- 数组是有序的,元素可以重复。
- 集合是无序的,元素不能重复。
- 字典是无序的,元素是键--值。
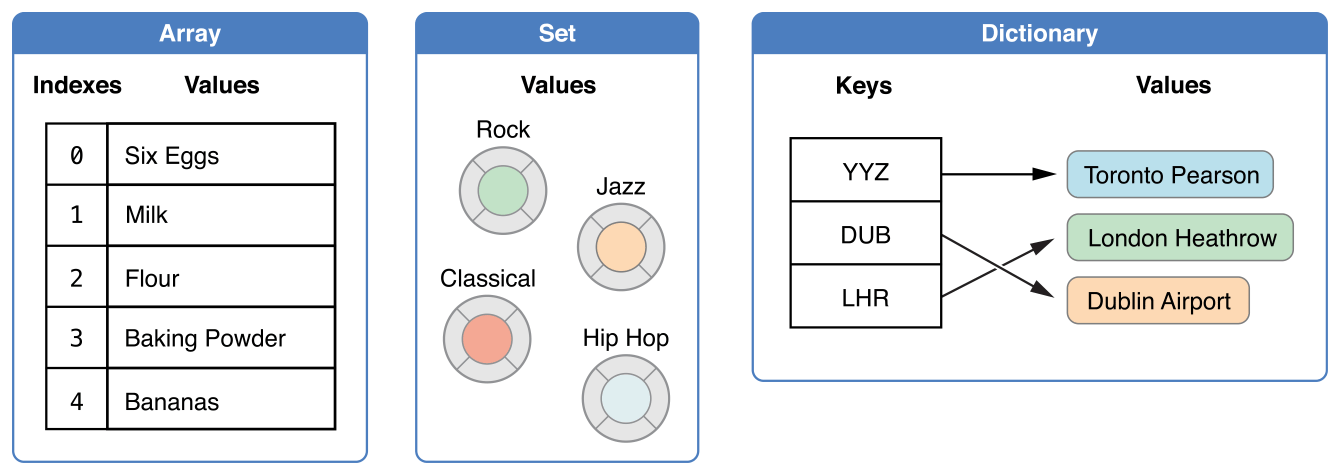
它们都是泛型,且类型严格统一。
Mutability of Collections
就是说var可以改变,let不可以改变。。。
Arrays
Array Type Shorthand Syntax
声明数组的两种方式:
Array[Element][Element],这一种用的比较多。
Creating an Empty Array
声明空数组的方法:var someInts = [Int]()
当已经知道类型了,就不用再声明类型:
someInts.append(3) // 现在是非空数组
someInts = [] // 现在是空数组,但类型仍然是Int
Creating an Array with a Default Value
申请固定长度有初始值的数组
var threeDouble = Array(repeating: 0.0, count: 3)
// threeDouble is of type [Double], and equals [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
Creating an Array by Adding Two Arrays Together
你有把相同类型的数组拼接起来
var anotherThreeDoubles = Array(repeating: 2.5, count: 3)
var sixDoubles = threeDoubles + anotherThreeDoubles
// [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 2.5, 2.5, 2.5]
Creating an Array with an Array Literal
就是正常的数组赋值方式
var shoppingList: [String] = ["Eggs", "Milk"]
var shoppingList = ["Eggs", "Milk"] // 可以省略掉类型声明,因为根据元素的字面值,可以推断出是字符串
Accessing and Modifying an Array
-
获取数组长度用
count -
是否是空数组用
isEmpty -
数组添加元素用
append(_:) -
拼接数组用
+= -
与字符串不同,数组中的元素可以用数字下标索引,
array[0]获取数组array的第一个元素。 -
也可以用数字下标修改元素。
-
可以用小范围替换大范围。
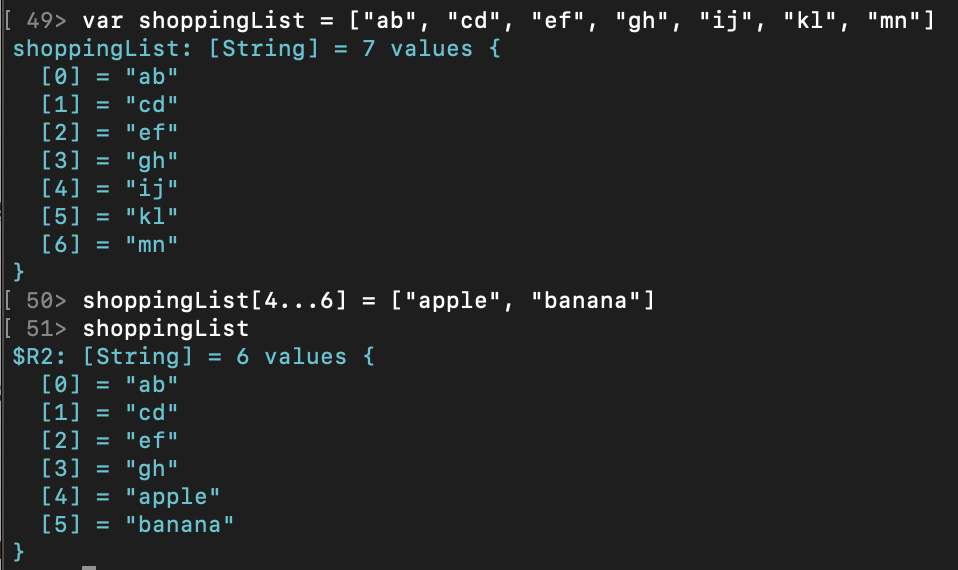
-
使用
insert(_:at:)插入元素。shoppingList.insert("Maple Syrup", at: 0) // 现在"Maple Syrup"是第一个元素了。 -
使用
remove(at:)可以移除元素,并且返回该元素。let mapleSyrup = shoppingList.remove(at: 0) // 现在"Maple Syrup"已经从shoppingList中移除了,并且mapleSyrup = "Maple Syrup" -
使用
removeLast()去移除数组的最后一个元素,并且返回该元素。
Iterating Over an Array
for item in shoppingList {
print(item)
}
如果你想在遍历的同时还要知道该元素的数字下标,可以使用enumerated()
for (index, value) in shoppingList.enumerated() {
print("Item \(index + 1): \(value)")
}
Sets
无序且元素互不相同
Hash Values for Set Types
集合可以散列的意思?看不太懂。
Set Type Syntax
只有一种定义方式Set<Element>
Creating and Initializing an Empty Set
var letters = Set<Character>()
// 如果已知类型
letters.insert("a")
letters = [] // Character类型的空集合
Creating a Set with an Array Literal
使用数组字面值的两种方式,Set是必须要明确说明的。
var favoriteGenres: Set<String> = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"]
var favoriteGenres: Set = ["Rock", "Classical", "Hip hop"]
Accessing and Modifying a Set
count计数isEmpty判空insert(_:)插入remove(_:)移除,返回移除的元素,若不存在,返回nilremoveAll()移除全部contains(_:)判断是否存在某元素
Iterating Over a Set
/* 不排序遍历 */
for genre in favoriteGenres {
print("\(genre)")
}
/* 排序遍历,从小到大 */
for genre in favoriteGenres.sorted() {
print("\(genre)")
}
Performing Set Operations(and this)
实现下面功能:
- 合并集合。
- 两个集合中哪些元素共有的。
- 两个集合中是否包含某些元素等。
Fundamental Set Operations
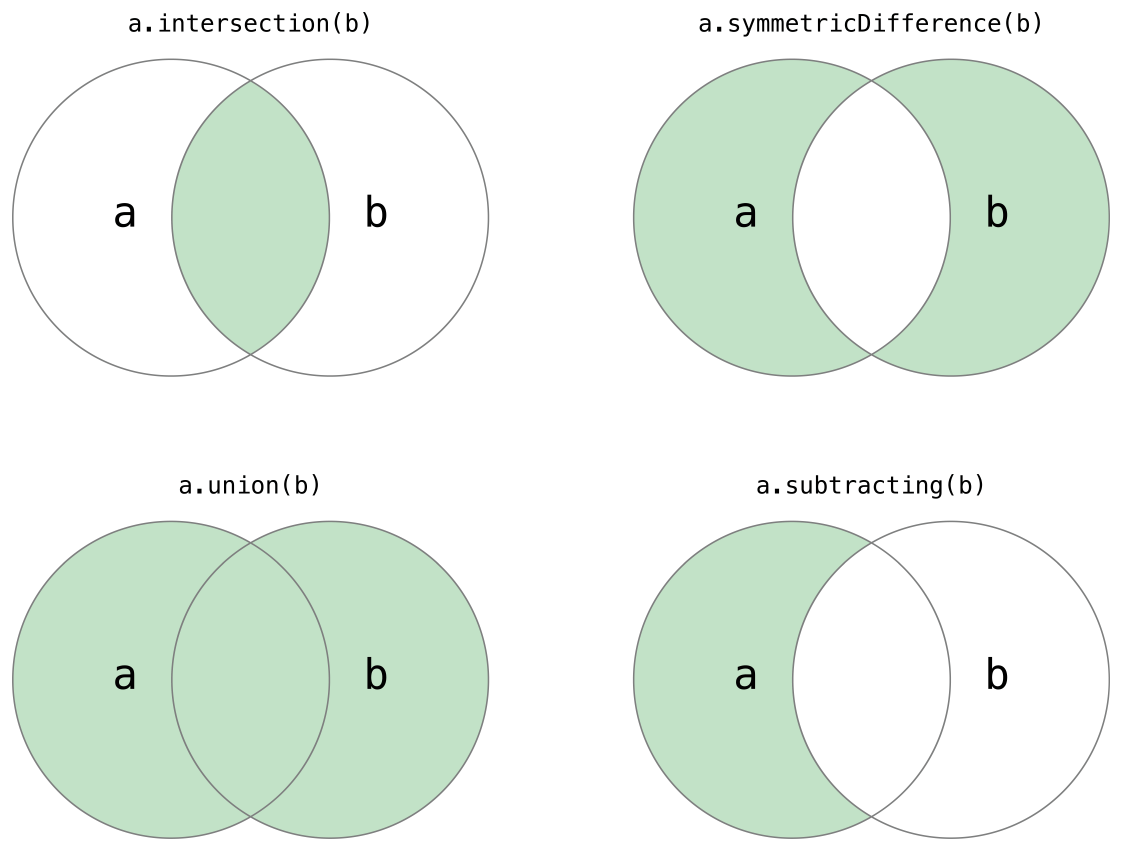
Set Membership and Equality
==判断是否相等isSubset(of:)判断是否是某集合的子集isSuperset(of:)判断是否是某集合的超集isStrictSubset(of:)判断是否是某集合的真子集isStrictSuperset(of:)判断是否是某集合的真超集
let houseAnimals: Set = ["🐶", "🐱"]
let farmAnimals: Set = ["🐮", "🐔", "🐑", "🐶", "🐱"]
let cityAnimals: Set = ["🐦", "🐭"]
houseAnimals.isSubset(of: farmAnimals) // true
farmAnimals.isSuperset(of: houseAnimals) // true
farmAnimals.isDisjoint(with: cityAnimals) // true
Dictionaries
无序,键值对的方式。
Dictionary Type Shorthand Syntax
定义字典的两种方式
Dictionary<Key, Value>
[Key: Value] // 这种更常用
Creating an Empty Dictionary
var namesOfIntegers = [Int: String]()
namesOfIntegers[16] = "sixteen" // namesOfIntegers now contains 1 key-value pair
namesOfIntegers = [:] // nameOfIntegers is once again an empty dictionary of type [Int: String]
Creating a Dictionary with a Dictionary Literal
var airports: [String: String] = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
var airports = ["YYZ": "Toronto Pearson", "DUB": "Dublin"]
Accessing and Modifying a Dictionary
count计数isEmpty判空- 新加键值对
airports["LHR"] = "London" - 更改键值对
airports["LHR"] = "London Heathrow" updateValue(_:forKey:)若存在则更新,且返回旧值。若不存在则新加,返回nilairports["APL"] = nil,赋值nil代表移除APL。removeValue(forKey:),存在则删除并返回值,不存在则返回nil
Iterating Over a Dictionary
for (airportCode, airportName) in airports {
print("\(airportCode): \(airportName)")
}
// LHR: London Heathrow
// YYZ: Toronto Pearson
/* 只要keys */
for airportCode in airports.keys {
print("Airport code: \(airportCode)")
}
// Airport code: LHR
// Airport code: YYZ
/* 只要values */
for airportName in airports.values {
print("Airport name: \(airportName)")
}
// Airport name: London Heathrow
// Airport name: Toronto
/* 将keys转换成数组 */
let airportCodes = [String](airports.keys)
// airportCodes is ["LHR", "YYZ"]
/* 将values转换成数组 */
let airportNames = [String](airports.values)
// airportNames is ["London Heathrow", "Toronto Pearson"]
可以使用sorted()在keys和values上排序。