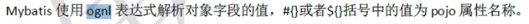pom
<dependencies>
<!--导入mybatis的坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.4</version>
</dependency>
<!--因为是数据库的操作还需要:添加mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!--日志坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.12</version>
</dependency>
<!--导入JUNIT依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
sqlmap
<mappers>
<!--<mapper resource="cn/itcast/dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>-->基于配置文件
<mapper class="cn.itcast.dao.IUserDao"></mapper>基于注解
</mappers>
映射
实体类中: private Date birthday; 数据库表中: birthday DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '生日'
sql脚本语句插入时可以直接写'2018-01-01'
传递数据到表中时直接可以使用user.setBirthday(new Date());
查询得到的结果也可以直接被封装到实体类上面
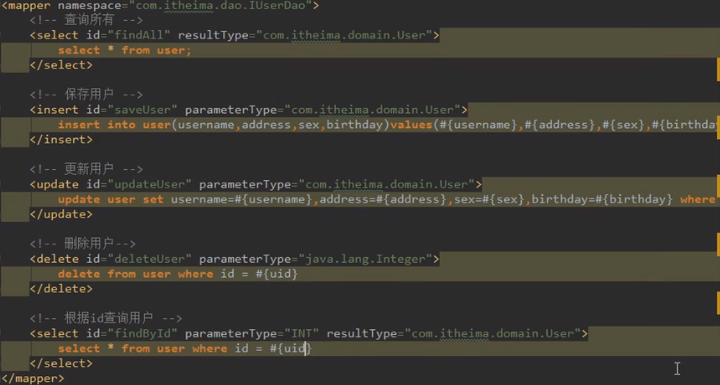
单一字段
接口中
void deleteUser (Integer userId)
映射文件中
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer"或者"Integer"或者"int">
delete from user where id = #{uid}
</delete>
只传递一个参数且为基本类型或者包装类型时,占位符具体写法不做要求
<!--
resultType也有"java.lang.Integer"或者"Integer"或者"int"这种写法
还有java.lang.String、Integer、string
-->
模糊查询
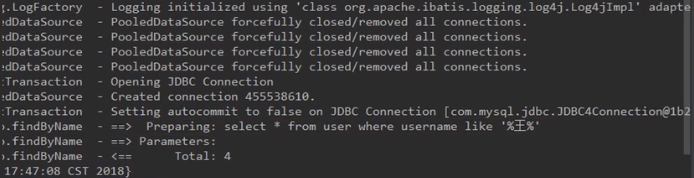
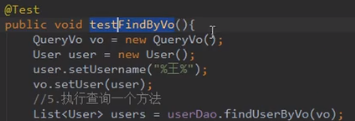
方式一:userDao.findByName("%王%")===》where username like #{name}
日志文件中的部分重要的信息:PreparedStatement的参数占位符
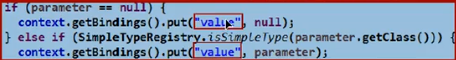
方式二(几乎不使用):===》where username like '%${value}%' 大括号里面的内容必须要是value 原因见下面源码截图
日志文件中的部分重要的信息:Statement对象的字符串拼接SQL
支持聚合函数查询
<select id = "findTotal" resultType="int">
select count(*)from user
</select>
获取自增id
写法一:select 1641812 结果为0;
写法二:insert into table (colum1,colum2,....) values(value1,value2,....)
select 1641812结果是上一条行记录所分配的自增id
mybatis中如何使用获取自增id
1.mybatis框架可以通过传入的这个参数类型:parameterType=User,然后反射出来里面的属性getXxx()中的Xxx,拿到值
2.配置插入操作后,获取刚才插入数据的id
keyProperty="id"对应实体类的id的属性名称
keyColumn="id"id的列名对应表
order="AFTER"什么时候执行获取id的操作,在执行插入之后
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" keyColumn="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select 1641812;
</selectKey>
insert into user(username, address, sex, birthday)values (#{username},#{address},#{sex},#{birthday});
</insert>
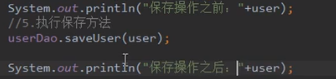
保存前打印结果为id=null 保存后打印结果为id=52
ognl表达式
parameterType
传递简单类型
pojo对象
包装对象
Object Graphic Navigation LanguageCallback
对象 图 导航 语言
它是通过对象的取值方法来获取数据,在写法上把get给省略了。
比如:我们获取用户的名称:
类中的写法:user.getUsername();
OGNL表达式的写法:user.username
IUserDao.xml中为什么能直接写username,而不用user.username呢:
因为在parameterType属性中已经提供了属性所属的类,所以此时不需要写对象名属性名
update user set username=#{username}, address=#{address}, sex=#{sex}, birthday=#{birthday} where id=#{id};
//username=#{username} ---- > username=user.username ---- > username=user.getUsername
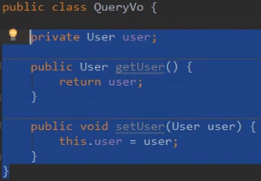
此时where username like #{name} 或者#{username}都是错误的 因为parameterType是QueryVo它没有这个属性
此时需要写成user.username:user是QueryVo里面的属性 username是user实体类里面的属性
返回类型和参数类型
参数类型使用ongl无法封装时会报错
返回类型封装结果实体类属性字段和表中字段不对应时不会报错 而是属性封装结果为null
windows上不区分大小写 linux严格区分大小写
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.itheima.domain.User">
select id as userID,username as userName,address as userAddress,sex as userSex,
birthday as useBirthday from user;
</select>
这种解决方式的执行效率是最高的,因为是在sql语句层面就解决了。
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.itheima.domain.User">
<!--主键段字段的对应-->
<id property="userId" colum="id"></id>
<!--非主键段字段的对应-->
<result property="userNmae" colum="username"></result>
<result property="userAddress" colum="address"></result>
<result property="userSex" colum="sex"></result>
<result property="userBirthday" colum="birthday"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--
注意:要加上resultMap属性,resultType不需要了
结果就可以封装了
-->
<select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap">
select * from user;
</select>
这种解决方法要多解析一点xml,执行效率变慢,但是开发效率快了。
其他的查询操作,也可以加上resultMap="userMap"属性。
properties属性
配置properties
可以在标签内部配置连接数据库的信息,也可以通过属性引用外部配置文件信息
1.resource属性:
用于指定配置文件的位置,是按照类路径的写法来写,并且必须存在于类路径下
2.url属性:
是要求按照url的写法来写配置文件的地址
URL:Uniform Resource Locator,统一资源定位符,可以唯一定位一个资源位置
写法:
http://localhost:8080/baidu.com
协议 主机 端口 URI
url="file:///E:/Idea_Projects/day0603_01mybatisCRUD/src/main/resources/jdbcConfig.properties"
* URI: Uniform Resource Identifier 统一资源标识符,可以在应用(项目)中唯一定位一个资源。
* Windows文件:用的是file协议 file:///
* 在resources下面建立一个属性文件jdbcConfig.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/txl_mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbcConfig.properties">
<!--<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/txl_mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>-->
</properties>
typeAlias属性
<!--使用typeAliases配置别名
只能配置domain中类的别名,从而让我们在用的时候少写一些包名或全限定类名
-->
<typeAliases>
<!--typeAlias用于配置别名,type属性指定实体类的全限定类名,alias属性指定别名。当指定了别名后就不区分大小写-->
<!--<typeAlias type="com.itheima.domain.User" alias="user"></typeAlias>-->
<!--用于指定要指定别名的包,当指定后,该包下的实体类都会注册别名,并且类名就是别名,不再区分大小写-->
<package name="com.itheima.domain"/>
</typeAliases>
mapper属性
<mappers>
<!--<mapper resource="com/itheima/Dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>-->
<!--package标签是用于指定dao接口所在的包,当指定完成之后,就不需要再写:
<mapper resource="com/itheima/Dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>或
<mapper class="com/itheima/Dao/IUserDao"></mapper>
-->
<package name="com.itheima.Dao"/>
</mappers>
动态语句之if
```
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String address;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
<!--根据条件查询-->
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.itheima.domain.User" parameterType="com.itheima.domain.User">
select * from user where 1 = 1
<!--判断传入的参数user中是否有username属性-->
<if test="username != null">
and username like #{username}
</if>
<!--判断传入的参数user中是否有sex属性-->
<if test="sex != null">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="address != null">
and address = #{address}
</if>
<if test="id != null">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="birthday != null">
and birthday = #{birthday}
</if>
</select>
* 这在一定程度上达到了动态SQL的目的,但是不好的一点就是:如果实体类有许多许多属性,那么就要写许多许多<if>标签。
```
动态语句之where
将where 1 = 1去掉了
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="com.itheima.domain.User" parameterType="com.itheima.domain.User" >
select * from user
<where >
<if test ="username != null" >
and username like
</if >
<if test ="sex != null" >
and sex =
</if >
<if test ="address != null" >
and address =
</if >
<if test ="id != null" >
and id =
</if >
<if test ="birthday != null" >
and birthday =
</if >
</where >
</select>
动态语句之foreach
```
解决这种子查询:select * from user where id in(41, 42, 43, 45)
<!--根据QueryVo中提供的id集合,查询用户信息-->
<select id="findUserInIds" resultType="com.itheima.domain.User" parameterType="com.itheima.domain.QueryVo">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="ids != null and ids.size() > 0">
<foreach collection="ids" open="and id in (" close=")" item="uid" separator=",">
<!--和item="uid"要一致-->
#{uid}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
```
动态语句之sql