数据结构
我们查看server.h中redisServer数据结构可以看出,其功能得有多复杂。因此在这里我会将其拆成一个个小块,有些内容会在后面单独进行详细分析。而且都做了详细的注释,在这里我就不贴出来。大致分为如下几个部分。
- 通用参数(General)
- 模块(Modules)
- 网络(Networking)
- 常见的命令回调函数
- 统计相关(stat)
- 配置信息(Configuration)
- AOF持久化相关(包括aof rewrite过程中,父子进程用于消除数据差异的管道)
- RDB持久化相关(包括RDB过程中,父子进程用于通信的管道)
- AOF或者主从复制下,命令传播相关
- 日志相关(logging)
- 主从复制(Replication (master)+Replication (slave))
- 主从复制的脚本缓存(Replication script cache)
- 主从同步相关(Synchronous replication)
- 系统限制(Limits)
- 阻塞客户端(Blocked clients)
- sort命令相关(Sort)
- 数据结构转换参数
- 时间缓存(time cache)
- 发布订阅(Pubsub)
- 集群(Cluster)
- Lazy free(表示删除过期键,是否启用后台线程异步删除)
- LUA脚本
- 延迟监控相关
- 服务端中互斥锁信息
- 系统硬件信息
服务端启动过程
通用设置
在main函数中,通用设置包括时区设置,hash种子设置等
123456789
| setlocale(LC_COLLATE,""); tzset(); /* Populates 'timezone' global. */ zmalloc_set_oom_handler(redisOutOfMemoryHandler); srand(time(NULL)^getpid()); gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); char hashseed[16]; //dict的种子 getRandomHexChars(hashseed,sizeof(hashseed)); dictSetHashFunctionSeed((uint8_t*)hashseed);
|
这里的hash种子供redis中字典数据结构使用的siphash算法使用
12345678910
| void dictSetHashFunctionSeed(uint8_t *seed) { memcpy(dict_hash_function_seed,seed,sizeof(dict_hash_function_seed));}uint64_t siphash(const uint8_t *in, const size_t inlen, const uint8_t *k);uint64_t siphash_nocase(const uint8_t *in, const size_t inlen, const uint8_t *k);uint64_t dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len) { return siphash(key,len,dict_hash_function_seed);}
|
模式选择
根据参数,来判断是否是哨兵模式。
12345678910
| server.sentinel_mode = checkForSentinelMode(argc,argv);int checkForSentinelMode(int argc, char **argv) { int j; if (strstr(argv[0],"redis-sentinel") != NULL) return 1; for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) if (!strcmp(argv[j],"--sentinel")) return 1; return 0;}
|
初始化服务端
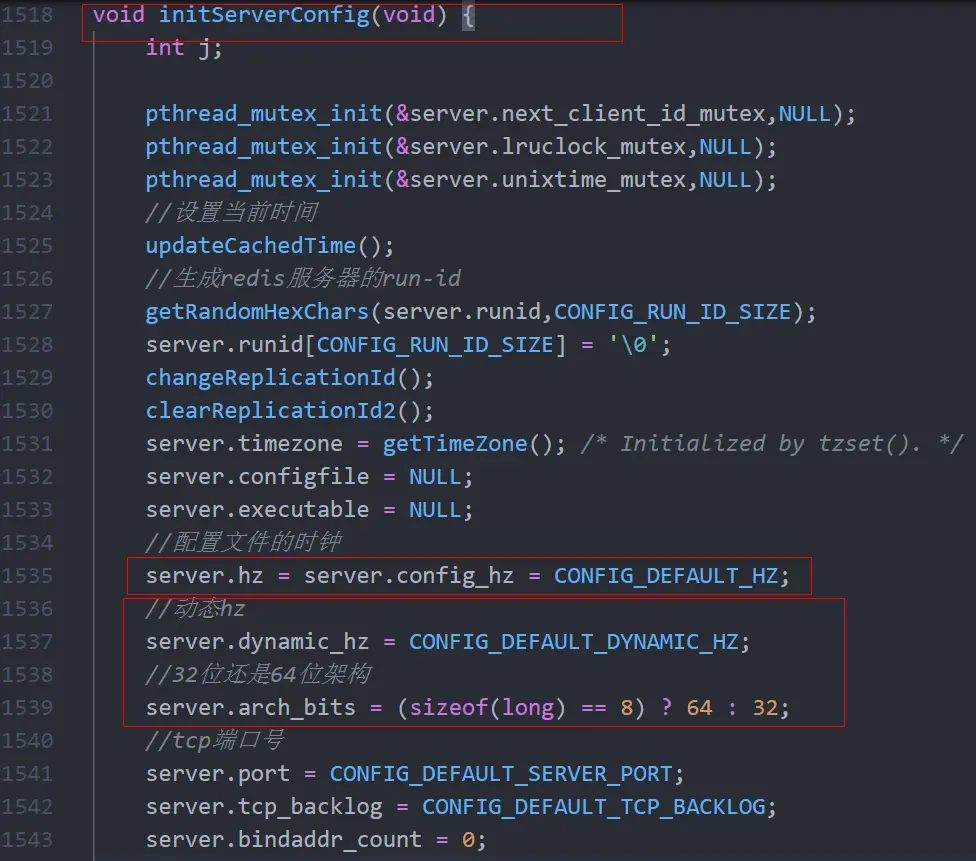
服务端的初始化,主要是函数initServerConfig。
其主要职责就是初始化redisServer数据结构中的各个成员变量
。
模块module初始化
这块没专门看,略过。
哨兵设置
根据前文所选的模式,如果选择的是哨兵模式,这里进入哨兵初始化流程。
1234
| if (server.sentinel_mode) { initSentinelConfig(); initSentinel(); }
|
是否需要rdb/aof校验
1234
| if (strstr(argv[0],"redis-check-rdb") != NULL) redis_check_rdb_main(argc,argv,NULL); else if (strstr(argv[0],"redis-check-aof") != NULL) redis_check_aof_main(argc,argv);
|
解析命令行参数
根据命令行参数,如是否设置配置文件,若设置则进行解析配置文件,覆盖默认参数设置。
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465
| if (argc >= 2) { j = 1; /* First option to parse in argv[] */ sds options = sdsempty(); char *configfile = NULL; /* Handle special options --help and --version */ if (strcmp(argv[1], "-v") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "--version") == 0) version(); if (strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0 || strcmp(argv[1], "-h") == 0) usage(); if (strcmp(argv[1], "--test-memory") == 0) { if (argc == 3) { memtest(atoi(argv[2]),50); exit(0); } else { fprintf(stderr,"Please specify the amount of memory to test in megabytes.\n"); fprintf(stderr,"Example: ./redis-server --test-memory 4096\n\n"); exit(1); } } /* First argument is the config file name? */ if (argv[j][0] != '-' || argv[j][1] != '-') { configfile = argv[j]; server.configfile = getAbsolutePath(configfile); /* Replace the config file in server.exec_argv with * its absolute path. */ zfree(server.exec_argv[j]); server.exec_argv[j] = zstrdup(server.configfile); j++; } /* All the other options are parsed and conceptually appended to the * configuration file. For instance --port 6380 will generate the * string "port 6380\n" to be parsed after the actual file name * is parsed, if any. */ while(j != argc) { if (argv[j][0] == '-' && argv[j][1] == '-') { /* Option name */ if (!strcmp(argv[j], "--check-rdb")) { /* Argument has no options, need to skip for parsing. */ j++; continue; } if (sdslen(options)) options = sdscat(options,"\n"); options = sdscat(options,argv[j]+2); options = sdscat(options," "); } else { /* Option argument */ options = sdscatrepr(options,argv[j],strlen(argv[j])); options = sdscat(options," "); } j++; } if (server.sentinel_mode && configfile && *configfile == '-') { serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Sentinel config from STDIN not allowed."); serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Sentinel needs config file on disk to save state. Exiting..."); exit(1); } resetServerSaveParams(); loadServerConfig(configfile,options); sdsfree(options); }
|
配置文件读取
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
| void loadServerConfig(char *filename, char *options) { sds config = sdsempty(); char buf[CONFIG_MAX_LINE+1]; /* Load the file content */ if (filename) { FILE *fp; if (filename[0] == '-' && filename[1] == '\0') { fp = stdin; } else { if ((fp = fopen(filename,"r")) == NULL) { serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Fatal error, can't open config file '%s'", filename); exit(1); } } while(fgets(buf,CONFIG_MAX_LINE+1,fp) != NULL) config = sdscat(config,buf); if (fp != stdin) fclose(fp); } /* Append the additional options */ if (options) { config = sdscat(config,"\n"); config = sdscat(config,options); } loadServerConfigFromString(config); sdsfree(config);}
|
是否后台运行
1234567891011121314151617
| void daemonize(void) { int fd; if (fork() != 0) exit(0); /* parent exits */ setsid(); /* create a new session */ /* Every output goes to /dev/null. If Redis is daemonized but * the 'logfile' is set to 'stdout' in the configuration file * it will not log at all. */ if ((fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR, 0)) != -1) { dup2(fd, STDIN_FILENO); dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO); dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO); if (fd > STDERR_FILENO) close(fd); }}
|
在这里需要说一下(面试会经常问),当然Redis中后台进程,貌似创建的比较简单,我们来看看纯正的后台进程过程:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647
| intdaemon_init(const char *pname, int facility){ int i; pid_t pid; if ( (pid = Fork()) < 0) //创建一个子进程 return (-1); else if (pid) _exit(0); /* parent terminates 父进程退出*/ //子进程继续运行 //此进程是子进程,所以肯定不是组长进程 /* child 1 continues... */ if (setsid() < 0) /* become session leader 创建会话,成为会话首进程,新的进程组的组长进程*/ return (-1); Signal(SIGHUP, SIG_IGN); //把挂起信号设置为忽略 if ( (pid = Fork()) < 0) //再创建一个子进程 return (-1); else if (pid) //父进程退出 _exit(0); /* child 1 terminates */ //第二个子进程继续运行,因为第二个子进程已经不是会话首进程了,所以永远不会获得控制终端 /* child 2 continues... */ daemon_proc = 1; /* for err_XXX() functions 再error.c中定义的变量*/ chdir("/"); /* change working directory 调整工作目录到根目录 */ /* close off file descriptors */ for (i = 0; i < MAXFD; i++) //关闭所有文件描述符 close(i); /* redirect stdin, stdout, and stderr to /dev/null 定义标准输入,标准输出和标准错误到/dev/null */ open("/dev/null", O_RDONLY); open("/dev/null", O_RDWR); open("/dev/null", O_RDWR); openlog(pname, LOG_PID, facility); //打开日志文件 return (0); /* success 函数运行成功 */}
|
==注意点==:
- setsid():确保当前进程变为新会话的会话头进程以及新进程组的进程组头进程,从而不再受终端控制。
- 忽略SIGHUP信号之后再次fork目的是确保本守护进程将来即使打开一个终端设备,也不会自动获取终端。当没有控制终端的一个会话头进程打开一个控制终端时,该终端自动成为这个会话头进程的控制终端。然后再次fork之后,我们确保新的子进程不再是一个会话头进程,从而不能自动获取一个控制终端。这里必须要忽略SIGHUP信号,因为会话头进程(即首次fork产生的子进程)终止时,其会话中的所有进程(即再次fork的子进程)都会收到SIGHUP信号。
- 更改根路径。
- 关闭继承来的所有套接字
- 重定向stdin、stdout和stderr,否则他会输出到屏幕上
初始化服务
信号设置
服务端打交道最多的是信号是SIGHUP和SIGPIPE,这两个信号默认行为是终止。而服务端随便就终止那肯定是不行的,因此我们需要对其进行忽略。
12
| signal(SIGHUP, SIG_IGN);signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
|
针对其他的信号,比如SIGINT信号,我们对其进行捕获然后redis进行收尾工作,避免进程被暴力kill。
12345678910111213
| void setupSignalHandlers(void) { struct sigaction act; /* When the SA_SIGINFO flag is set in sa_flags then sa_sigaction is used. * Otherwise, sa_handler is used. */ sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask); act.sa_flags = 0; act.sa_handler = sigShutdownHandler; sigaction(SIGTERM, &act, NULL); sigaction(SIGINT, &act, NULL); return;}
|
syslog设置
syslog是Linux系统自带的,主要是为daemon进程提供日志服务,我们在前面讲过。daemon进程无法打印到终端,那如何方便的接受输出的日志呢?Linux系统提供了syslog服务,该服务支持打印各种级别日志以及输出位置(本地或远程均可).
1234
| if (server.syslog_enabled) { openlog(server.syslog_ident, LOG_PID | LOG_NDELAY | LOG_NOWAIT, server.syslog_facility); }
|
服务端部分动态对象分配内存
12345678910111213141516
| server.hz = server.config_hz; server.pid = getpid(); server.current_client = NULL; server.clients = listCreate(); server.clients_index = raxNew(); server.clients_to_close = listCreate(); server.slaves = listCreate(); server.monitors = listCreate(); server.clients_pending_write = listCreate(); server.slaveseldb = -1; /* Force to emit the first SELECT command. */ server.unblocked_clients = listCreate(); server.ready_keys = listCreate(); server.clients_waiting_acks = listCreate(); server.get_ack_from_slaves = 0; server.clients_paused = 0; server.system_memory_size = zmalloc_get_memory_size();
|
创建共享对象
Redis是非常注重内存消耗的,有些常用的对象,采用引用计数的方式进行复用。
123456789101112131415161718
| createSharedObjects(); shared.crlf = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("\r\n")); shared.ok = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("+OK\r\n")); shared.err = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("-ERR\r\n")); shared.emptybulk = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("$0\r\n\r\n")); shared.czero = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew(":0\r\n")); shared.cone = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew(":1\r\n")); shared.cnegone = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew(":-1\r\n")); shared.nullbulk = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("$-1\r\n")); shared.nullmultibulk = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("*-1\r\n")); shared.emptymultibulk = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("*0\r\n")); shared.pong = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("+PONG\r\n")); shared.queued = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("+QUEUED\r\n")); shared.emptyscan = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("*2\r\n$1\r\n0\r\n*0\r\n")); shared.wrongtypeerr = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew( "-WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value\r\n"));....
|
根据系统限制调整打开得文件数
网络模型(reactor)初始化
Redis支持Unix和TCP两种模型,当服务端和客户端都在本机时,Unix域套接字通信更快。因为他不需要协议头解析等等。
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425
| server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+CONFIG_FDSET_INCR); if (server.el == NULL) { serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Failed creating the event loop. Error message: '%s'", strerror(errno)); exit(1); } server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum); /* Open the TCP listening socket for the user commands. */ if (server.port != 0 && listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == C_ERR) exit(1); /* Open the listening Unix domain socket. */ if (server.unixsocket != NULL) { unlink(server.unixsocket); /* don't care if this fails */ server.sofd = anetUnixServer(server.neterr,server.unixsocket, server.unixsocketperm, server.tcp_backlog); if (server.sofd == ANET_ERR) { serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Opening Unix socket: %s", server.neterr); exit(1); } anetNonBlock(NULL,server.sofd); }
|
LRU策略中过期池初始化
12345678910111213
| void evictionPoolAlloc(void) { struct evictionPoolEntry *ep; int j; ep = zmalloc(sizeof(*ep)*EVPOOL_SIZE); for (j = 0; j < EVPOOL_SIZE; j++) { ep[j].idle = 0; ep[j].key = NULL; ep[j].cached = sdsnewlen(NULL,EVPOOL_CACHED_SDS_SIZE); ep[j].dbid = 0; } EvictionPoolLRU = ep;}
|
初始化rdb和aof信息
1234567891011121314
| server.rdb_child_pid = -1; server.aof_child_pid = -1; server.rdb_child_type = RDB_CHILD_TYPE_NONE; server.rdb_bgsave_scheduled = 0; server.child_info_pipe[0] = -1; server.child_info_pipe[1] = -1; server.child_info_data.magic = 0; aofRewriteBufferReset(); server.aof_buf = sdsempty(); server.lastsave = time(NULL); /* At startup we consider the DB saved. */ server.lastbgsave_try = 0; /* At startup we never tried to BGSAVE. */ server.rdb_save_time_last = -1; server.rdb_save_time_start = -1; server.dirty = 0;
|
初始化状态信息
123456789101112131415
| resetServerStats(); /* A few stats we don't want to reset: server startup time, and peak mem. */server.stat_starttime = time(NULL);server.stat_peak_memory = 0;server.stat_rdb_cow_bytes = 0;server.stat_aof_cow_bytes = 0;server.cron_malloc_stats.zmalloc_used = 0;server.cron_malloc_stats.process_rss = 0;server.cron_malloc_stats.allocator_allocated = 0;server.cron_malloc_stats.allocator_active = 0;server.cron_malloc_stats.allocator_resident = 0;server.lastbgsave_status = C_OK;server.aof_last_write_status = C_OK;server.aof_last_write_errno = 0;server.repl_good_slaves_count = 0;
|
注册事件
在服务端网络编程中,主要包括三类事件:文件事件、定时事件和信号事件(信号前面已经说了)。
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031
| /* Create the timer callback, this is our way to process many background * operations incrementally, like clients timeout, eviction of unaccessed * expired keys and so forth. */if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) { serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers."); exit(1);}/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix * domain sockets. */for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) { if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE, acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) { serverPanic( "Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event."); }}if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE, acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) serverPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event.");/* Register a readable event for the pipe used to awake the event loop * when a blocked client in a module needs attention. */if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.module_blocked_pipe[0], AE_READABLE, moduleBlockedClientPipeReadable,NULL) == AE_ERR) { serverPanic( "Error registering the readable event for the module " "blocked clients subsystem.");}
|
这里采用回调的方式注册事件,结合IO复用技术实现高效的网络模型。
- 复制初始化等等。
- 一些lua虚拟机和脚本添加
慢日志初始化
12345
| void slowlogInit(void) { server.slowlog = listCreate(); server.slowlog_entry_id = 0; listSetFreeMethod(server.slowlog,slowlogFreeEntry);}
|
后台任务线程创建
这里后台线程主要包括三类,见下面宏定义
12345
| /* Background job opcodes */
|
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536
| /* Initialize the background system, spawning the thread. */void bioInit(void) { pthread_attr_t attr; pthread_t thread; size_t stacksize; int j; /* Initialization of state vars and objects */ for (j = 0; j < BIO_NUM_OPS; j++) { pthread_mutex_init(&bio_mutex[j],NULL); pthread_cond_init(&bio_newjob_cond[j],NULL); pthread_cond_init(&bio_step_cond[j],NULL); bio_jobs[j] = listCreate(); bio_pending[j] = 0; } /* Set the stack size as by default it may be small in some system */ pthread_attr_init(&attr); pthread_attr_getstacksize(&attr,&stacksize); if (!stacksize) stacksize = 1; /* The world is full of Solaris Fixes */ while (stacksize < REDIS_THREAD_STACK_SIZE) stacksize *= 2; pthread_attr_setstacksize(&attr, stacksize); /* Ready to spawn our threads. We use the single argument the thread * function accepts in order to pass the job ID the thread is * responsible of. */ for (j = 0; j < BIO_NUM_OPS; j++) { void *arg = (void*)(unsigned long) j; if (pthread_create(&thread,&attr,bioProcessBackgroundJobs,arg) != 0) { serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal: Can't initialize Background Jobs."); exit(1); } bio_threads[j] = thread; }}
|
lua脚本相关
其他
外部模块加载
1234567891011121314151617
| void moduleLoadFromQueue(void) { listIter li; listNode *ln; listRewind(server.loadmodule_queue,&li); while((ln = listNext(&li))) { struct moduleLoadQueueEntry *loadmod = ln->value; if (moduleLoad(loadmod->path,(void **)loadmod->argv,loadmod->argc) == C_ERR) { serverLog(LL_WARNING, "Can't load module from %s: server aborting", loadmod->path); exit(1); } }}
|
磁盘加载数据
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334
| void loadDataFromDisk(void) { long long start = ustime(); if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON) { if (loadAppendOnlyFile(server.aof_filename) == C_OK) serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB loaded from append only file: %.3f seconds",(float)(ustime()-start)/1000000); } else { rdbSaveInfo rsi = RDB_SAVE_INFO_INIT; if (rdbLoad(server.rdb_filename,&rsi) == C_OK) { serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB loaded from disk: %.3f seconds", (float)(ustime()-start)/1000000); /* Restore the replication ID / offset from the RDB file. */ if (server.masterhost && rsi.repl_id_is_set && rsi.repl_offset != -1 && /* Note that older implementations may save a repl_stream_db * of -1 inside the RDB file in a wrong way, see more information * in function rdbPopulateSaveInfo. */ rsi.repl_stream_db != -1) { memcpy(server.replid,rsi.repl_id,sizeof(server.replid)); server.master_repl_offset = rsi.repl_offset; /* If we are a slave, create a cached master from this * information, in order to allow partial resynchronizations * with masters. */ replicationCacheMasterUsingMyself(); selectDb(server.cached_master,rsi.repl_stream_db); } } else if (errno != ENOENT) { serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal error loading the DB: %s. Exiting.",strerror(errno)); exit(1); } }}
|
事件循环前准备
12
| aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep); aeSetAfterSleepProc(server.el,afterSleep);
|
beforeSleep
- 运行fast cycle模式,进行过期键处理
- 向所有的从节点发送ACK请求
- 解阻塞从节点
- 处理阻塞的客户端
- 将AOF刷盘
- 处理挂起的写请求
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253
| void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { UNUSED(eventLoop); /* Call the Redis Cluster before sleep function. Note that this function * may change the state of Redis Cluster (from ok to fail or vice versa), * so it's a good idea to call it before serving the unblocked clients * later in this function. */ if (server.cluster_enabled) clusterBeforeSleep(); /* Run a fast expire cycle (the called function will return * ASAP if a fast cycle is not needed). */ if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL) activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST); /* Send all the slaves an ACK request if at least one client blocked * during the previous event loop iteration. */ if (server.get_ack_from_slaves) { robj *argv[3]; argv[0] = createStringObject("REPLCONF",8); argv[1] = createStringObject("GETACK",6); argv[2] = createStringObject("*",1); /* Not used argument. */ replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves, server.slaveseldb, argv, 3); decrRefCount(argv[0]); decrRefCount(argv[1]); decrRefCount(argv[2]); server.get_ack_from_slaves = 0; } /* Unblock all the clients blocked for synchronous replication * in WAIT. */ if (listLength(server.clients_waiting_acks)) processClientsWaitingReplicas(); /* Check if there are clients unblocked by modules that implement * blocking commands. */ moduleHandleBlockedClients(); /* Try to process pending commands for clients that were just unblocked. */ if (listLength(server.unblocked_clients)) processUnblockedClients(); /* Write the AOF buffer on disk */ flushAppendOnlyFile(0); /* Handle writes with pending output buffers. */ handleClientsWithPendingWrites(); /* Before we are going to sleep, let the threads access the dataset by * releasing the GIL. Redis main thread will not touch anything at this * time. */ if (moduleCount()) moduleReleaseGIL();}
|
进入事件主循环
123456789101112131415
| void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; while (!eventLoop->stop) { // 这很重要,写AOF文件在这里进行 if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP); }}//而after函数是在aeProcessEvents函数中//表示睡眠一段时间之后执行 /* After sleep callback. */ if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP) eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop);
|
在aeProcessEvents中包含网络文件事件以及定时事件,这两类事件可以通过IO复用很好的集成在一起。下篇文章,在具体分析一下吧。
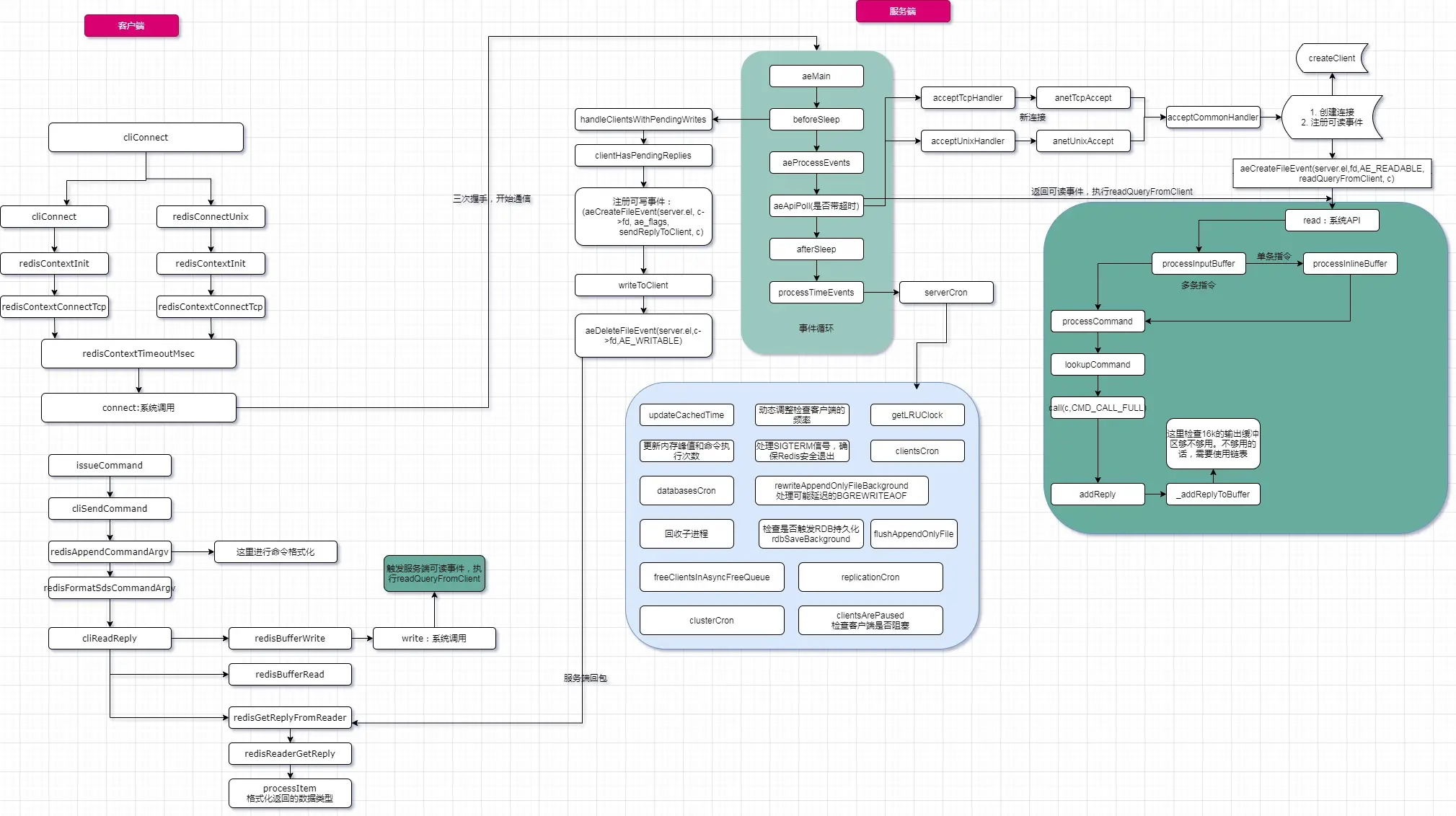
请求整体流程
一张图,天下我有。