vuex是什么呢
vuex简单来说:对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中的管理(读/写) ; 我的理解就是vuex是一个管理者,管理的方式是集中式管理,管理的对象即是vue.js应用程序中的众多组件的共享部分。它的核心就是 store(仓库),仓库是用来干什么的?你就当它用来储存东西的。
为什么会出现vuex呢
由于Vue是单向数据流,子组件内部不能直接修改从父级传递过来的数据,子组件与子组件之间无法相互传递数据。如果我们想让两个子组件之间进行通信的话,可以借助子组件 A 向父组件传值,父组件接收子组件 A 的数据后再传给 B 组件这样的方式进行通信。
但是这样会有一个问题,就是如果子组件 A 的父组件上面还有一层爷爷组件,或者还有更多祖父类型的层级,那么是不是会很麻烦。
因此,我们会想到能不能我们将一个共有的数据存在一个特定的地方,用的时候自己去拿,这样就不需要一层层传值,于是乎Vuex 就应运而生了。
什么场景我们需要应用vuex呢
1.小应用不建议使用Vuex,因为小项目使用 Vuex 可能会比较繁琐冗余;
2.中大型单页应用,因为要考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择;
vuex的运行流程
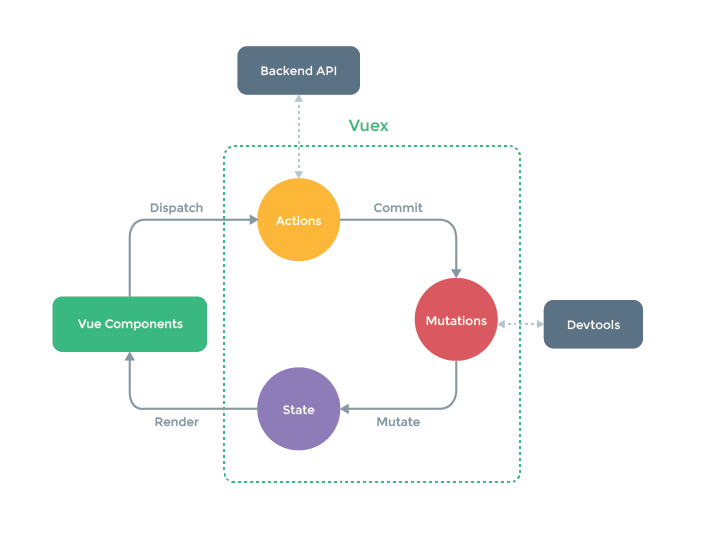
vuex的特点
针对非异步操作
components中可以不用store.dispatch,直接触发action,再执行commit触发mutation去改变state
针对异步操作
components上store.dispatch一个action,得到数据后再执行commit触发mutation去改变state
vuex的各模块详解及使用
1.state的使用
- 单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。
- mapState 当一个组件需要获取多个状态时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。
- 注意:store中的state必须放在vue的computed里去使用,不要放在data里。
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: mapState({
count: state => state.count,
countAlia: 'count',
countPlusLocalState(state){
return state.couunt + this.localCount
}
})
// ...mapState({count})扩展运算符
}
getters的使用
- 从store中的state中派生出一些状态
*mapGetters辅助函数仅仅是将store中的getters映射到局部计算属性 - getters可以认为是store的计算属性
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{id: 1, text: '...', done: true},
{id: 2, text: '...', done: false}
]
},
getters: {
// 对state进行额外的扩展,过滤并返回已完成的state
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
}
}
})
// 在computed中使用
computed: {
doneTodos () {
// 所有东西都被挂载在了this.$store上
return this.$store.getters.doneTodos
}
// 或者如下取得所有getters
...mapGetters(['doneTodos'])
}
3.mutations
- 更改vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法是提交mutation(不能直接调用句柄,必须通过触发)
- mutations就是vue中的methods
- 每个mutation都有一个字符串的事件类型(type)和一个回调函数(handler)
- 使用常量代替mutation事件类型
- mutation必须是同步函数,更改state必须是同步的去更改。若异步的更改必须先交给dispatch包裹action发起异步请求,响应后再交给mutation修改state。
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
import { SOME_MUTATION } from './mutation-types'
export default {
methods: {
test() {
// commit之后就会去修改state
this.$store.commit(SOME_MUTATION)
},
...mapMutations([
'SOME_MUTATION'
// 映射this.increment() 为this.$store.commit('SOME_MUTATION')
])
}
}
4.actions
- action提交的是mutation
- action可以包含任意异步操作,之后再提交给mutation改变state
- 过mapActions函数可以生成methods中函数
- 触发actions用store.dispatch调用,提交mutation用commit
- view->store.dispatch(‘increment’)->action->commit(‘SOME_MUTATION’)
// 定义actions
actions: {
// 连个异步操作,先后执行mutation,异步变同步
async actionA({commit}) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB({dispatch, commit}) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待actionA完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData()) // commit后面可以带数据,可以交给mutation去修改state
}
}
// 调用actions
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
test() {
store.dispatch('actionB')
},
...mapActions([
'actionB'
// 映射this.increment()
// this.$store.dispatch('actionB')
])
}
}
5.modules
Vuex运行我们将store分割到模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters、甚至是嵌套子模块—从上至下进行类似的分割。