CC框架
CC是一个组件化框架,与ARouter路由框架不同的是,它是一个总线式的组件化框架,不需要下沉接口,应用是面向通信协议编程,组件总线只负责通信,即转发调用请求和返回执行结果。
框架图
CC中最基础的概念是IComponent(qibilly.com/CC-website/…),任何组件需要暴露给外部调用的能力都需要实现这个接口。因为CC支持跨app进行组件化调用,所以整体的结构图可以如下所示:
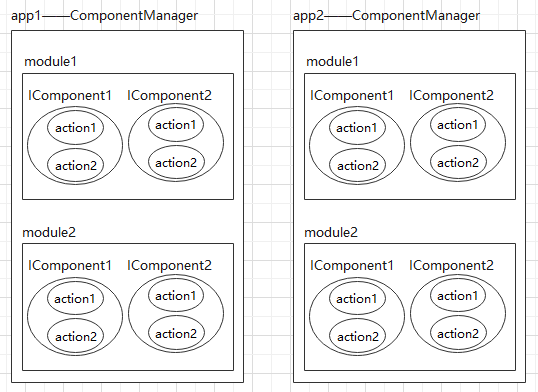
每个app都有多个module,每个module都有多个IComponent,每个IComponent可以处理多个action,所有的IComponent都会在编译时自动注册到应用的ComponentManager单例中进行统一管理,所有的组件调用都是通过这个管理类进行。
组件调用流程图
-
CC是组件调用的基础,是组件调用的发起者,调用组件需要有组件名称componentName是必须的,其他参数都是可配置:
/** * 组件名称 */ private String componentName; /** * 组件中某个功能的名称,用以区别同一个组件中不同功能的调用 */ private String actionName; private final Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>(); /** * 回调对象 */ private IComponentCallback callback; /** * 是否异步执行 */ private boolean async; private final List<ICCInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); private boolean callbackOnMainThread; /** * 调用超时时间,默认值(同步调用:2000, 异步调用:0) */ private long timeout = -1; long timeoutAt; -
ComponentManager是组件的注册管理器,也是组件调用的处理者,所有的组件调用都在ComponentManager中统一处理。具体的处理逻辑由ChainProcessor和Chain来进行处理。主要的过程就是拦截器的处理,先执行自定义的拦截器,再执行CC内置的拦截器。
-
如果在本app内能找到对应的componentName则调用LocalCCInterceptor处理组件调用,否则就调用RemoteCCInterceptor处理跨进程组件调用。
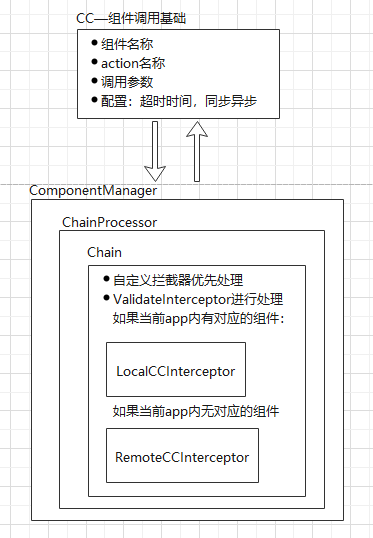
LocalCCInterceptor:
当前app内的组件拦截器,主要处理线程切换的工作,使得组件调用在对应的线程中执行。
- 如果组件不存在,则返回错误
- 判断是否需要在主线程执行,以及是否需要切换线程
- 不需要切换线程,则直接执行
- 具体的调用在LocalCCRunnable中执行(需要传入一个是否需要切换线程的标志,用于决定是否需要等待结果,Object.wait())
public CCResult intercept(Chain chain) {
CC cc = chain.getCC();
IComponent component = ComponentManager.getComponentByName(cc.getComponentName());
if (component == null) {
CC.verboseLog(cc.getCallId(), "component not found in this app. maybe 2 reasons:"
+ "\n1. CC.enableRemoteCC changed to false"
+ "\n2. Component named \"%s\" is a IDynamicComponent but now is unregistered"
);
return CCResult.error(CCResult.CODE_ERROR_NO_COMPONENT_FOUND);
}
try {
String callId = cc.getCallId();
if (CC.VERBOSE_LOG) {
CC.verboseLog(callId, "start component:%s, cc: %s", component.getClass().getName(), cc.toString());
}
boolean shouldSwitchThread = false;
LocalCCRunnable runnable = new LocalCCRunnable(cc, component);
if (component instanceof IMainThread) {
//当前是否在主线程
boolean curIsMainThread = Looper.myLooper() == Looper.getMainLooper();
//该action是否应该在主线程运行
Boolean runOnMainThread = ((IMainThread) component).shouldActionRunOnMainThread(cc.getActionName(), cc);
//是否需要切换线程执行 component.onCall(cc) 方法
shouldSwitchThread = runOnMainThread != null && runOnMainThread ^ curIsMainThread;
if (shouldSwitchThread) {
runnable.setShouldSwitchThread(true);
if (runOnMainThread) {
//需要在主线程运行,但是当前线程不是主线程
ComponentManager.mainThread(runnable);
} else {
//需要在子线程运行,但当前线程不是子线程
ComponentManager.threadPool(runnable);
}
}
}
if (!shouldSwitchThread) {
//不需要切换线程,直接运行
runnable.run();
}
//兼容以下情况:
// 1. 不需要切换线程,但需要等待异步实现调用CC.sendCCResult(...)
// 2. 需要切换线程,等待切换后的线程调用组件后调用CC.sendCCResult(...)
if (!cc.isFinished()) {
chain.proceed();
}
} catch(Exception e) {
return CCResult.defaultExceptionResult(e);
}
return cc.getResult();
}
调用的同步和异步
同步或异步调用由CC的配置项async来决定,在ComponentManager进行组件调用时来判断是直接执行,还是放入线程池中执行:
/**
* 组件调用统一入口
* @param cc 组件调用指令
* @return 组件调用结果(同步调用的返回值)
*/
static CCResult call(CC cc) {
String callId = cc.getCallId();
Chain chain = new Chain(cc);
if (!cc.isWithoutGlobalInterceptor()) {
chain.addInterceptors(INTERCEPTORS);
}
chain.addInterceptors(cc.getInterceptors());
// 有效性校验放在自定义拦截器之后执行,优先执行自定义拦截器,让其可以拦截到所有组件调用
// 执行实际调用的拦截器在校验有效性结束后再添加
chain.addInterceptor(ValidateInterceptor.getInstance());
ChainProcessor processor = new ChainProcessor(chain);
//异步调用,放到线程池中运行
if (cc.isAsync()) {
if (CC.VERBOSE_LOG) {
CC.verboseLog(callId, "put into thread pool");
}
CC_THREAD_POOL.submit(processor);
//异步调用时此方法返回null,CCResult通过callback回调
return null;
} else {
//同步调用,直接执行
CCResult ccResult;
try {
ccResult = processor.call();
} catch (Exception e) {
ccResult = CCResult.defaultExceptionResult(e);
}
if (CC.VERBOSE_LOG) {
CC.verboseLog(callId, "cc finished.CCResult:" + ccResult);
}
//同步调用的返回结果,永不为null,默认为CCResult.defaultNullResult()
return ccResult;
}
}
组件执行的同步或异步
如果组件的业务是同步执行的,那么每次onCall()执行完就可以得到结果 ,本身onCall()如果返回false说明是同步调用,返回true说明是异步调用。
public interface IComponent {
/**
* 定义组件名称
*/
String getName();
/**
* 调用此组件时执行的方法(此方法只在LocalCCInterceptor中被调用)
* 注:执行完成后必须调用CC.sendCCResult(callId, CCResult.success(result));
* @param cc 调用信息
* @return 是否延迟回调结果 {@link CC#sendCCResult(String, CCResult)}
* false:否(同步实现,在return之前回调结果)
* true:是(异步实现,本次CC调用将等待回调结果)
*/
boolean onCall(CC cc);
}
异步执行的情况需要分两步考虑:
-
调用方等待结果返回——这个逻辑在WaitResultInterceptor中处理,因为它是最后一个拦截器,所以可以在被调用时获知本次组件调用是否完成,如果未完成,则进行等待(由Object.wait()实现)。
class Wait4ResultInterceptor implements ICCInterceptor { //-------------------------单例模式 start -------------- /** 单例模式Holder */ private static class Wait4ResultInterceptorHolder { private static final Wait4ResultInterceptor INSTANCE = new Wait4ResultInterceptor(); } private Wait4ResultInterceptor (){} /** 获取Wait4ResultInterceptor的单例对象 */ static Wait4ResultInterceptor getInstance() { return Wait4ResultInterceptorHolder.INSTANCE; } //-------------------------单例模式 end -------------- @Override public CCResult intercept(Chain chain) { CC cc = chain.getCC(); cc.wait4Result(); return cc.getResult(); } }其中CC.wait4Result()的逻辑:——只有在当前的调用未完成时才会等待
void wait4Result() { //等待调用CC.sendCCResult(callId, result) synchronized (wait4resultLock) { if (!isFinished()) { try { verboseLog(callId, "start waiting for CC.sendCCResult(...)"); waiting = true; wait4resultLock.wait(); verboseLog(callId, "end waiting for CC.sendCCResult(...)"); } catch (InterruptedException ignored) { } } } } -
被调用方返回结果:
当业务完成时,必须调用CC提供的静态方法sendCCResult(),它会调用CC.setResult4Waiting()设置结果并唤醒所有等待结果的线程。
/** * 在任意位置回调结果 * 组件的onCall方法被调用后,<b>必须确保所有分支均会调用</b>到此方法将组件调用结果回调给调用方 * @param callId 回调对象的调用id * @param ccResult 回调的结果 */ public static void sendCCResult(String callId, CCResult ccResult) { if (VERBOSE_LOG) { verboseLog(callId, "CCResult received by CC.sendCCResult(...).CCResult:" + ccResult); } CC cc = CCMonitor.getById(callId); if (cc != null) { if (cc.markFinished()) { if (ccResult == null) { ccResult = CCResult.defaultNullResult(); logError("CC.sendCCResult called, But ccResult is null, set it to CCResult.defaultNullResult(). " + "ComponentName=" + cc.getComponentName()); } cc.setResult4Waiting(ccResult); } else { logError("CC.sendCCResult called, But ccResult is null. " + "ComponentName=" + cc.getComponentName()); } } else { log("CCResult received, but cannot found callId:" + callId); } }(但是感觉这个依赖业务方保证调用逻辑正确会有比较高的风险,毕竟组件化之后,会依赖其他组件提供的能力,如果处理不当,会造成线程一直等待,某些调用始终无法结束。并且,有些业务设置超时时间也不合适。)