主要内容
1. 使用外部的Servlet容器和JSP支持
2. 外部Servlet容器启动SpringBoot应用原理。
1. 使用嵌入式Servlet容器的优缺点
1. 优点:
简单,便携。
不用安装tomcat环境,默认直接打成jar包即可运行。
2. 缺点:
默认不支持JSP
优化定制嵌入式tomcat复杂
(写定制器,配置server.属性,适合实现简单的定制)
2. 使用外部的Servlet容器
外置的Servet容器:应用打成war包
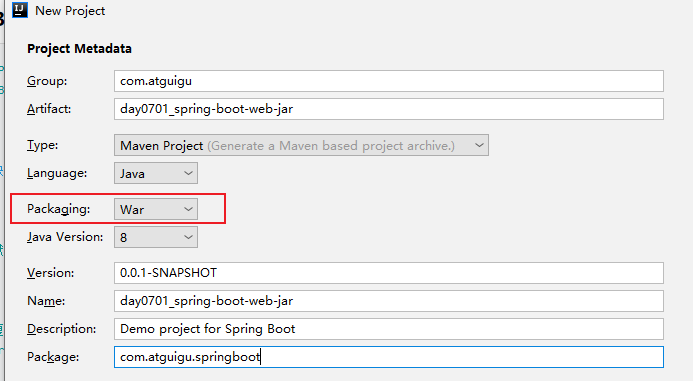
1. 创建一个SpringBoot,war项目:
打包方式是war:就可以使用JSP了。
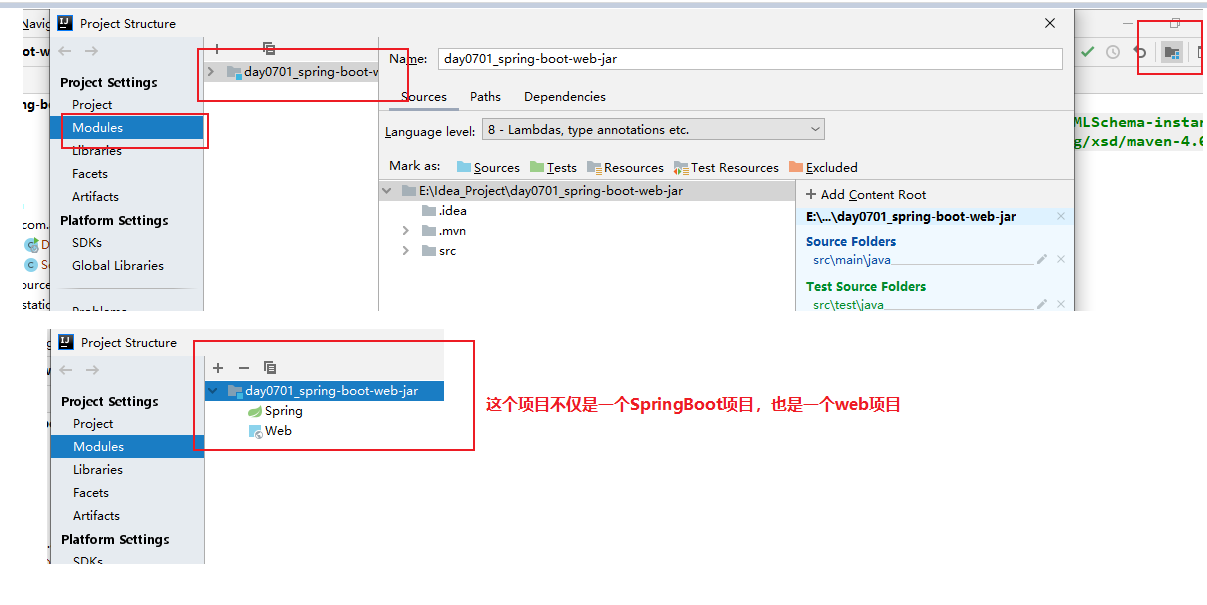
2. 补全项目的目录结构
这个项目既是一个SpringBoot项目,也是一个web项目
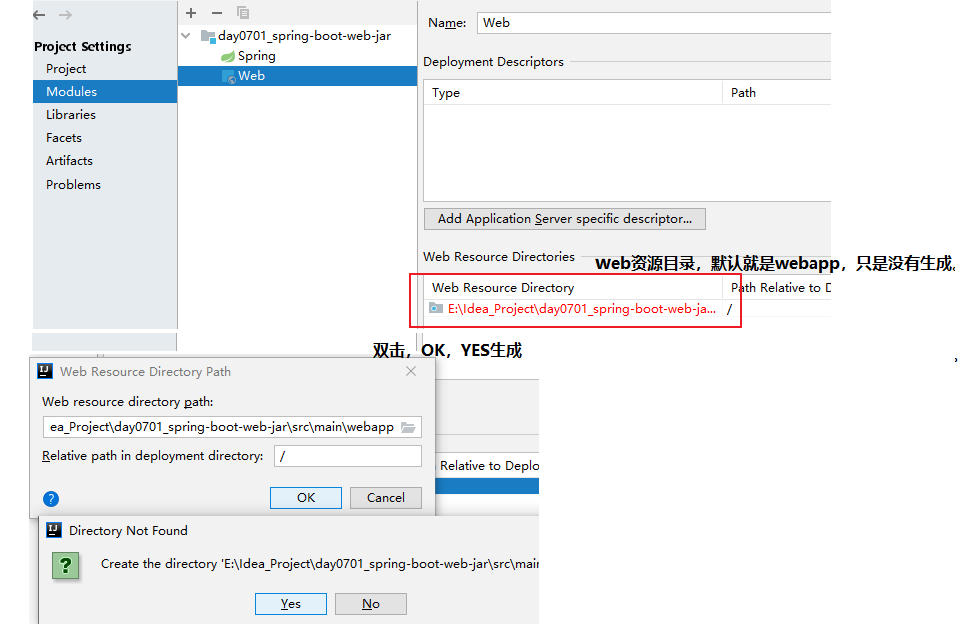
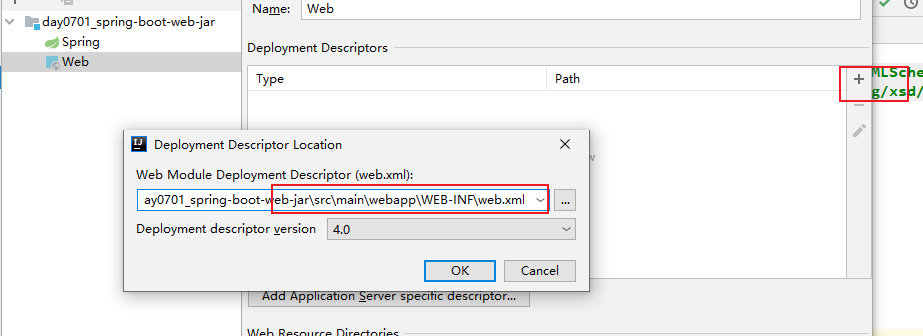
3. 生成web.xml文件
4. 将服务器整合到IDEA中(另一种方式或者打成war包放到服务器上)
5. 测试一下:
1. Controller映射请求,跳转到JSP页面
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/abc")
public String hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","你好");
//没有引入Thymeleaf对应场景的starter
return "success";
}
}
2. 配置解析规则:前后缀
# 配置解析规则
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
3. 写一个success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>success</h1>
<h3>${msg}</h3>
</body>
</html>
2.1 使用外置的Servley容器的步骤
1. 创建工程时指定war包(war包才能解析JSP)
补全目录结构
2. 将嵌入式的tomcat指定为provide
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
意思是目标环境已经有tomcat,打包时不需要带上tomcat。
3. 必须写一个继承SpringBootServletInitializer的子类
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
//SpringApplicationBuilder application:是Spring应用的构建器。
//调用sources方法,传入项目的主程序类(主入口类)
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
}
目的就是调用configure()方法
4. 启动服务器就可以使用了。
3. 使用外部的Servlet容器启动SpringBoot的原理
3.1 上一章回顾
上一章的重点是:
生成了一个继承SpringBootServletInitializer的子类
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
//SpringApplicationBuilder application:是Spring应用的构建器。
//调用sources方法,传入项目的主程序类(主入口类)
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
}
目的就是调用configure()方法
SpringApplicationBuilder application:是Spring应用的构建器。
调用sources方法,传入项目的主程序类(主入口类)
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
SpringBoot应用随着外部服务器的启动,也就启动起来了。
3.2 原理分析
jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法,启动IOC容器,创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用,再启动IOC容器。
为什么tomcat能启动SpringBoot应用?
最核心的点就是SpringBootServletInitializer
1. 背景:
Servlet 3.0之后就有一项规范。
8.2.4 Shared libraries / runtimes pluggability
在8.2.4共享库和运行时插件章节,主要定义了一个规则。
规则:
1. 服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面的
ServletContainerInitializer接口实例。
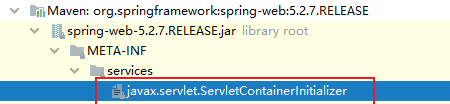
2. 创建这个实例,要到哪里去找?
implementation of the ServletContainerInitializer MUST bundle in the
META-INF/services directory of the jar file a file
called javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer,
ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在了jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,而且
必须有一个文件叫做javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer。
这个文件的内容指向它的实现类。
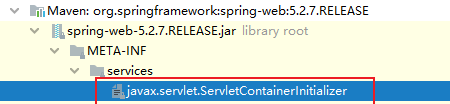
3. 里面的内容
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
3. 还可以使用HandlesTypes这个注解
在应用启动的时候,加载我们感兴趣的类。
2. 流程
1. 启动tomcat服务器
2. org/springframework/spring-web/5.2.7.RELEASE/spring-web-5.2.7.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
Spring的web模块里面有这个文件,其内容:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
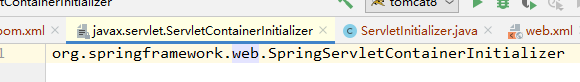
相当于我们应用在启动的时候,就要创建这个模块的ServletContainerInitializer的实现
SpringServletContainerInitializer对象。
3. 进入SpringServletContainerInitializer对象看一下。
@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class})
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
public SpringServletContainerInitializer() {
}
它有一个@HandlesTypes注解:在应用启动的时候,加载我们感兴趣的类。
将 @HandlesTypes标注的所有类型的这个类都传入onStartup()方法中,然后判断如果不是
接口的话就实例化。
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList();
Iterator var4;
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
var4 = webAppInitializerClasses.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Class<?> waiClass = (Class)var4.next();
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass, new Class[0]).newInstance());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", var7);
}
}
}
}
4. 每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup方法
while(var4.hasNext()) {
WebApplicationInitializer initializer = (WebApplicationInitializer)var4.next();
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
5. 我们看一下WebApplicationInitializer的实现:
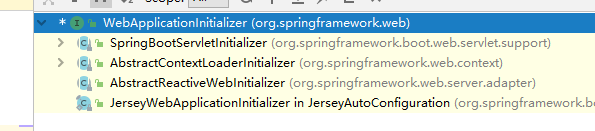
其中有一个ServletInitializer的子类
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
}
6. 由于启动Tomcat时会执行
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
}
相当于我们ServletInitializer这个类会被创建对象,并执行startUp方法。
因为ServletInitializer继承了WebApplicationInitializer
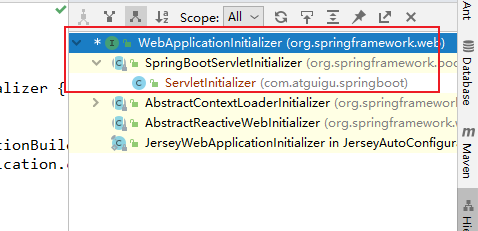
7. SpringBootServletInitializer的实例,执行onStartup的时候会创建一个根容器。
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
//创建一个根容器
WebApplicationContext rootApplicationContext = this.createRootApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (rootApplicationContext != null) {
servletContext.addListener(new SpringBootServletInitializer.SpringBootContextLoaderListener(rootApplicationContext, servletContext));
} else {
this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
//创建根容器的createRootApplicationContext(servletContext);的方法
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//1. 创建SpringApplicationBuilder构建器
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = this.createSpringApplicationBuilder();
builder.main(this.getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = this.getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, (Object)null);
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent)});
}
builder.initializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer[]{new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext)});
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext.class);
//调用configure()方法:子类重写了该方法,并传入主入口程序类。
builder = this.configure(builder);
builder.listeners(new ApplicationListener[]{new SpringBootServletInitializer.WebEnvironmentPropertySourceInitializer(servletContext)});
//使用builder创建一个Spring应用。
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getAllSources().isEmpty() && MergedAnnotations.from(this.getClass(), SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY).isPresent(Configuration.class)) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(this.getClass()));
}
Assert.state(!application.getAllSources().isEmpty(), "No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.addPrimarySources(Collections.singleton(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class));
}
application.setRegisterShutdownHook(false);
//启动Spring应用
return this.run(application);
}
8. 回到SpringBoot应用中的代码
SpringBootServletInitializer的子类重写的这个configure()方法,并传入主入口程序类。
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
SpringBootServletInitializer的子类重写的这个configure()方法,并传入主入口程序类。
9. Spring的应有就启动了,并且创建IOC容器
启动Spring应用:
return this.run(application);
protected WebApplicationContext run(SpringApplication application) {
return (WebApplicationContext)application.run(new String[0]);
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//创建IOC容器
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
4 小结
说白了根据Servlet3.0的规则标准,在服务启动的时候会加载SpringBootServletInitializer的实现
类。
这个实例主要重写了SpringBootServletInitializer的configure()方法。
configure告诉了主程序入口所在的地方。
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(Day0701SpringBootWebJarApplication.class);
}
然后应用一启动,就知道SpringBoot的主程序入口在哪了。
然后知道了主程序,就可以启动Servlet容器,再来启动SpringBoot应用。
是一个相反的过程,先启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用。
