muduo源码剖析学习总结
一、简介
muduo 是一个基于 Reactor 模式的现代 C++ 网络库,它采用非阻塞 IO 模型,基于事件驱动和回调,原生支持多核多线程,适合编写 Linux 服务端多线程网络应用程序
二、源码
我一直觉得看源码得有头,“头”的意思是从一个案例处理,去揭开她的面纱;
我们从muduo库的一个使用案例中出发,一步一步来读取源码:
案例:muduo_test.cpp
#include <muduo/base/Logging.h>
#include <muduo/base/Timestamp.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpServer.h>
#include <muduo/net/EventLoop.h>
#include <muduo/net/TcpConnection.h>
using namespace muduo;
using namespace muduo::net;
void onConnection(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn)
{
LOG_INFO << "EchoServer - " << conn->peerAddress().toIpPort() << " -> "
<< conn->localAddress().toIpPort() << " is "
<< (conn->connected() ? "UP" : "DOWN");
}
void onMessage(const TcpConnectionPtr &conn,
Buffer *buf,
Timestamp time)
{
muduo::string msg(buf->retrieveAllAsString());
LOG_INFO << conn->name() << " echo " << msg.size() << " bytes, "
<< "data received at " << time.toString();
conn->send(msg);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
EventLoop loop;
//地址初始化
InetAddress addr("127.0.0.1", 8988);
TcpServer server(&loop, addr, "echo");
server.setConnectionCallback(&onConnection);
server.setMessageCallback(&onMessage);
server.start();
loop.loop();
return 0;
}
根据这个,我们看一下步骤;
实例化 EventLoop
EventLoop::EventLoop() : looping_(false), quit_(false), eventHandling_(false), callingPendingFunctors_(false), iteration_(0), threadId_(CurrentThread::tid()), //确定使用那种IO线程 poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this)), timerQueue_(new TimerQueue(this)), wakeupFd_(createEventfd()), //通道初始化,//事件分发器 wakeupChannel_(new Channel(this, wakeupFd_)), currentActiveChannel_(NULL) { LOG_DEBUG << "EventLoop created " << this << " in thread " << threadId_; if (t_loopInThisThread) { LOG_FATAL << "Another EventLoop " << t_loopInThisThread << " exists in this thread " << threadId_; } else { t_loopInThisThread = this; } //设置readCallback_回调(read) wakeupChannel_->setReadCallback( std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this)); // we are always reading the wakeupfd wakeupChannel_->enableReading(); }这里面很重要的是
poller_(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this))这句,这一句就决定了了,我们后面使用哪种IO,比如:在linux平台下,我们一般使用的是EPOLL;看一下源码:static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop);会发现这个是一个静态函数,顺着找到这个静态函数的实现:
Poller* Poller::newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop) { if (::getenv("MUDUO_USE_POLL")) { return new PollPoller(loop); } else { return new EPollPoller(loop); } }我们选择
EPollPoller来看:EPollPoller::EPollPoller(EventLoop* loop) : Poller(loop), epollfd_(::epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC)), events_(kInitEventListSize) { if (epollfd_ < 0) { LOG_SYSFATAL << "EPollPoller::EPollPoller"; } }其实很惊喜的回发现了
epoll_create1函数,是不是有种似曾相识的感觉;没错,这个就是我们最常见的EPOLL的实现,epoll_create -> epoll_ctl -> epoll_wait;一会发现,mudo也是这么做的;注册----监控-----回调
在
EventLoop实例化中海油一个比较重要的是回调函数的设置,没注意的话,后面可能找不到这个函数wakeupChannel_->setReadCallback( std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this));对
Channel对象中readCallback_进行赋值,至于这个的作用,后续代码中说明到这,基本流程的第一步就已经完成了,我们大概总结一下
EventLoop都做了些什么?- 确定使用的IO是哪种,Epoll还是poll
- 创建事件描述符
- 事件分发器channel
- 设置事件分发器的read回调
InetAddress 地址初始化
这个就不多说了,主要就是一些地址、ip的操作,之前我们编写基础通信的时候也是经历过的
TcpServer 网络库
TcpServer::TcpServer(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr, const string& nameArg, Option option) : loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)), ipPort_(listenAddr.toIpPort()), name_(nameArg), acceptor_(new Acceptor(loop, listenAddr, option == kReusePort)), threadPool_(new EventLoopThreadPool(loop, name_)), connectionCallback_(defaultConnectionCallback), messageCallback_(defaultMessageCallback), nextConnId_(1) { //设置connectionCallback_ acceptor_->setNewConnectionCallback( std::bind(&TcpServer::newConnection, this, _1, _2)); }在
TcpServer构造函数中,主要注意这些函数acceptor_(new Acceptor(loop, listenAddr, option == kReusePort)),看一下构造函数:
Acceptor::Acceptor(EventLoop* loop, const InetAddress& listenAddr, bool reuseport) : loop_(loop), acceptSocket_(sockets::createNonblockingOrDie(listenAddr.family())), acceptChannel_(loop, acceptSocket_.fd()), listenning_(false), idleFd_(::open("/dev/null", O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC)) { assert(idleFd_ >= 0); acceptSocket_.setReuseAddr(true); acceptSocket_.setReusePort(reuseport); acceptSocket_.bindAddress(listenAddr); //Channel设置回调,当sockfd可读时掉用设置的回调 acceptChannel_.setReadCallback( std::bind(&Acceptor::handleRead, this)); }这一段代码就是在网络编程中的设置地址、端口这些,主要看一下
handleRead函数void Acceptor::handleRead() { //判断是否在IO线程 loop_->assertInLoopThread(); //客户的地址 InetAddress peerAddr; //FIXME loop until no more //获得连接的描述符 int connfd = acceptSocket_.accept(&peerAddr); if (connfd >= 0) { // string hostport = peerAddr.toIpPort(); // LOG_TRACE << "Accepts of " << hostport; if (newConnectionCallback_) { //TcpServer注册的,创建新的con,并且加入TcpServer的ConnectionMap中。 newConnectionCallback_(connfd, peerAddr); } else { sockets::close(connfd); } } else { LOG_SYSERR << "in Acceptor::handleRead"; // Read the section named "The special problem of // accept()ing when you can't" in libev's doc. // By Marc Lehmann, author of libev. if (errno == EMFILE) { ::close(idleFd_); idleFd_ = ::accept(acceptSocket_.fd(), NULL, NULL); ::close(idleFd_); idleFd_ = ::open("/dev/null", O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC); } } }这里就是创建一个新的连接做的一系列操作,其中主要是这个
newConnectionCallback_(connfd, peerAddr);这个函数是在
TcpServer中进行回调操作的看一下代码:
void TcpServer::newConnection(int sockfd, const InetAddress& peerAddr) { loop_->assertInLoopThread(); EventLoop* ioLoop = threadPool_->getNextLoop(); char buf[64]; snprintf(buf, sizeof buf, "-%s#%d", ipPort_.c_str(), nextConnId_); ++nextConnId_; string connName = name_ + buf; LOG_INFO << "TcpServer::newConnection [" << name_ << "] - new connection [" << connName << "] from " << peerAddr.toIpPort(); InetAddress localAddr(sockets::getLocalAddr(sockfd)); // FIXME poll with zero timeout to double confirm the new connection // FIXME use make_shared if necessary //后面循环回调函数handleXXXXX TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop, connName, sockfd, localAddr, peerAddr)); connections_[connName] = conn;////将新构建的con加入server的map中 conn->setConnectionCallback(connectionCallback_);//muduo默认的 conn->setMessageCallback(messageCallback_);//muduo默认的 conn->setWriteCompleteCallback(writeCompleteCallback_); conn->setCloseCallback( std::bind(&TcpServer::removeConnection, this, _1)); // FIXME: unsafe ioLoop->runInLoop(std::bind(&TcpConnection::connectEstablished, conn));//在某个线程池的loop中加入这个con }看一下主要函数:
TcpConnectionPtr conn(new TcpConnection(ioLoop, connName, sockfd, localAddr, peerAddr));这里面的设置函数会在loop中使用
TcpConnection::TcpConnection(EventLoop* loop, const string& nameArg, int sockfd, const InetAddress& localAddr, const InetAddress& peerAddr) : loop_(CHECK_NOTNULL(loop)), name_(nameArg), state_(kConnecting), reading_(true), socket_(new Socket(sockfd)), channel_(new Channel(loop, sockfd)), localAddr_(localAddr), peerAddr_(peerAddr), highWaterMark_(64*1024*1024) { channel_->setReadCallback( std::bind(&TcpConnection::handleRead, this, _1)); channel_->setWriteCallback( std::bind(&TcpConnection::handleWrite, this)); channel_->setCloseCallback( std::bind(&TcpConnection::handleClose, this)); channel_->setErrorCallback( std::bind(&TcpConnection::handleError, this)); LOG_DEBUG << "TcpConnection::ctor[" << name_ << "] at " << this << " fd=" << sockfd; socket_->setKeepAlive(true); }这里面设置了大量回调函数,handleRead、handleWrite、handleClose、handleError
后面用到可以再这里面找到;
回到
TcpServer中,看一下刚才需要的connectionCallback_就在这里acceptor_->setNewConnectionCallback( std::bind(&TcpServer::newConnection, this, _1, _2));
loop 函数
这个函数就是整套代码的核心所在,其实里面最核心的就是
epoll_wait函数,话不多说,看代码void EventLoop::loop() { assert(!looping_); assertInLoopThread(); looping_ = true; quit_ = false; // FIXME: what if someone calls quit() before loop() ? LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " start looping"; while (!quit_) { //将活动线程队列置空 activeChannels_.clear(); //获得活动文件描述符的数量,并且获得活动的channel队列 pollReturnTime_ = poller_->poll(kPollTimeMs, &activeChannels_); //增加Poll次数 ++iteration_; if (Logger::logLevel() <= Logger::TRACE) { printActiveChannels(); } // TODO sort channel by priority //事件处理状态 eventHandling_ = true; for (Channel* channel : activeChannels_) { //获得当前活动的事件 currentActiveChannel_ = channel; //处理事件,传递一个poll的阻塞时间 currentActiveChannel_->handleEvent(pollReturnTime_); } //将当前活动事件置为空 currentActiveChannel_ = NULL; //退出事件处理状态 eventHandling_ = false; //处理用户在其他线程注册给IO线程的事件 doPendingFunctors(); } LOG_TRACE << "EventLoop " << this << " stop looping"; //退出LOOPING状态 looping_ = false; }调用的这个函数
Timestamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList* activeChannels) { LOG_TRACE << "fd total count " << channels_.size(); int numEvents = ::epoll_wait(epollfd_, &*events_.begin(), static_cast<int>(events_.size()), timeoutMs); int savedErrno = errno; Timestamp now(Timestamp::now()); if (numEvents > 0) { LOG_TRACE << numEvents << " events happened"; fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels); if (implicit_cast<size_t>(numEvents) == events_.size()) { events_.resize(events_.size()*2); } } else if (numEvents == 0) { LOG_TRACE << "nothing happened"; } else { // error happens, log uncommon ones if (savedErrno != EINTR) { errno = savedErrno; LOG_SYSERR << "EPollPoller::poll()"; } } return now; }
三、总结
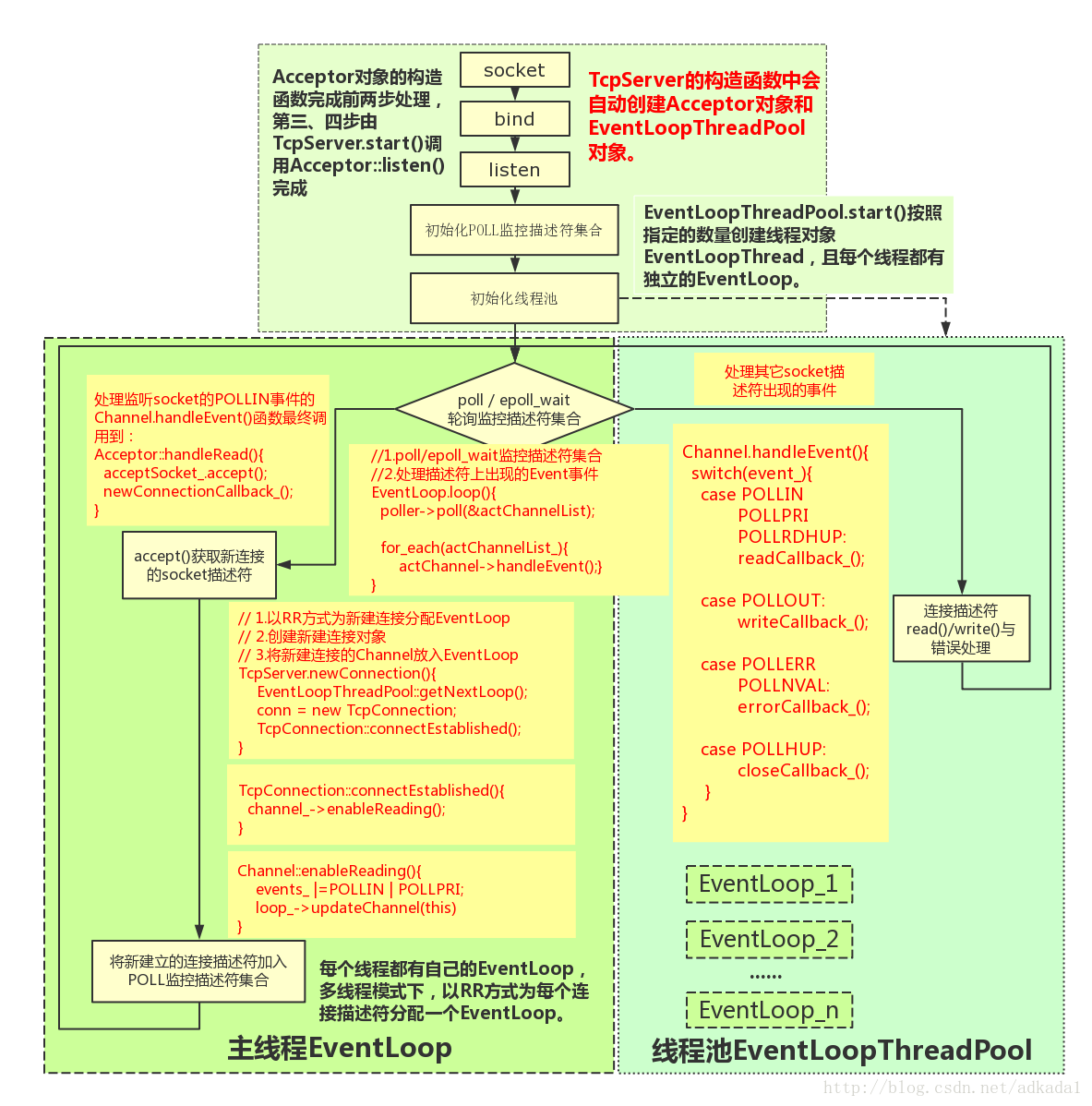
到此为止,我只是大概的粗读了一下muduo库的源码,还有很多模块的设计以及处理方式值得进一步研究,后面附一张网上的流程图
历史文章优选:
想了解学习更多C++后台服务器方面的知识,请关注: 微信公众号:====CPP后台服务器开发====