Swaager2配置 主要为开发者自己创建一个Docket来用户显示Bean:
@Configuration @EnableSwagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean public Docket createRestApi() { return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .pathMapping("/") .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.nvn.controller")) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build().apiInfo(new ApiInfoBuilder() .title("SpringBoot整合Swagger") .description("SpringBoot整合Swagger,详细信息......") .version("9.0") .contact(new Contact("啊啊啊啊","blog.csdn.net","aaa@gmail.com")) .license("The Apache License") .licenseUrl("www.baidu.com") .build()); } }
创建测试接口:
@RestController @Api(tags = "用户管理相关接口") @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/")
@ApiOperation("添加用户的接口")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "username", value = "用户名", defaultValue = "李四"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "address", value = "用户地址", defaultValue = "深圳", required = true)
}
)
public RespBean addUser(String username, @RequestParam(required = true) String address) {
return new RespBean();
}
@GetMapping("/")
@ApiOperation("根据id查询用户的接口")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户id", defaultValue = "99", required = true)
public User getUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
return user;
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
@ApiOperation("根据id更新用户的接口")
public User updateUserById(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
}
这里边涉及到多个API,我来向小伙伴们分别说明:
@Api注解可以用来标记当前Controller的功能。 @ApiOperation注解用来标记一个方法的作用。 @ApiImplicitParam注解用来描述一个参数,可以配置参数的中文含义,也可以给参数设置默认值,这样在接口测试的时候可以避免手动输入。 如果有多个参数,则需要使用多个@ApiImplicitParam注解来描述,多个@ApiImplicitParam注解需要放在一个@ApiImplicitParams注解中。 需要注意的是,@ApiImplicitParam注解中虽然可以指定参数是必填的,但是却不能代替@RequestParam(required = true),前者的必填只是在Swagger2框架内必填,抛弃了Swagger2,这个限制就没用了,所以假如开发者需要指定一个参数必填,@RequestParam(required = true)注解还是不能省略。 如果参数是一个对象(例如上文的更新接口),对于参数的描述也可以放在实体类中。例如下面一段代码:
@ApiModel public class User { @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户id") private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户名") private String username; @ApiModelProperty(value = "用户地址") private String address; //getter/setter }
Swaager2界面如下
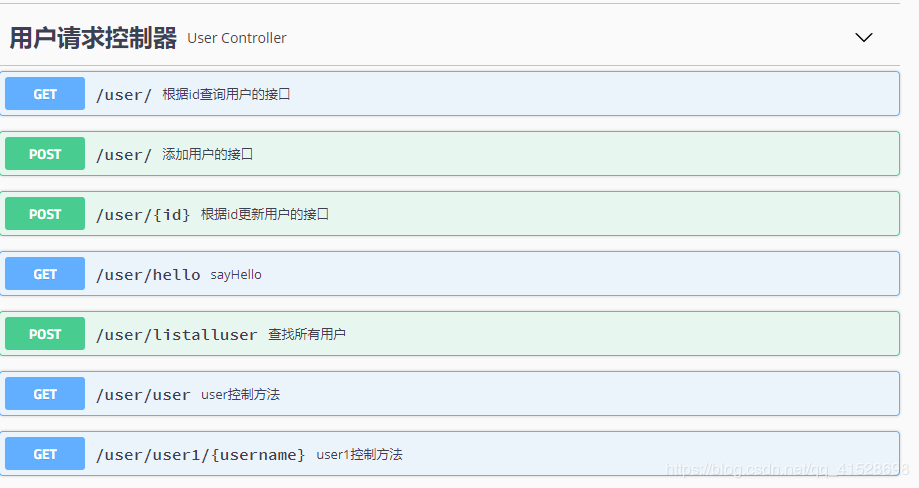
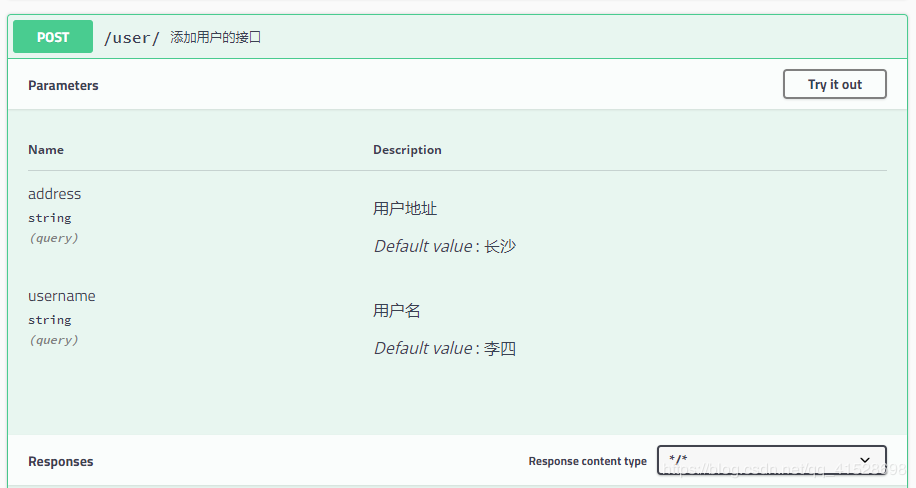
@Api:用在请求的类上,表示对类的说明 tags="说明该类的作用,可以在UI界面上看到的注解" value="该参数没什么意义,在UI界面上也看到,所以不需要配置"
@ApiOperation:用在请求的方法上,说明方法的用途、作用 value="说明方法的用途、作用" notes="方法的备注说明"
@ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,表示一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
name:参数名
value:参数的汉字说明、解释
required:参数是否必须传
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
· header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
· query --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
· path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
· body(不常用)
· form(不常用)
dataType:参数类型,默认String,其它值dataType="Integer"
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用在请求的方法上,表示一组响应 @ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息 code:数字,例如400 message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好" response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:用于响应类上,表示一个返回响应数据的信息 (这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景, 请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候) @ApiModelProperty:用在属性上,描述响应类的属性
1. @Api:用在请求的类上,说明该类的作用
@Api:用在请求的类上,说明该类的作用
tags="说明该类的作用"
value="该参数没什么意义,所以不需要配置"
示例
@Api(tags="APP用户注册Controller").
-
@ApiOperation:用在请求的方法上,说明方法的作用 示例 @ApiOperation(value="用户注册",notes="手机号、密码都是必输项,年龄随边填,但必须是数字").
-
@ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,包含一组参数说明 @ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,包含一组参数说明 @ApiImplicitParam:用在 @ApiImplicitParams 注解中,指定一个请求参数的配置信息
name:参数名 value:参数的汉字说明、解释 required:参数是否必须传 paramType:参数放在哪个地方 · header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader · query --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestParam · path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable · body(不常用) · form(不常用)
dataType:参数类型,默认String,其它值dataType="Integer"
defaultValue:参数的默认值
示例
@ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(name="mobile",value="手机号",required=true,paramType="form"), @ApiImplicitParam(name="password",value="密码",required=true,paramType="form"), @ApiImplicitParam(name="age",value="年龄",required=true,paramType="form",dataType="Integer") })
- @ApiResponses:用于请求的方法上,表示一组响应 @ApiResponses:用于请求的方法上,表示一组响应 @ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息 code:数字,例如400 message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好" response:抛出异常的类
示例
@ApiOperation(value = "select1请求",notes = "多个参数,多种的查询参数类型") @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"), @ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对") })
- @ApiModel:用于响应类上,表示一个返回响应数据的信息
@ApiModel:用于响应类上,表示一个返回响应数据的信息 (这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景, 请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候) @ApiModelProperty:用在属性上,描述响应类的属性 示例
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.io.Serializable;
@ApiModel(description= "返回响应数据") public class RestMessage implements Serializable{
@ApiModelProperty(value = "是否成功")
private boolean success=true;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "返回对象")
private Object data;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "错误编号")
private Integer errCode;
@ApiModelProperty(value = "错误信息")
private String message;
/* getter/setter */
}
在Swaager2配置类中配置扫描路径:
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo())//配置Swagger信息 // .enable(false)//是否启用Swagger---true:(默认)正常使用;false:禁用,页面显示无法加载. select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.ahy.swagger.controller"))//--->设置需要扫描的包 // .select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())//--->扫描所有 // .select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.none())//--->不扫描 // .select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withClassAnnotation(RestController.class))//--->扫描带有指定注解的类 // .select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(GetMapping.class))//--->扫描带有指定注解的方法 .paths(PathSelectors.ant("/hello1/**"))//扫描指定路径 .build();
根据项目环境决定是否启用Swagger
准备工作

加载Swagger之前先判断环境,开发环境可用Swagger
@Configuration//声明当前类为配置类 @EnableSwagger2//启用Swagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { //修改默认配置bean @Bean public Docket myDocket(Environment environment){ //设置需要显示Swagger的环境 Profiles profiles = Profiles.of("dev"); //判断当前是否处于设定的环境中 boolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles); return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2) .apiInfo(apiInfo())//配置Swagger信息 .enable(flag)//是否启用Swagger---true:正常使用;false:禁用,页面显示无法加载 .select().apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.ahy.swagger.controller"))//--->设置需要扫描的包 .build(); }
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfo(
"测试文档",//swagger标题
"A-p-i-A-p-i-A-p-i",//swagger描述
"v1.0",//swagger版本
"https://swagger.io/",//服务条款Url
new Contact("robot001","www.baidu.com","@email"),//联系人信息
"Apache 2.0",// 许可证
"http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",// 许可证Url
new ArrayList<>()
);
}
}
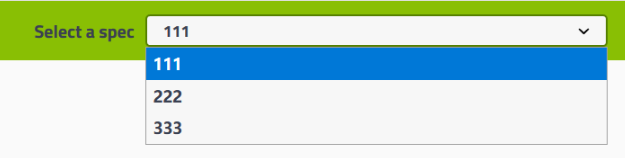
多人协作,设置不同分组的Swagger
@Configuration//声明当前类为配置类 @EnableSwagger2//启用Swagger2 public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean public Docket myDocket1(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("111"); } @Bean public Docket myDocket2(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("222"); } @Bean public Docket myDocket3(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("333"); } }