前言
缓存穿透概念
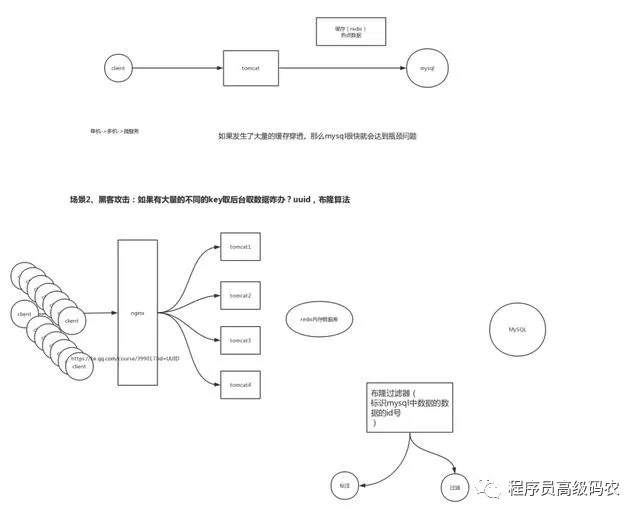
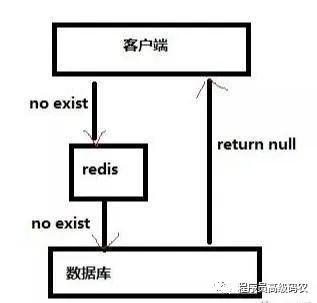
当查询一个一定不存在的数据,由于缓存不命中,去查询数据库也无法查询出结果,因此不会写入到缓存中,这会导致每个查询都去请求数据库,造成缓存穿透。
解决方案:
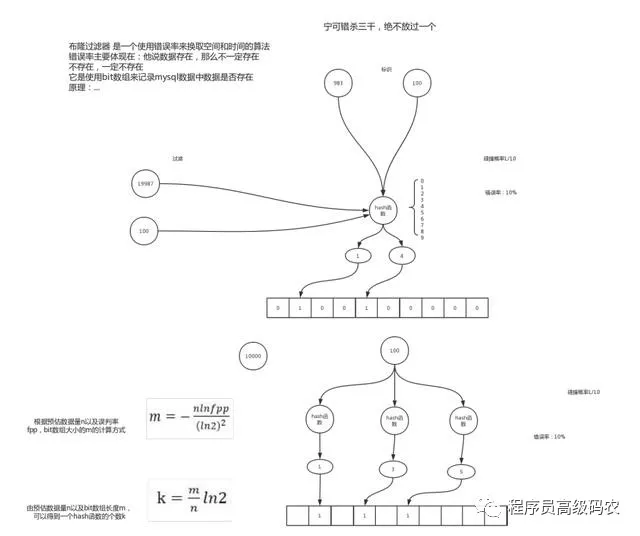
布隆过滤对所有的可能查询的参数以hash形式存储,在控制器层先进行校验,不符合则丢弃,从而避免了对底层存储系统的查询压力。bloomfilter就类似于一个hash set,用于快速判某个元素是否存在于集合中,其典型的应用场景就是快速判断一个key是否存在于某容器,不存在就直接返回。举例:将真实正确Id在添加完成之后便加入到过滤器当中,每次再进行查询时,先确认要查询的Id是否在过滤器中,如果不在,则说明Id为非法Id。
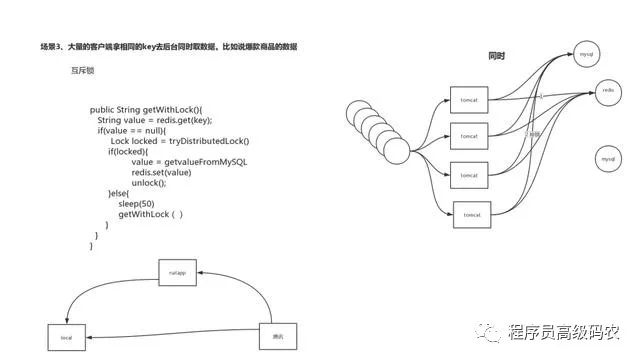
缓存空对象当从数据库查询不到值,就把参数和控制缓存起来,设置一个简短的过期时间(因为缓存是需要内存的,如果有过多空值key,占用内存多),在该时间段如果有携带此参数再次请求,就可以直接返回。可能导致该段时间缓存层和数据库数据不一致,对于需要保持一致性的业务有影响。
小编觉得学习的话,就得视频+代码+课件配合着学习,这样才能够理解的最够透彻,掌握到知识的精髓,这不,已经都给大家准备好了,大家可以好好学习一波!!!!
BloomFilter_Test.java (手写布隆过滤器代码)
import com.google.common.hash.Funnels;import com.google.common.hash.Hashing;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;import redis.clients.jedis.Pipeline;import redis.clients.jedis.Response;import java.nio.charset.Charset;public class BloomFilter_Test { private JedisPool jedisPool = null; private Jedis jedis = null; //要存储的数据量·· private static long n = 10000; //所能容忍错误率 private static double fpp = 0.01F; //bit数组长度 private static long numBits = optimalNumOfBits(n, fpp); //hash函数个数 private int numHashFunctions = optimalNumOfHashFunctions(n, numBits); public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(numBits);// long[] indexs = new BloomFilter_Test().getIndexs("hello"); BloomFilter_Test filterTest = new BloomFilter_Test(); filterTest.init(); int ex_count = 0; int ne_count = 0; /** * 存在:不一定存在 * 不存在:一定不存在 */ for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {// filterTest.put("bf",100 + i + ""); boolean exist = filterTest.isExist("bf", 100 + i + ""); if(exist){ ex_count++; }else{ ne_count++; } } //ex_count:6729 ne_count 3271 System.out.println("ex_count:" + ex_count + "\t" + "ne_count " + ne_count); } public void init(){ //测试连接redis jedisPool = new JedisPool("192.168.150.111", 6379); jedis = jedisPool.getResource(); } private long getCount(){ Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined(); Response<Long> bf = pipeline.bitcount("bf"); pipeline.sync(); Long count = bf.get(); pipeline.close(); return count; } /** * 判断keys是否存在于集合where中 */ public boolean isExist(String where, String key) { long[] indexs = getIndexs(key); boolean result; //这里使用了Redis管道来降低过滤器运行当中访问Redis次数 降低Redis并发量 Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined(); try { for (long index : indexs) { pipeline.getbit(where, index); } result = !pipeline.syncAndReturnAll().contains(false); } finally { pipeline.close(); }// if (!result) {// put(where, key);// } return result; } /** * 将key存入redis bitmap */ private void put(String where, String key) { long[] indexs = getIndexs(key); //这里使用了Redis管道来降低过滤器运行当中访问Redis次数 降低Redis并发量 Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined(); try { for (long index : indexs) { pipeline.setbit(where, index, true); } pipeline.sync(); /** * 把数据存储到mysql中 */ } finally { pipeline.close(); } } /** * 根据key获取bitmap下标方法来自guava */ public long[] getIndexs(String key) { long hash1 = hash(key); long hash2 = hash1 >>> 16; long[] result = new long[numHashFunctions]; for (int i = 0; i < numHashFunctions; i++) { long combinedHash = hash1 + i * hash2; if (combinedHash < 0) { combinedHash = ~combinedHash; } result[i] = combinedHash % numBits; } return result; } /** * 获取一个hash值 方法来自guava */ private long hash(String key) { Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); return Hashing.murmur3_128().hashObject(key, Funnels.stringFunnel(charset)).asLong(); } private static int optimalNumOfHashFunctions(long n, long m) { return Math.max(1, (int) Math.round((double) m / n * Math.log(2))); } private static long optimalNumOfBits(long n, double p) { if (p == 0) { p = Double.MIN_VALUE; } return (long) (-n * Math.log(p) / (Math.log(2) * Math.log(2))); }}图解布隆过滤器实现
Redis缓存穿透终极解决方案,手写布隆过滤器,学习视频+代码+课件

关注公众号:Java架构师联盟,每日更新技术好文