Promise为什么会出现
为了解决回调地狱
Promise与事件循环
Promise在初始化时,传入的函数是同步执行的,然后注册 then 回调。注册完之后,继续往下执行同步代码,在这之前,then 中回调不会执行。同步代码块执行完毕后,才会在事件循环中检测是否有可用的 promise 回调,如果有,那么执行,如果没有,继续下一个事件循环。
- Promise 构造函数是同步执行的,promise.then 中的函数是异步执行的。
JS异步编程发展
回调函数
回调函数是异步操作最基本的方法。简单,容易理解和实现
ajax(url, () => {
// 处理逻辑
})
但是有一个致命的缺点,就是容易写出回调地狱,这种代码的可读性和可维护性都非常差,非常混乱
ajax(url, () => {
// 处理逻辑
ajax(url1, () => {
// 处理逻辑
ajax(url2, () => {
// 处理逻辑
})
})
})
Promise
- Promise 必须为以下三种状态之一:Pending、Fulfilled和Rejected。一旦Promise 被 resolve 或 reject,不能再迁移至其他任何状态。
- Promise 可以实现链式调用,避免了大量的嵌套
const hjjtest = new Promise((resolve, reject)=> {
setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000);
}).then((result)=> {
console.log(result); // 1
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // (*)
setTimeout(() => resolve(result * 2), 1000);
});
}).then((result)=> { // (**)
console.log(result); // 2
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(result * 2), 1000);
});
}).then((result)=> {
console.log(result); // 4
});
co库 + 生成器Generators/yield
Generator函数是ES6提供的一种异步解决方案,其最大的特点就是可以控制函数的执行
因为手动迭代Generator函数很麻烦,实现逻辑有点绕,所以实际开发一般会配合co库去完成
安装co库: npm install co
一个在node.js中简单使用的例子
co(function* () {
const r1 = yield readFile('./1.txt');
const r2 = yield readFile('./2.txt');
const r3 = yield readFile('./3.txt');
const r4 = yield readFile('./4.txt');
})
async/await
- async/await 可以让异步代码看起来像同步代码
async function test(){
let res = await this.$http.post('rest/admin_users', this.model)
let res2 = await this.$http.get(`rest/admin_users/${this.id}`)
return result = res + res2
}
- 缺点
- async/await将异步代码改造成了同步代码,如果多个异步代码没有依赖性 却使用了await会导致性能上的降低 如下
function timeoutPromise(interval) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function(){
resolve("done");
}, interval);
});
};
async function timeTest() {
await timeoutPromise(3000);
await timeoutPromise(3000);
await timeoutPromise(3000);
}
let startTime = Date.now();
timeTest().then(() => {
let finishTime = Date.now();
let timeTaken = finishTime - startTime;
console.log("花费时间: " + timeTaken);
})
可以用Promise.all代替
手写一个符合Promise A+规范的Promise
- 基础版
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.state = PENDING
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
const resolve = value => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.value = value
}
}
const reject = reason => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (err) {
reject(err)
}
}
then(successFn, failFn) {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
successFn(this.value)
}
if (this.state === REJECTED) {
failFn(this.reason)
}
}
}
- 解决异步实现 也就是说当then调用的时候,state还是pending状态。所以需要在then调用的时候,将成功和失败方法存到各自的数组,一旦reject或者resolve,再调用它们。
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.state = PENDING
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
this.successCallbackArr = []
this.failCallbackArr = []
const resolve = value => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = FULFILLED
this.value = value
}
}
const reject = reason => {
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.state = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (err) {
reject(err)
}
}
then(successFn, failFn) {
if (this.state === FULFILLED) {
successFn(this.value)
}
if (this.state === REJECTED) {
failFn(this.reason)
}
if (this.state === PENDING) {
this.successCallbackArr.push(() => {
successFn(this.value)
})
this.failCallbackArr.push(() => {
failFn(this.reason)
})
}
}
}
- 解决链式调用
我认为这部分的代码是实现Promise的精髓所在,也是比较复杂的一部分。没搞懂要多花点时间。
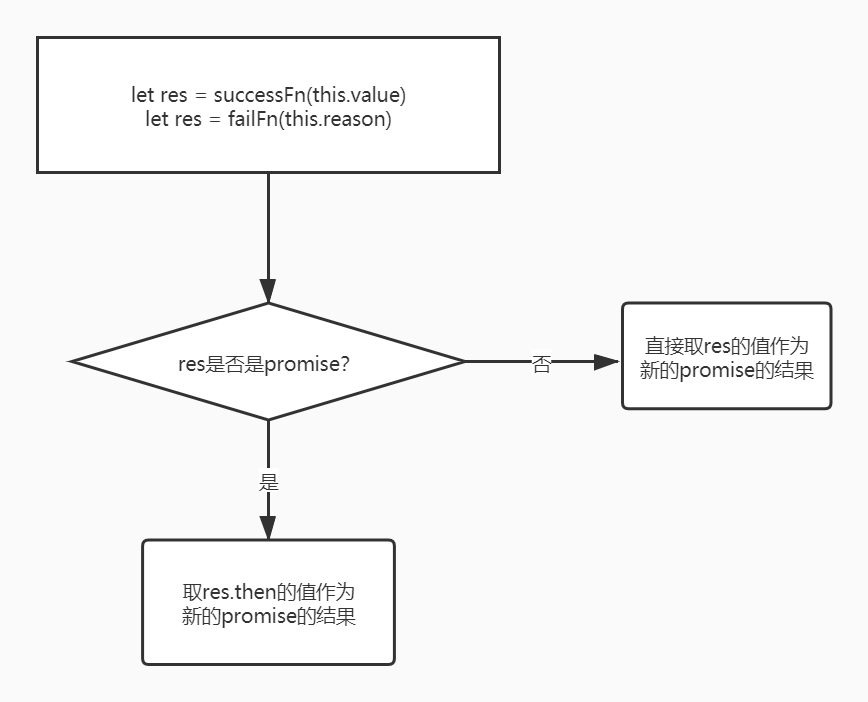
successFn(this.value)
将单行的成功回调处理函数替换成如下代码,失败亦是,pending状态下的也要更换
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function() {
try {
const res = successFn(this.data)
if (res instanceof myPromise) {
res.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(ret)
}
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
})
- 解决其他问题
// successFn如果不是函数,就忽略successFn,直接返回value
successFn = typeof successFn === 'function' ? successFn : value => value;
// failFn如果不是函数,就忽略failFn,直接扔出错误
failFn = typeof failFn === 'function' ? failFn : err => { throw err };
- 完整版
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
class myPromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
this.successCallbackArr = []
this.failCallbackArr = []
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = FULFILLED
this.value = value
this.successCallbackArr.forEach(fn => fn())
}
}
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = REJECTED
this.reason = reason
this.failCallbackArr.forEach(fn => fn())
}
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(successFn, failFn) {
successFn = typeof successFn === 'function' ? successFn : value => value
failFn = typeof failFn === 'function' ? failFn : err => { throw err }
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function() {
try {
const ret = successFn(this.data)
if (ret instanceof Promise) {
ret.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(ret)
}
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
})
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function() {
try {
const res = failFn(this.reason)
if (res instanceof Promise) {
res.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(res)
}
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
})
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
return new myPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.successCallbackArr.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const res = successFn(this.value)
if (res instanceof Promise) {
res.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(res)
}
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
})
this.failCallbackArr.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
const res = failFn(this.reason)
if (res instanceof Promise) {
res.then(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve(res)
}
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
})
})
}
}
}
介绍Promise的其他方法
- Promise.all
Promise.all方法返回一个Promise实例,此实例在参数内所有的 promise都resolve后或参数中不包含 promise 时回调完成(resolve); 如果参数中promise有一个失败rejected,此实例回调失败(reject),失败的原因是第一个失败promise的结果。
它通常在启动多个异步任务并发运行并为其结果创建承诺之后使用,以便人们可以等待所有任务完成。 - Promise.race
Promise.race方法返回一个promise,一旦迭代器中的某个promise resolve或reject,返回的promise就会resolve或reject。等于是里面最快的一个promise - Promise的resolve方法和reject方法
该方法返回一个以给定值解析后的Promise 对象。如果这个值是一个promise ,那么将返回这个promise;如果这个值是thenable(即带有"then" 方法),返回的promise会follow这个thenable的对象,采用它的最终状态 否则返回的promise将以此值完成。 - Promise.Finally
这个方法意思是 不管Promise最后的状态如何,都要执行一些最后的操作。 这些最后的操作就放到finally中
相关知识
JS的同步与异步
宏任务和微任务
参考文章
优雅的异步处理
BAT前端经典面试问题:史上最最最详细的手写Promise教程
Promise的源码实现(完美符合Promise/A+规范)
简单实现Promise
MDN文档