客户端
数据结构
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061
| /* With multiplexing we need to take per-client state. * Clients are taken in a linked list. */typedef struct client { uint64_t id; /* Client incremental unique ID. */ int fd; /* Client socket. */ redisDb *db; /* Pointer to currently SELECTed DB. */ robj *name; /* As set by CLIENT SETNAME. */ sds querybuf; /* Buffer we use to accumulate client queries. */ size_t qb_pos; /* The position we have read in querybuf. */ sds pending_querybuf; /* If this client is flagged as master, this buffer represents the yet not applied portion of the replication stream that we are receiving from the master. */ size_t querybuf_peak; /* Recent (100ms or more) peak of querybuf size. */ int argc; /* Num of arguments of current command. */ robj **argv; /* Arguments of current command. */ struct redisCommand *cmd, *lastcmd; /* Last command executed. */ int reqtype; /* Request protocol type: PROTO_REQ_* */ int multibulklen; /* Number of multi bulk arguments left to read. */ long bulklen; /* Length of bulk argument in multi bulk request. */ list *reply; /* List of reply objects to send to the client. */ unsigned long long reply_bytes; /* Tot bytes of objects in reply list. */ size_t sentlen; /* Amount of bytes already sent in the current buffer or object being sent. */ time_t ctime; /* Client creation time. */ time_t lastinteraction; /* Time of the last interaction, used for timeout */ time_t obuf_soft_limit_reached_time; int flags; /* Client flags: CLIENT_* macros. */ int authenticated; /* When requirepass is non-NULL. */ int replstate; /* Replication state if this is a slave. */ int repl_put_online_on_ack; /* Install slave write handler on ACK. */ int repldbfd; /* Replication DB file descriptor. */ off_t repldboff; /* Replication DB file offset. */ off_t repldbsize; /* Replication DB file size. */ sds replpreamble; /* Replication DB preamble. */ long long read_reploff; /* Read replication offset if this is a master. */ long long reploff; /* Applied replication offset if this is a master. */ long long repl_ack_off; /* Replication ack offset, if this is a slave. */ long long repl_ack_time;/* Replication ack time, if this is a slave. */ long long psync_initial_offset; /* FULLRESYNC reply offset other slaves copying this slave output buffer should use. */ char replid[CONFIG_RUN_ID_SIZE+1]; /* Master replication ID (if master). */ int slave_listening_port; /* As configured with: SLAVECONF listening-port */ char slave_ip[NET_IP_STR_LEN]; /* Optionally given by REPLCONF ip-address */ int slave_capa; /* Slave capabilities: SLAVE_CAPA_* bitwise OR. */ multiState mstate; /* MULTI/EXEC state */ int btype; /* Type of blocking op if CLIENT_BLOCKED. */ blockingState bpop; /* blocking state */ long long woff; /* Last write global replication offset. */ list *watched_keys; /* Keys WATCHED for MULTI/EXEC CAS */ dict *pubsub_channels; /* channels a client is interested in (SUBSCRIBE) */ list *pubsub_patterns; /* patterns a client is interested in (SUBSCRIBE) */ sds peerid; /* Cached peer ID. */ listNode *client_list_node; /* list node in client list */ /* Response buffer */ int bufpos; char buf[PROTO_REPLY_CHUNK_BYTES];} client;
|
第一眼看上去,发现,我擦一个客户端数据结构是真的多啊。这让我杂记啊,没事。不用全部都记住。记几个重要的就行。

配置文件

客户端命令
12345678910111213
| "id -- Return the ID of the current connection.","getname -- Return the name of the current connection.","kill <ip:port> -- Kill connection made from <ip:port>.","kill <option> <value> [option value ...] -- Kill connections. Options are:"," addr <ip:port> -- Kill connection made from <ip:port>"," type (normal|master|replica|pubsub) -- Kill connections by type."," skipme (yes|no) -- Skip killing current connection (default: yes).","list [options ...] -- Return information about client connections. Options:"," type (normal|master|replica|pubsub) -- Return clients of specified type.","pause <timeout> -- Suspend all Redis clients for <timout> milliseconds.","reply (on|off|skip) -- Control the replies sent to the current connection.","setname <name> -- Assign the name <name> to the current connection.","unblock <clientid> [TIMEOUT|ERROR] -- Unblock the specified blocked client."
|
- client list->查看客户端的信息
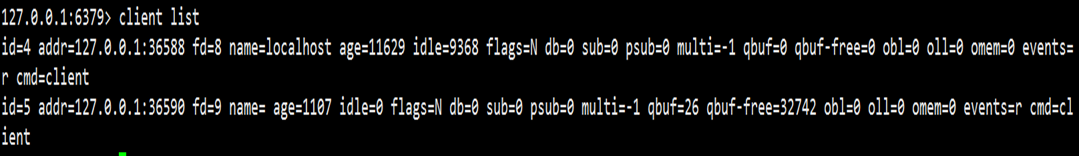
其中
- flags表示客户端类型N-表示普通客户端,M-表示master等等
1234567891011121314151617
| int getClientTypeByName(char *name) { if (!strcasecmp(name,"normal")) return CLIENT_TYPE_NORMAL; else if (!strcasecmp(name,"slave")) return CLIENT_TYPE_SLAVE; else if (!strcasecmp(name,"replica")) return CLIENT_TYPE_SLAVE; else if (!strcasecmp(name,"pubsub")) return CLIENT_TYPE_PUBSUB; else if (!strcasecmp(name,"master")) return CLIENT_TYPE_MASTER; else return -1;}char *getClientTypeName(int class) { switch(class) { case CLIENT_TYPE_NORMAL: return "normal"; case CLIENT_TYPE_SLAVE: return "slave"; case CLIENT_TYPE_PUBSUB: return "pubsub"; case CLIENT_TYPE_MASTER: return "master"; default: return NULL; }}
|
- obl代表固定缓冲区的长度
- oll代表动态缓冲区列表的长度
- omem代表使用的字节数
- events表示事件类型(r/w)
- cmd记录最后一次执行的命令
具体信息见函数
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253
| /* Concatenate a string representing the state of a client in an human * readable format, into the sds string 's'. */sds catClientInfoString(sds s, client *client) { char flags[16], events[3], *p; int emask; p = flags; if (client->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) { if (client->flags & CLIENT_MONITOR) *p++ = 'O'; else *p++ = 'S'; } if (client->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) *p++ = 'M'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB) *p++ = 'P'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) *p++ = 'x'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) *p++ = 'b'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_DIRTY_CAS) *p++ = 'd'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY) *p++ = 'c'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_UNBLOCKED) *p++ = 'u'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP) *p++ = 'A'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_UNIX_SOCKET) *p++ = 'U'; if (client->flags & CLIENT_READONLY) *p++ = 'r'; if (p == flags) *p++ = 'N'; *p++ = '\0'; emask = client->fd == -1 ? 0 : aeGetFileEvents(server.el,client->fd); p = events; if (emask & AE_READABLE) *p++ = 'r'; if (emask & AE_WRITABLE) *p++ = 'w'; *p = '\0'; return sdscatfmt(s, "id=%U addr=%s fd=%i name=%s age=%I idle=%I flags=%s db=%i sub=%i psub=%i multi=%i qbuf=%U qbuf-free=%U obl=%U oll=%U omem=%U events=%s cmd=%s", (unsigned long long) client->id, getClientPeerId(client), client->fd, client->name ? (char*)client->name->ptr : "", (long long)(server.unixtime - client->ctime), (long long)(server.unixtime - client->lastinteraction), flags, client->db->id, (int) dictSize(client->pubsub_channels), (int) listLength(client->pubsub_patterns), (client->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) ? client->mstate.count : -1, (unsigned long long) sdslen(client->querybuf), (unsigned long long) sdsavail(client->querybuf), (unsigned long long) client->bufpos, (unsigned long long) listLength(client->reply), (unsigned long long) getClientOutputBufferMemoryUsage(client), events, client->lastcmd ? client->lastcmd->name : "NULL");}
|
- info clients–>查看所有客户端
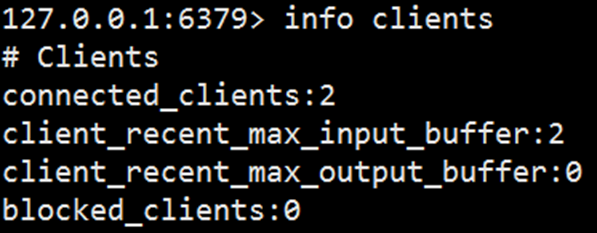
- connected_clients:代表当前Redis节点的客户端连接数,需要重点监控,一旦超过maxclients,新的客户端连接将被拒绝。
- client_longest_output_list:当前所有输出缓冲区中队列对象个数的最大值。
- client_biggest_input_buf:当前所有输入缓冲区中占用的最大容量。
- blocked_clients:正在执行阻塞命令(例如blpop、brpop、brpoplpush)的客户端个数
客户端关闭
- 调用client kill命令
- 不符合协议格式的命令
- 客户端超时
- 输入缓冲区超过阈值1G
- 输出缓冲区超出阈值(软限制和硬限制,超过硬限制客户端立即关闭,超过软限制且持续指定秒后再关闭)
格式为client-output-buffer-limit
client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0
client-output-buffer-limit replica 256mb 64mb 60
client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60
其中class表示客户端类型,超过hard limit客户端立即关闭,超过soft limit且持续soft seconds后再关闭。
class取值:
normal -> normal clients including MONITOR clients
slave -> slave clients
pubsub -> clients subscribed to at least one pubsub channel or pattern
注意点:对于client的检测是在serverCron定时函数中进行
。
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637
|
|
由于redis是单线程的,所以他不可能一直循环来检测客户端。其中客户端超时检测是在serverCron的clientsCron中进行,serverCron是一个周期函数,每100ms执行一次。server.hz表示serverCron函数的调用频率,默认为10。 clientsCron函数中为了每秒钟都能循环一次所有客户端,所以每次循环次数为iterations = numclients/server.hz。如果客户端多的话,可能会导致redis主线程的阻塞。因此,5.0引入了动态hz,见配置文件dynamic-hz,默认打开。
服务端
数据库
数据库存储在redisDb结构中,而在服务端redisServer结构中保存着redisDb对象和个数,个数可以在配置文件中进行更新(见配置文件中的dbnum)
数据结构
12345678910
| typedef struct redisDb { dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */ dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */ dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/ dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */ dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */ int id; /* Database ID */ long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */ list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */} redisDb;
|
而redisServer中都包含redisDb数据结构。表示当前使用的是哪个db。
12345678910111213141516
| struct redisServer { /* General */ pid_t pid; /* Main process pid. */ char *configfile; /* Absolute config file path, or NULL */ char *executable; /* Absolute executable file path. */ char **exec_argv; /* Executable argv vector (copy). */ int dynamic_hz; /* Change hz value depending on
|
数据库切换
而数据库的切换是使用select来执行的。当执行select命令时,实际上是将第n个db指向客户端的db对象,c->db = &server.db[id];
123456
| int selectDb(client *c, int id) { if (id < 0 || id >= server.dbnum) return C_ERR; c->db = &server.db[id]; return C_OK;}
|
键空间
由前文可知redis可以有多个数据库,而不同数据库之间是互不影响的,那如何做到的呢?键空间可以理解成C++里面的名称空间,用来隔离。数据存储在redisDb中的dict对象。因此对键的操作,基本都是基于键空间来操作的。
本质其实就是每个redisDd中的dict对象
。很好理解,因为选择了不同的db,那肯定这个对象下面的数据也不一样。
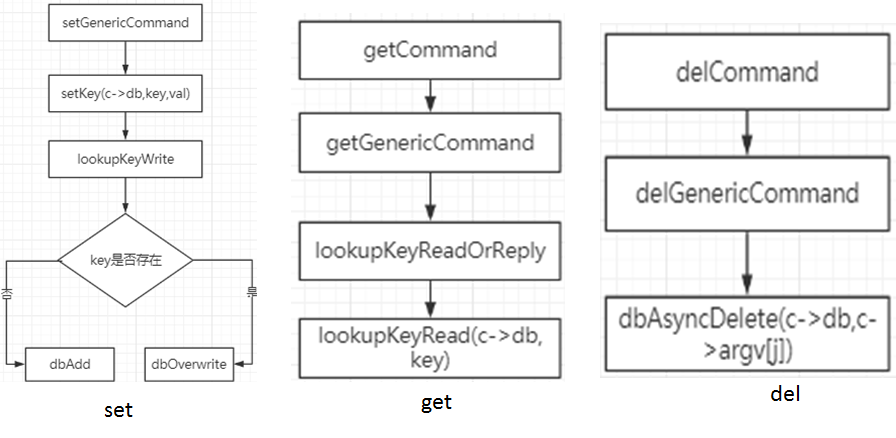
12345678910
| void setKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) { if (lookupKeyWrite(db,key) == NULL) { dbAdd(db,key,val); } else { dbOverwrite(db,key,val); } incrRefCount(val); removeExpire(db,key); signalModifiedKey(db,key);}
|
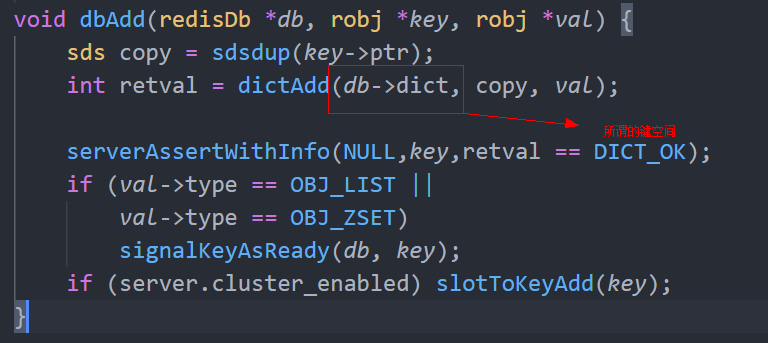
过期键
在redis中过期键保存在redisDb中expires变量里,expires是dict指针类型。
储存方式
12345
| de = dictAddOrFind(db->expires,dictGetKey(kde)); dictSetSignedIntegerVal(de,when);
|
- 设置过期时间
相对方式:expire ,单位秒; pexpire ,单位毫秒
绝对方式:expireat ,单位秒; pexpireat < timestamp >,单位毫秒。其他命令都会转成pexpireat
如expire命令: setExpire(c,c->db,key,when)—->de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr)—->dictAddOrFind(db->expires,dictGetKey(de))
- 删除过期时间
persist ,具体函数为removeExpire(c->db,c->argv[1])—->dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr)
- 查看键剩余时间
查看过期时间:
ttl ,秒单位;pttl ,毫秒
lookupKeyReadWithFlags—->getExpire—->ttl = expire-mstime();
- 键过期策略

redis中采用的是定期删除和惰性删除两种
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118119120121122123124125126127128129130131132133134135136137138139140141142143144145146147148149150151152153154155156157158159160161162163
| void activeExpireCycle(int type) { /* This function has some global state in order to continue the work * incrementally across calls. */ static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */ //timelimit_exit,超时退出 static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */ static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /*上一次执行快速定期删除的时间点 When last fast cycle ran. */ int j, iteration = 0; int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL; long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed; /* When clients are paused the dataset should be static not just from the * POV of clients not being able to write, but also from the POV of * expires and evictions of keys not being performed. */ if (clientsArePaused()) return; if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) { /* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exit * for time limit. Also don't repeat a fast cycle for the same period * as the fast cycle total duration itself. */ if (!timelimit_exit) return; if (start < last_fast_cycle + ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION*2) return; last_fast_cycle = start; } /* We usually should test CRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with * two exceptions: * * 1) Don't test more DBs than we have. * 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs * in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want * expired keys to use memory for too much time. */ if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum; /* We can use at max ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC percentage of CPU time * per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of * server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of * microseconds we can spend in this function. */ // 最多允许25%的CPU时间用于过期Key清理 // 若hz=1,则一次activeExpireCycle最多只能执行250ms // 若hz=10,则一次activeExpireCycle最多只能执行25ms timelimit = 1000000*ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC/server.hz/100; timelimit_exit = 0; if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1; //如果是ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST,时间限制为ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) timelimit = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION; /* in microseconds. */ /* Accumulate some global stats as we expire keys, to have some idea * about the number of keys that are already logically expired, but still * existing inside the database. */ long total_sampled = 0; long total_expired = 0; //timelimit_exit超时的话,我们也不会循环遍历下一个 for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) { int expired; redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum); /* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time * in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to * distribute the time evenly across DBs. */ current_db++; /* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle more than 25% * of the keys were expired. */ do { unsigned long num, slots; long long now, ttl_sum; int ttl_samples; iteration++; /* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */ if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) { db->avg_ttl = 0; break; } slots = dictSlots(db->expires); now = mstime(); /* When there are less than 1% filled slots getting random * keys is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times... * The dictionary will be resized asap. */ if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE && (num*100/slots < 1)) break; /* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys * with an expire set, checking for expired ones. */ expired = 0; ttl_sum = 0; ttl_samples = 0; // 一次取ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP个Key,判断是否过期 if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP) num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP; while (num--) { dictEntry *de; long long ttl; //随机从过期键表中抽出一个键,并获取他的ttl if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break; ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now; //判断他是否过期,如果过期就对其进行删除操作,至于是同步还是异步,那就随便你 if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++; if (ttl > 0) { /* We want the average TTL of keys yet not expired. */ ttl_sum += ttl; ttl_samples++; } total_sampled++; } total_expired += expired; /* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */ if (ttl_samples) { long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples; /* Do a simple running average with a few samples. * We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2% * and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */ if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl; db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50); } /* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to * expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the * caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. * * 每迭代16次就来计算函数已经运行的时间,如果这个时间超过了之前的限定时间timelimit, * 就将timelimit_exit这个标志置为1,说明程序超时,需要强制退出了 * */ if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */ elapsed = ustime()-start; if (elapsed > timelimit) { timelimit_exit = 1; server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++; break; } } /* We don't repeat the cycle if there are less than 25% of keys * found expired in the current DB. */ /** * ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP是我们每个循环希望查到的过期键的个数,如果我们每次循环过后,被清理的过期键的个数超过了我们期望的四分之一,我们就会继续这个循环,因为这说明当前数据库中过期键的个数比较多 * ,需要继续清理,如果没有达到我们期望的四分之一,就跳出while循环,遍历下一个数据库 * */ } while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4); } elapsed = ustime()-start; latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000); /* Update our estimate of keys existing but yet to be expired. * Running average with this sample accounting for 5%. */ double current_perc; if (total_sampled) { current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled; } else current_perc = 0; server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+ (server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);}
|
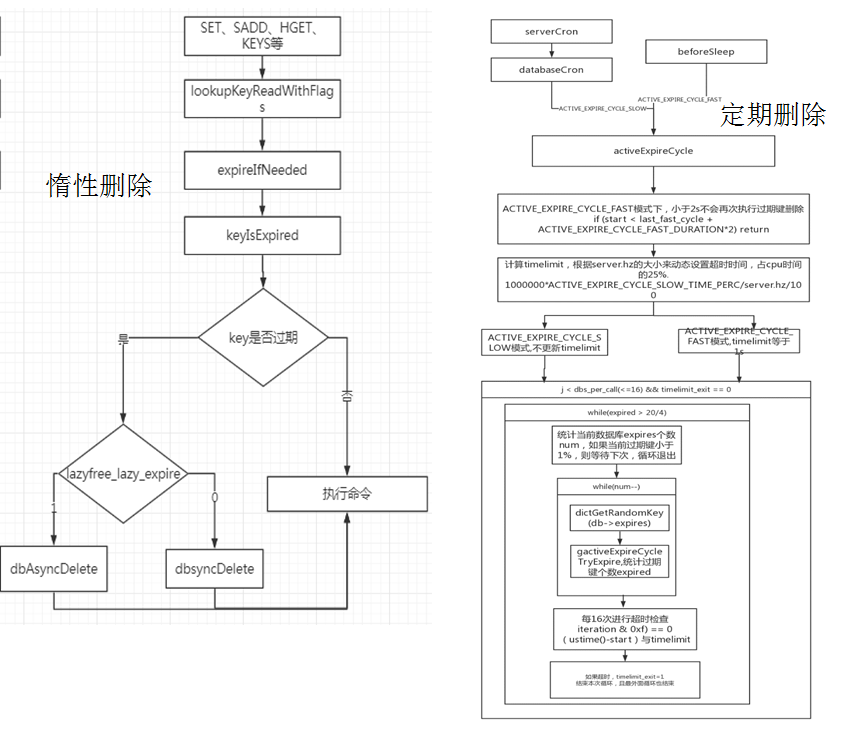
- REDIS_EXPIRELOOKUPS_TIME_PERC是单位时间内分配给activeExpireCycle函数执行的CPU比例,默认为25.
- 每次循环最多16个库。
- 每个库要求找到过期键达到5个就行(需要注意的是,因为每个库是随机选取一个key的,所以数据量不能太少,太少随机效果不好)。
- 在每个库里面,每次随机选取20个key。检查是否是过期键,过期就计数一次。每隔16次检查一下时间是否超过限制,如果超过需要退出循环。不在继续查找。
对于过期键对RDB/AOF/主从的影响,我将会融入在后面具体模块中
。
数据库通知
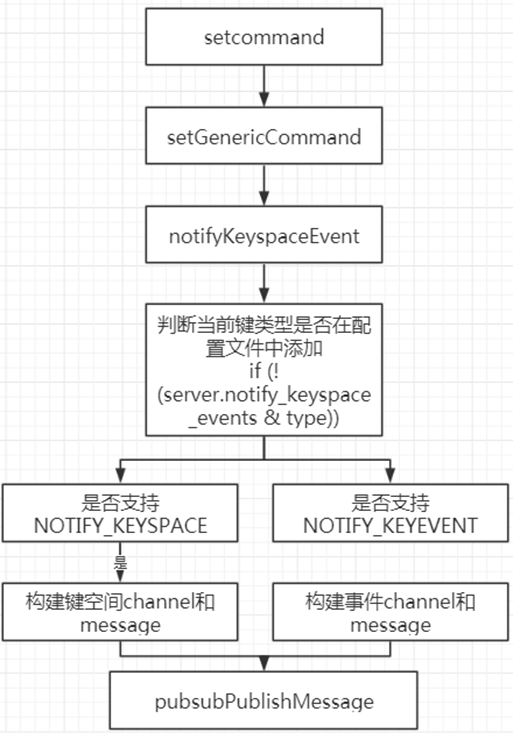
数据库通知主要是利用redis中支持发布订阅模式,让客户端通过订阅给定的频道或者模式(保存在client和server的pubsub_channels和pubsub_patterns,但保存的内容不一样)来获悉数据库中键的变化。主要分为键空间通知和事件通知两类,要开启该功能需要在配置文件中设置参数。见notify-keyspace-events
键空间通知——某个键执行了什么命令
keyspace@:
事件通知——某个事件被哪些命令执行
keyevent@:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142
| void notifyKeyspaceEvent(int type, char *event, robj *key, int dbid) { sds chan; robj *chanobj, *eventobj; int len = -1; char buf[24]; /* If any modules are interested in events, notify the module system now. * This bypasses the notifications configuration, but the module engine * will only call event subscribers if the event type matches the types * they are interested in. */ moduleNotifyKeyspaceEvent(type, event, key, dbid); /* If notifications for this class of events are off, return ASAP. */ if (!(server.notify_keyspace_events & type)) return; eventobj = createStringObject(event,strlen(event)); /* __keyspace@<db>__:<key> <event> notifications. */ if (server.notify_keyspace_events & NOTIFY_KEYSPACE) { chan = sdsnewlen("__keyspace@",11); len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),dbid); chan = sdscatlen(chan, buf, len); chan = sdscatlen(chan, "__:", 3); chan = sdscatsds(chan, key->ptr); chanobj = createObject(OBJ_STRING, chan); pubsubPublishMessage(chanobj, eventobj); decrRefCount(chanobj); } /* __keyevent@<db>__:<event> <key> notifications. */ if (server.notify_keyspace_events & NOTIFY_KEYEVENT) { chan = sdsnewlen("__keyevent@",11); if (len == -1) len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),dbid); chan = sdscatlen(chan, buf, len); chan = sdscatlen(chan, "__:", 3); chan = sdscatsds(chan, eventobj->ptr); chanobj = createObject(OBJ_STRING, chan); pubsubPublishMessage(chanobj, key); decrRefCount(chanobj); } decrRefCount(eventobj);}
|
参数说明
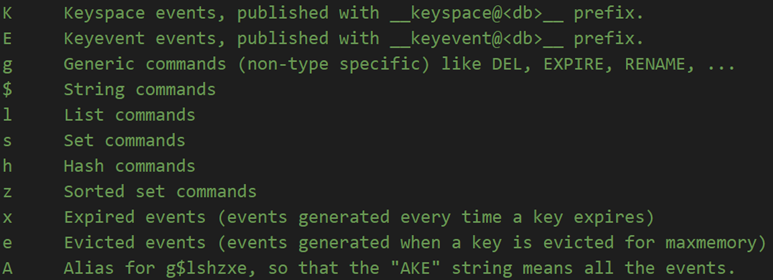
当然要启用的话,必须要在配置文件中进行设置:格式如下notify-keyspace-events Elg,若要启用配置K和E必须要至少开启一个。











