
if (ps.openCount > ps.closeCount) // if we can add a close parentheses, add it
queue.add(new ParenthesisStr(ps.openCount, ps.closeCount + 1, ps.str + ")"));
}
}
return result;
}
public static class ParenthesisStr {
int openCount = 0;
int closeCount = 0;
String str;
public ParenthesisStr(int openCount, int closeCount, String str) {
this.openCount = openCount;
this.closeCount = closeCount;
this.str = str;
}
}
题目
Educative 原题
自身理解
解法