1 RunLoop初探
1.1 RunLoop是什么?
我们都知道RunLoop是一种循环机制,但具体是什么样的就需要从源码出发来分析:
void CFRunLoopRun(void) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
int32_t result;
do {
result = CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
} while (kCFRunLoopRunStopped != result && kCFRunLoopRunFinished != result);
}
从源码中可以得知RunLoop本质上是一个do-while循环,但跟普通循环不同的是,RunLoop可以做到让线程不需要处理任务的时候就休眠,需要处理任务就忙起来。总结一下其作用就是:
- 保持程序的持续运行。
- 处理APP中的各种时间(触摸、定时器、performSelector等)
- 节省CPU资源、提高程序性能。
1.2 RunLoop与线程的关系
RunLoop与线程有着密不可分的关系,我们通过跟踪CFRunLoopGetMain()的源码可以看到:
# CFRunLoopGetMain()函数内部实现
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetMain(void) {
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
static CFRunLoopRef __main = NULL; // no retain needed
if (!__main) __main = _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_main_thread_np()); // no CAS needed
return __main;
}
# _CFRunLoopGet0()函数内部实现
CF_EXPORT CFRunLoopRef _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) {
if (pthread_equal(t, kNilPthreadT)) {
t = pthread_main_thread_np();
}
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
if (!__CFRunLoops) {
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
// 建立了一个字典dict用来存储线程和RunLoop的关系
CFMutableDictionaryRef dict = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, 0, NULL, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
// 通过__CFRunLoopCreate()创建了mainLoop
CFRunLoopRef mainLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(pthread_main_thread_np());
// 奖线程与RunLoop以key-value的方式进行绑定,类似于 dict[@"pthread_main_thread_np"] = mainLoop
CFDictionarySetValue(dict, pthreadPointer(pthread_main_thread_np()), mainLoop);
if (!OSAtomicCompareAndSwapPtrBarrier(NULL, dict, (void * volatile *)&__CFRunLoops)) {
CFRelease(dict);
}
CFRelease(mainLoop);
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
}
// 上面实现的是主线程的RunLoop,如果此处获取不到loop,那么肯定是传进来的线程不同,也就是子线程
CFRunLoopRef loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
if (!loop) {
// 创建子线程的loop
CFRunLoopRef newLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(t);
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
if (!loop) {
// 将子线程和与其对应的loop绑定起来
CFDictionarySetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t), newLoop);
loop = newLoop;
}
// don’t release run loops inside the loopsLock, because CFRunLoopDeallocate may end up taking it
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
CFRelease(newLoop);
}
if (pthread_equal(t, pthread_self())) {
_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoop, (void *)loop, NULL);
if (0 == _CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr)) {
_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoopCntr, (void *)(PTHREAD_DESTRUCTOR_ITERATIONS-1), (void (*)(void *))__CFFinalizeRunLoop);
}
}
return loop;
}
从源码与官方文档的解释中我们可以得到一些信息:
RunLoop与线程是绑定的,每条线程都有一个与之对应的RunLoop对象。- 主线程的
RunLoop是默认创建好的,在应用程序启动时会自行启动,而子线程的RunLoop需要我们手动获取并启动。 - 不能自己创建
RunLoop对象,但可以获取系统的RunLoop对象。
1.3 RunLoop的结构
我们可以先查看源码:
struct __CFRunLoop {
CFRuntimeBase _base;
pthread_mutex_t _lock; /* locked for accessing mode list */
__CFPort _wakeUpPort; // used for CFRunLoopWakeUp
Boolean _unused;
volatile _per_run_data *_perRunData; // reset for runs of the run loop
pthread_t _pthread; // 绑定的线程
uint32_t _winthread;
CFMutableSetRef _commonModes; // Mode的集合
CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems; // Item的集合
CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode; // 当前的mode
CFMutableSetRef _modes;
struct _block_item *_blocks_head;
struct _block_item *_blocks_tail;
CFAbsoluteTime _runTime;
CFAbsoluteTime _sleepTime;
CFTypeRef _counterpart;
};
typedef struct __CFRunLoopMode *CFRunLoopModeRef;
struct __CFRunLoopMode {
CFRuntimeBase _base;
pthread_mutex_t _lock; /* must have the run loop locked before locking this */
CFStringRef _name;
Boolean _stopped;
char _padding[3];
CFMutableSetRef _sources0; // sources0事件
CFMutableSetRef _sources1; // sources1事件
CFMutableArrayRef _observers; // observers事件
CFMutableArrayRef _timers; // timers事件
CFMutableDictionaryRef _portToV1SourceMap;
__CFPortSet _portSet;
CFIndex _observerMask;
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS
dispatch_source_t _timerSource; // GCD定时器
dispatch_queue_t _queue;
Boolean _timerFired; // set to true by the source when a timer has fired
Boolean _dispatchTimerArmed;
#endif
#if USE_MK_TIMER_TOO
mach_port_t _timerPort;
Boolean _mkTimerArmed;
#endif
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
DWORD _msgQMask;
void (*_msgPump)(void);
#endif
uint64_t _timerSoftDeadline; /* TSR */
uint64_t _timerHardDeadline; /* TSR */
};
通过分析以上源码我们可以得出结论:
- 线程与RunLoop是一对一的绑定。
- 一个RunLoop对象可以包含多个mode。
- 一个CFRunLoopMode对象又可以包含多个事件,例如sources0、source1、observers、timers。
1.4 RunLoop的六大事件item
RunLoop中一共有六大事件item,它们分别是:
block: __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK__
调用timer: __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_TIMER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__
响应source0: __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION__触摸事件
响应source1: __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE1_PERFORM_FUNCTION__系统端口事件
GCD主队列: __CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__
observer源: __CFNOTIFICATIONCENTER_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER__
2 RunLoop原理
2.1 RunLoop的启动
RunLoop的运行主要依赖于两个方法CFRunLoopRun和CFRunLoopRunInMode,先来查看一下源码:
//默认在kCFRunLoopDefaultMode下运行runloop
void CFRunLoopRun(void) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
int32_t result;
do {
result = CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
} while (kCFRunLoopRunStopped != result && kCFRunLoopRunFinished != result);
}
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunInMode(CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
return CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), modeName, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled);
}
从方法的参数可以看出,CFRunLoopRun是在默认的mode下运行当前线程的RunLoop,CFRunLoopRunInMode是在指定的mode下运行当前线程的RunLoop。从这里也能看出虽然有很多的mode,但是RunLoop在只能在指定的一种mode下运行,被指定的mode即是currentMode。这两个函数都调用的CFRunLoopRunSpecific,所以我们需要再进一步了解CFRunLoopRunSpecific里都干了什么。
2.2 CFRunLoopRunSpecific
/*
* 指定mode运行runloop
* @param rl 当前运行的runloop
* @param modeName 需要运行的mode的name
* @param seconds runloop的超时时间
* @param returnAfterSourceHandled 是否处理完事件就返回
*/
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) { /* DOES CALLOUT */
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
if (__CFRunLoopIsDeallocating(rl)) return kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
__CFRunLoopLock(rl);
//根据modeName找到本次运行的mode
CFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(rl, modeName, false);
//如果没找到 || mode中没有注册任何事件,则就此停止,不进入循环
if (NULL == currentMode || __CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, currentMode, rl->_currentMode)) {
Boolean did = false;
if (currentMode) __CFRunLoopModeUnlock(currentMode);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
return did ? kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource : kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
volatile _per_run_data *previousPerRun = __CFRunLoopPushPerRunData(rl);
//取上一次运行的mode
CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode = rl->_currentMode;
//如果本次mode和上次的mode一致
rl->_currentMode = currentMode;
//初始化一个result为kCFRunLoopRunFinished
int32_t result = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
// 1.通知observer即将进入runloop
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopEntry ) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);
result = __CFRunLoopRun(rl, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled, previousMode);
// 10.通知observer已退出runloop
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopExit ) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);
__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(currentMode);
__CFRunLoopPopPerRunData(rl, previousPerRun);
rl->_currentMode = previousMode;
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
return result;
}
从以上代码可以得知:
- RunLoop运行必须要指定一个mode,否则不会运行。
- mode中必须至少要包含一个item,否则也不会运行。
- 最核心的函数是
__CFRunLoopRun,因为在它之前之后分别是即将进入RunLoop和已经退出RunLoop。
接下来就看一下__CFRunLoopRun的源码:
static int32_t __CFRunLoopRun(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopModeRef rlm, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle, CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode) {
//获取系统启动后的CPU运行时间,用于控制超时时间
uint64_t startTSR = mach_absolute_time();
// 判断当前runloop的状态是否关闭
if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {
__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);
return kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (rlm->_stopped) {
rlm->_stopped = false;
return kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
}
//mach端口,在内核中,消息在端口之间传递。 初始为0
mach_port_name_t dispatchPort = MACH_PORT_NULL;
//判断是否为主线程
Boolean libdispatchQSafe = pthread_main_np() && ((HANDLE_DISPATCH_ON_BASE_INVOCATION_ONLY && NULL == previousMode) || (!HANDLE_DISPATCH_ON_BASE_INVOCATION_ONLY && 0 == _CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ)));
//如果在主线程 && runloop是主线程的runloop && 该mode是commonMode,则给mach端口赋值为主线程收发消息的端口
if (libdispatchQSafe && (CFRunLoopGetMain() == rl) && CFSetContainsValue(rl->_commonModes, rlm->_name)) dispatchPort = _dispatch_get_main_queue_port_4CF();
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS
mach_port_name_t modeQueuePort = MACH_PORT_NULL;
if (rlm->_queue) {
//mode赋值为dispatch端口_dispatch_runloop_root_queue_perform_4CF
modeQueuePort = _dispatch_runloop_root_queue_get_port_4CF(rlm->_queue);
if (!modeQueuePort) {
CRASH("Unable to get port for run loop mode queue (%d)", -1);
}
}
#endif
dispatch_source_t timeout_timer = NULL;
struct __timeout_context *timeout_context = (struct __timeout_context *)malloc(sizeof(*timeout_context));
if (seconds <= 0.0) { // instant timeout
seconds = 0.0;
timeout_context->termTSR = 0ULL;
// 1.0e10 == 1* 10^10
} else if (seconds <= TIMER_INTERVAL_LIMIT) {
//seconds为超时时间,超时时执行__CFRunLoopTimeout函数
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, DISPATCH_QUEUE_OVERCOMMIT);
timeout_timer = dispatch_source_create(DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER, 0, 0, queue);
dispatch_retain(timeout_timer);
timeout_context->ds = timeout_timer;
timeout_context->rl = (CFRunLoopRef)CFRetain(rl);
timeout_context->termTSR = startTSR + __CFTimeIntervalToTSR(seconds);
dispatch_set_context(timeout_timer, timeout_context); // source gets ownership of context
dispatch_source_set_event_handler_f(timeout_timer, __CFRunLoopTimeout);
dispatch_source_set_cancel_handler_f(timeout_timer, __CFRunLoopTimeoutCancel);
uint64_t ns_at = (uint64_t)((__CFTSRToTimeInterval(startTSR) + seconds) * 1000000000ULL);
dispatch_source_set_timer(timeout_timer, dispatch_time(1, ns_at), DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER, 1000ULL);
dispatch_resume(timeout_timer);
} else { // infinite timeout
//永不超时 - 永动机
seconds = 9999999999.0;
timeout_context->termTSR = UINT64_MAX;
}
//标志位默认为true
Boolean didDispatchPortLastTime = true;
//记录最后runloop状态,用于return
int32_t retVal = 0;
// itmes
do {
//初始化一个存放内核消息的缓冲池
uint8_t msg_buffer[3 * 1024];
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
mach_msg_header_t *msg = NULL;
mach_port_t livePort = MACH_PORT_NULL;
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
HANDLE livePort = NULL;
Boolean windowsMessageReceived = false;
#endif
//取所有需要监听的port
__CFPortSet waitSet = rlm->_portSet;
//设置RunLoop为可以被唤醒状态
__CFRunLoopUnsetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);
/// 2. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Timer 回调。
if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeSources)
/// 3. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 即将触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
/// 执行被加入的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
/// 4. RunLoop 触发 Source0 (非port) 回调。
Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(rl, rlm, stopAfterHandle);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {
/// 执行被加入的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
}
//如果没有Sources0事件处理 并且 没有超时,poll为false
//如果有Sources0事件处理 或者 超时,poll都为true
Boolean poll = sourceHandledThisLoop || (0ULL == timeout_context->termTSR);
//第一次do..whil循环不会走该分支,因为didDispatchPortLastTime初始化是true
if (MACH_PORT_NULL != dispatchPort && !didDispatchPortLastTime) {
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
//从缓冲区读取消息
msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;
/// 5. 如果有 Source1 (基于port) 处于 ready 状态,直接处理这个 Source1 然后跳转去处理消息。
if (__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, 0)) {
//如果接收到了消息的话,前往第9步开始处理msg
goto handle_msg;
}
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
if (__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(NULL, &dispatchPort, 0, 0, &livePort, NULL)) {
goto handle_msg;
}
#endif
}
didDispatchPortLastTime = false;
/// 6.通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程即将进入休眠(sleep)。
if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting)) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
//设置RunLoop为休眠状态
__CFRunLoopSetSleeping(rl);
// do not do any user callouts after this point (after notifying of sleeping)
// Must push the local-to-this-activation ports in on every loop
// iteration, as this mode could be run re-entrantly and we don’t
// want these ports to get serviced.
__CFPortSetInsert(dispatchPort, waitSet);
__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS
//这里有个内循环,用于接收等待端口的消息
//进入此循环后,线程进入休眠,直到收到新消息才跳出该循环,继续执行run loop
do {
if (kCFUseCollectableAllocator) {
objc_clear_stack(0);
memset(msg_buffer, 0, sizeof(msg_buffer));
}
msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;
//7.接收waitSet端口的消息
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY);
//收到消息之后,livePort的值为msg->msgh_local_port,
if (modeQueuePort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == modeQueuePort) {
// Drain the internal queue. If one of the callout blocks sets the timerFired flag, break out and service the timer.
while (_dispatch_runloop_root_queue_perform_4CF(rlm->_queue));
if (rlm->_timerFired) {
// Leave livePort as the queue port, and service timers below
rlm->_timerFired = false;
break;
} else {
if (msg && msg != (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer) free(msg);
}
} else {
// Go ahead and leave the inner loop.
break;
}
} while (1);
#else
if (kCFUseCollectableAllocator) {
objc_clear_stack(0);
memset(msg_buffer, 0, sizeof(msg_buffer));
}
msg = (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer;
/// 7. 调用 mach_msg 等待接受 mach_port 的消息。线程将进入休眠, 直到被下面某一个事件唤醒。
/// • 一个基于 port 的Source 的事件。
/// • 一个 Timer 到时间了
/// • RunLoop 自身的超时时间到了
/// • 被其他什么调用者手动唤醒
// mach 事务 - 指令
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY);
#endif
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
// Here, use the app-supplied message queue mask. They will set this if they are interested in having this run loop receive windows messages.
__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(waitSet, NULL, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, rlm->_msgQMask, &livePort, &windowsMessageReceived);
#endif
__CFRunLoopLock(rl);
__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);
// Must remove the local-to-this-activation ports in on every loop
// iteration, as this mode could be run re-entrantly and we don’t
// want these ports to get serviced. Also, we don’t want them left
// in there if this function returns.
__CFPortSetRemove(dispatchPort, waitSet);
__CFRunLoopSetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);
// user callouts now OK again
//取消runloop的休眠状态
__CFRunLoopUnsetSleeping(rl);
/// 8. 通知 Observers: RunLoop 的线程刚刚被唤醒了。
if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting)) __CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
/// 收到消息,处理消息。
handle_msg:;
__CFRunLoopSetIgnoreWakeUps(rl);
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
if (windowsMessageReceived) {
// These Win32 APIs cause a callout, so make sure we’re unlocked first and relocked after
__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
if (rlm->_msgPump) {
rlm->_msgPump();
} else {
MSG msg;
if (PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE | PM_NOYIELD)) {
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
__CFRunLoopLock(rl);
__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);
sourceHandledThisLoop = true;
// To prevent starvation of sources other than the message queue, we check again to see if any other sources need to be serviced
// Use 0 for the mask so windows messages are ignored this time. Also use 0 for the timeout, because we’re just checking to see if the things are signalled right now -- we will wait on them again later.
// NOTE: Ignore the dispatch source (it’s not in the wait set anymore) and also don’t run the observers here since we are polling.
__CFRunLoopSetSleeping(rl);
__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
__CFRunLoopWaitForMultipleObjects(waitSet, NULL, 0, 0, &livePort, NULL);
__CFRunLoopLock(rl);
__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);
__CFRunLoopUnsetSleeping(rl);
// If we have a new live port then it will be handled below as normal
}
#endif
if (MACH_PORT_NULL == livePort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_NOTHING();
// handle nothing
} else if (livePort == rl->_wakeUpPort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_WAKEUP();
// do nothing on Mac OS
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
// Always reset the wake up port, or risk spinning forever
ResetEvent(rl->_wakeUpPort);
#endif
}
#if USE_DISPATCH_SOURCE_FOR_TIMERS
else if (modeQueuePort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == modeQueuePort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_TIMER();
/// 9.1 如果一个 Timer 到时间了,触发这个Timer的回调。
if (!__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time())) {
// Re-arm the next timer, because we apparently fired early
__CFArmNextTimerInMode(rlm, rl);
}
}
#endif
#if USE_MK_TIMER_TOO
else if (rlm->_timerPort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == rlm->_timerPort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_TIMER();
// On Windows, we have observed an issue where the timer port is set before the time which we requested it to be set. For example, we set the fire time to be TSR 167646765860, but it is actually observed firing at TSR 167646764145, which is 1715 ticks early. The result is that, when __CFRunLoopDoTimers checks to see if any of the run loop timers should be firing, it appears to be 'too early' for the next timer, and no timers are handled.
// In this case, the timer port has been automatically reset (since it was returned from MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx), and if we do not re-arm it, then no timers will ever be serviced again unless something adjusts the timer list (e.g. adding or removing timers). The fix for the issue is to reset the timer here if CFRunLoopDoTimers did not handle a timer itself. 9308754
if (!__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time())) {
// Re-arm the next timer
__CFArmNextTimerInMode(rlm, rl);
}
}
#endif
/// 9.2 如果有dispatch到main_queue的block,执行block
else if (livePort == dispatchPort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_DISPATCH();
__CFRunLoopModeUnlock(rlm);
__CFRunLoopUnlock(rl);
_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ, (void *)6, NULL);
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
void *msg = 0;
#endif
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);
_CFSetTSD(__CFTSDKeyIsInGCDMainQ, (void *)0, NULL);
__CFRunLoopLock(rl);
__CFRunLoopModeLock(rlm);
sourceHandledThisLoop = true;
didDispatchPortLastTime = true;
} else {
/// 9.3 如果一个 Source1 (基于port) 发出事件了,处理这个事件
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_SOURCE();
// Despite the name, this works for windows handles as well
CFRunLoopSourceRef rls = __CFRunLoopModeFindSourceForMachPort(rl, rlm, livePort);
if (rls) {
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
mach_msg_header_t *reply = NULL;
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls, msg, msg->msgh_size, &reply) || sourceHandledThisLoop;
if (NULL != reply) {
(void)mach_msg(reply, MACH_SEND_MSG, reply->msgh_size, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL, 0, MACH_PORT_NULL);
CFAllocatorDeallocate(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, reply);
}
#elif DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_WINDOWS
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls) || sourceHandledThisLoop;
#endif
}
}
#if DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_MACOSX || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED || DEPLOYMENT_TARGET_EMBEDDED_MINI
if (msg && msg != (mach_msg_header_t *)msg_buffer) free(msg);
#endif
/// 执行加入到Loop的block
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {
/// 进入loop时参数说处理完事件就返回。
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;
} else if (timeout_context->termTSR < mach_absolute_time()) {
/// 超出传入参数标记的超时时间了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;
} else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {
/// 被外部调用者强制停止了
__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (rlm->_stopped) {
/// 自动停止了
rlm->_stopped = false;
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
} else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, rlm, previousMode)) {
/// source/timer/observer一个都没有了
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
/// 如果没超时,mode里没空,loop也没被停止,那继续loop。
} while (0 == retVal);
if (timeout_timer) {
dispatch_source_cancel(timeout_timer);
dispatch_release(timeout_timer);
} else {
free(timeout_context);
}
return retVal;
}
上面的代码很复杂很繁琐,总结下来的话其实就是这样一张比较有名的图:
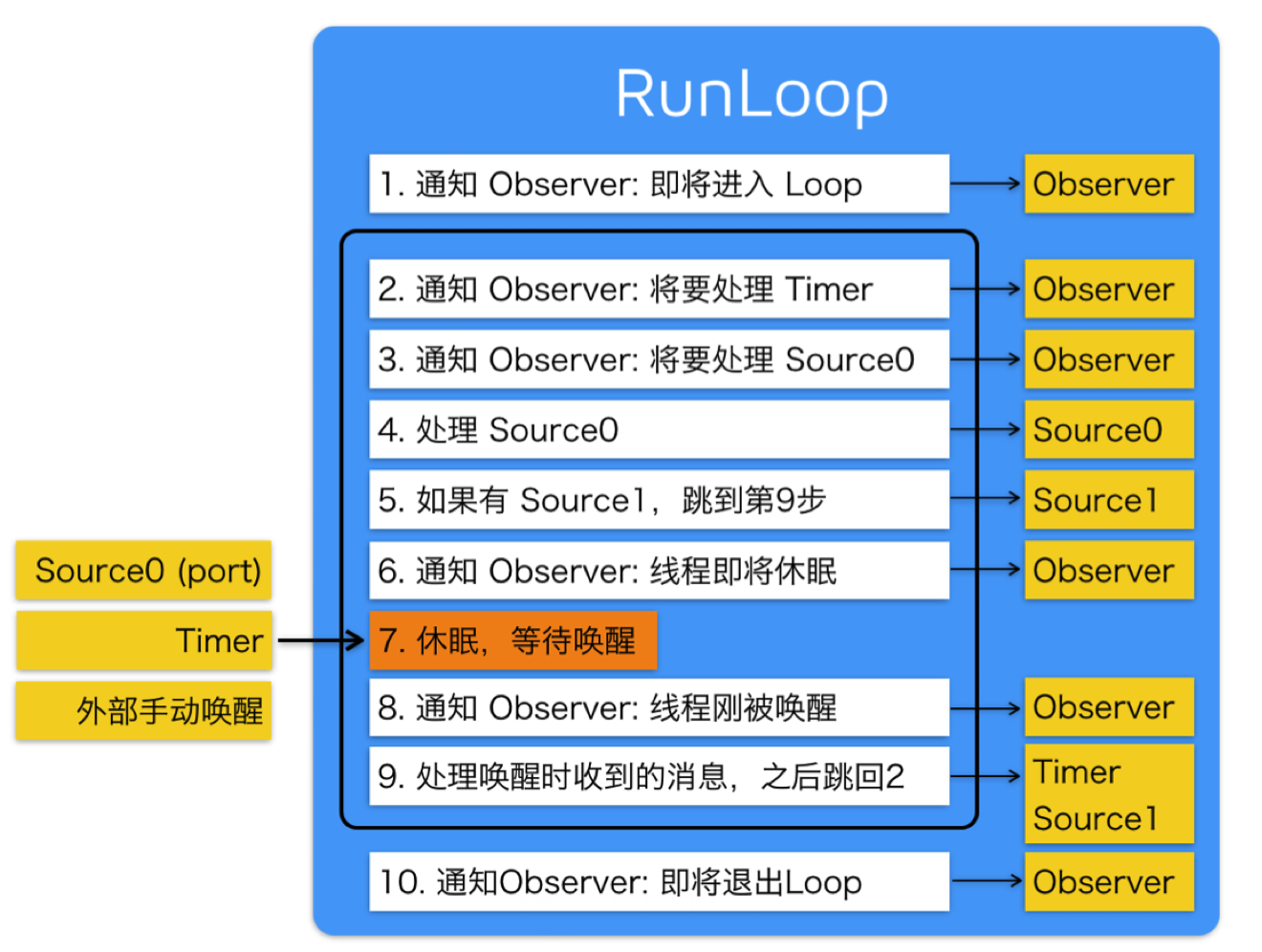
笔者能力有限,这就是我对RunLoop底层的大概分析了,如有错误请指正。