简介
MyBatis提供了一级缓存的方案来优化数据库会话之间重复查询的问题,每个SqlSession都有自己的缓存,不同的会话之间的缓存互不影响。在MyBatis框架中一级缓存是通过HashMap实现的,默认作用范围是SqlSession。
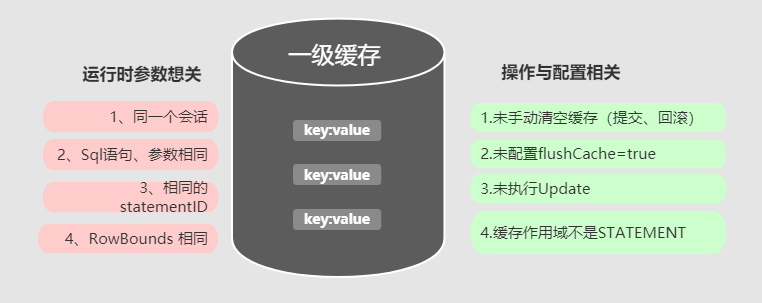
缓存命中场景
当执行条件完全相同的sql 时,就会命中MyBatis的一级缓存。那么条件完全相同是指那些条件呢?
- 同一个会话
- 参数相同,
sql相同 Statement相同- 未手动清空缓存(提交,回滚,
update操作), - 缓存的作用域不是
STATEMENT
一级缓存实验
-
当查询条件完全一样时,命中缓存
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = mapper.selectById(10); User user1 = mapper.selectById(10); System.out.println(user == user1); // true -
当会话不同时,无法命中缓存
// 会话不相同 UserMapper userMapper = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user2 = userMapper.selectById(10); System.out.println(user == user2); // false -
当参数不同时, 无法命中缓存
User user3 = mapper.selectById(11); System.out.println(user == user3); // false -
statementId不同时,无法命中缓存// statementId不同 // com.kxj.mybatis.UserMapper.selectById // com.kxj.mybatis.UserMapper.selectById3 User user4 = mapper.selectById3(11); System.out.println(user == user4); // false -
RowBounds不同时,无法命中缓存
// RowBounds不同 默认 RowBounds.DEFAULT RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0, 10); List<Object> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.kxj.mybatis.UserMapper.selectById", 10, rowBounds); System.out.println(list.get(0) == user); // false List<Object> list1 = sqlSession.selectList("com.kxj.mybatis.UserMapper.selectById", 10, RowBounds.DEFAULT); System.out.println(list1.get(0) == user); // true -
手动清空缓存(提交或者回滚),无法命中缓存
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = userMapper.selectById(10); // 提交 sqlSession.commit(); // 或者 sqlSession.rollback(); User user1 = userMapper.selectById(10); System.out.println(user == user1); // false -
配置
flushCache = true,无法命中缓存/ * * @Select({"select * from users where id=#{1}"}) * @Options(flushCache = Options.FlushCachePolicy.TRUE) * User selectById3(Integer id); * / User user2 = userMapper.selectById3(10); User user3 = userMapper.selectById3(10); System.out.println(user2 == user3); // false -
查询中执行
update(实质上会清空缓存),无法命中缓存// 执行update操作 User user4 = userMapper.selectById(10); userMapper.setName(10, "kxj"); User user5 = userMapper.selectById(10); System.out.println(user4 == user5); // false -
缓存的作用域是
STATEMENT,无法命中缓存// 缓存的作用域是STATEMENT // <setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/> User user6 = userMapper.selectById(10); User user7 = userMapper.selectById(10); System.out.println(user6 == user7); // false
总结命中场景
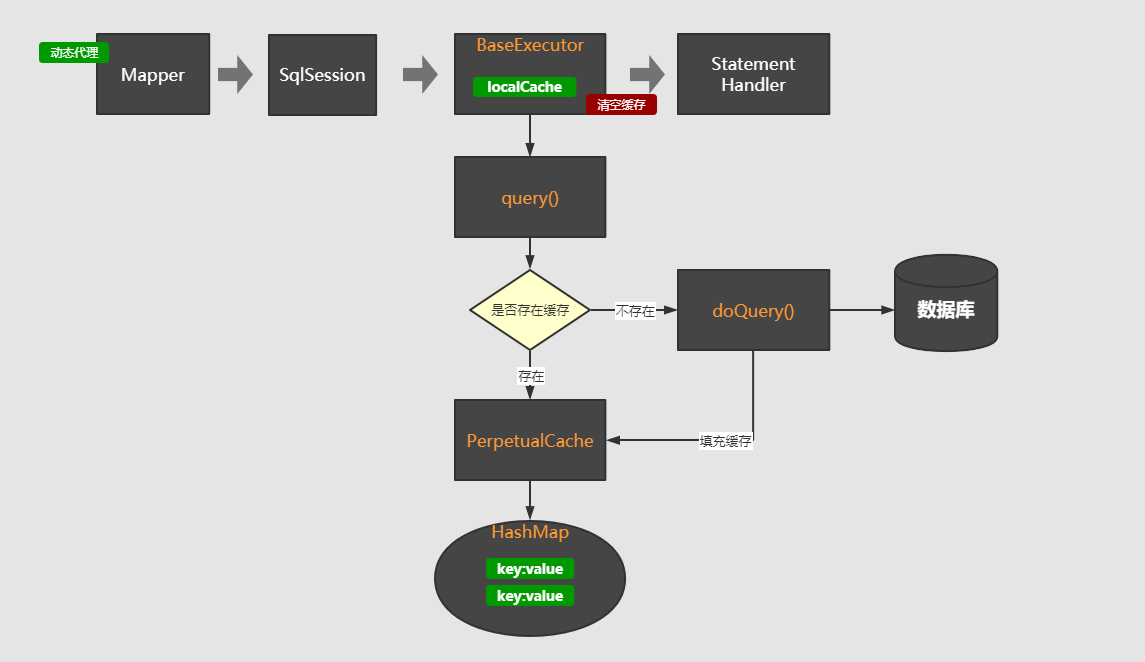
执行过程
每个SqlSession会话中会创建Executor执行器,在BaseExcutor执行器中维护了localCache。
- 用户发起查询请求,创建会话
- 调用
Executor的query方法 - 调用
BaseExecutor的query方法 - 判断
BaseExecutor中缓存(localCache)是否存在 - 存在从缓存中取
- 不存在调用子类的
doQuery方法,从数据库查询,并设置进缓存
源代码分析
一级缓存主要需要研究BaseExecutor类,BaseExecutor是实现了Executor接口的抽象类,主要功能有改、查、缓存维护、事务管理以及提交,批处理刷新等。
-
BaseExecutor维护了localCache这个成员变量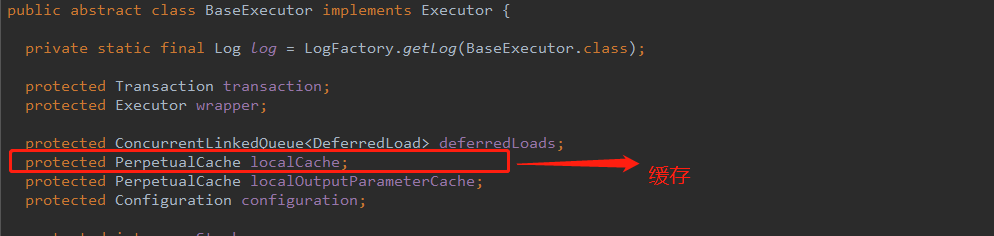
-
localCache的作用范围(SESSION,STATEMENT),默认SESSION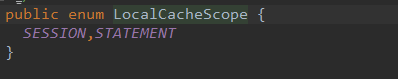
-
缓存的类型是
PrepetualCache,查看源代码,内部实际上维护了一个HashMap,一级缓存的操作实际上是对这个map的操作。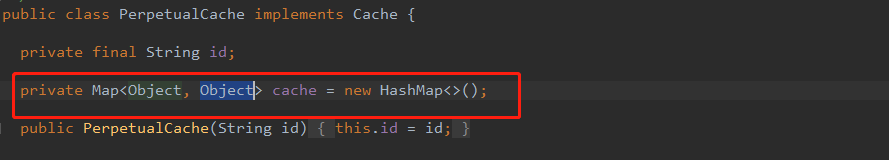
-
Executor会调用BaseExecutor的query方法,同时会生成CacheKey
-
这个
CacheKey相同时,就会命中缓存,查看源代码查看到CacheKey的属性。它和 MappedStatement的ID,分页信息,Sql本身和Sql中的参数,环境相关。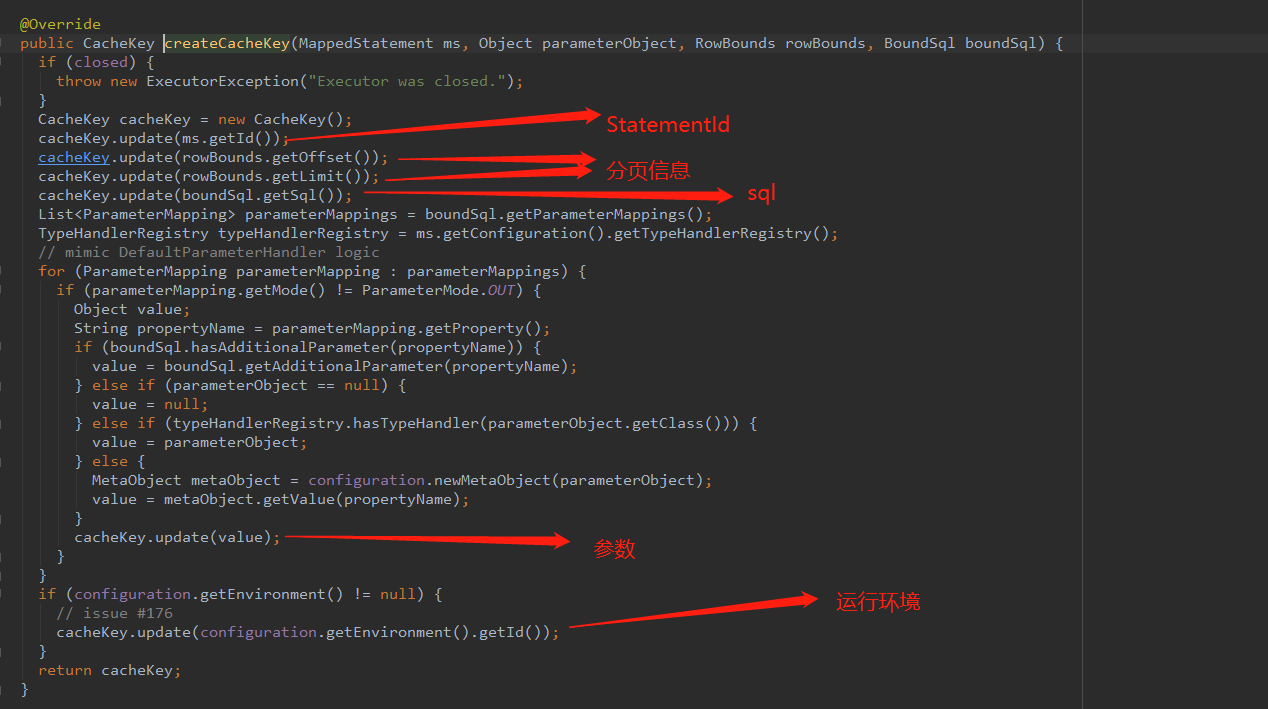
-
查看
query方法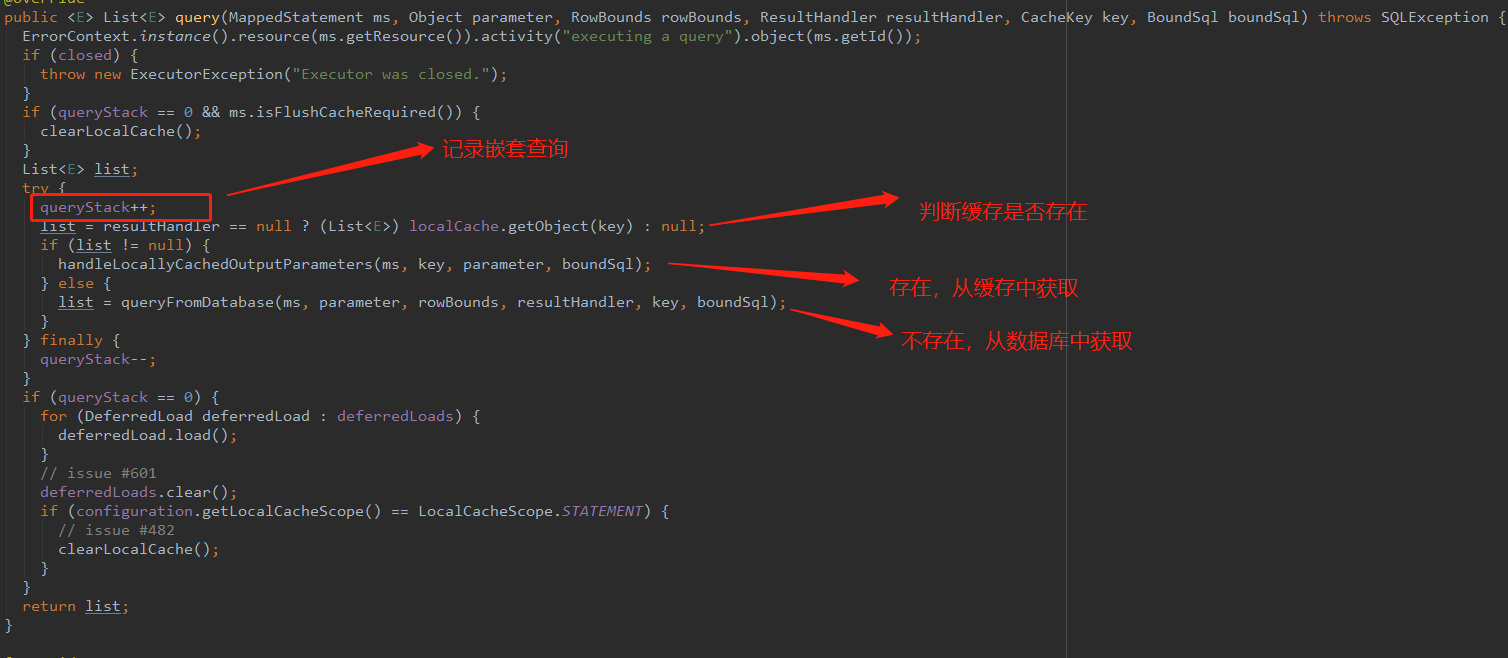
-
当执行提交,回滚,更新等操作时会清空缓存
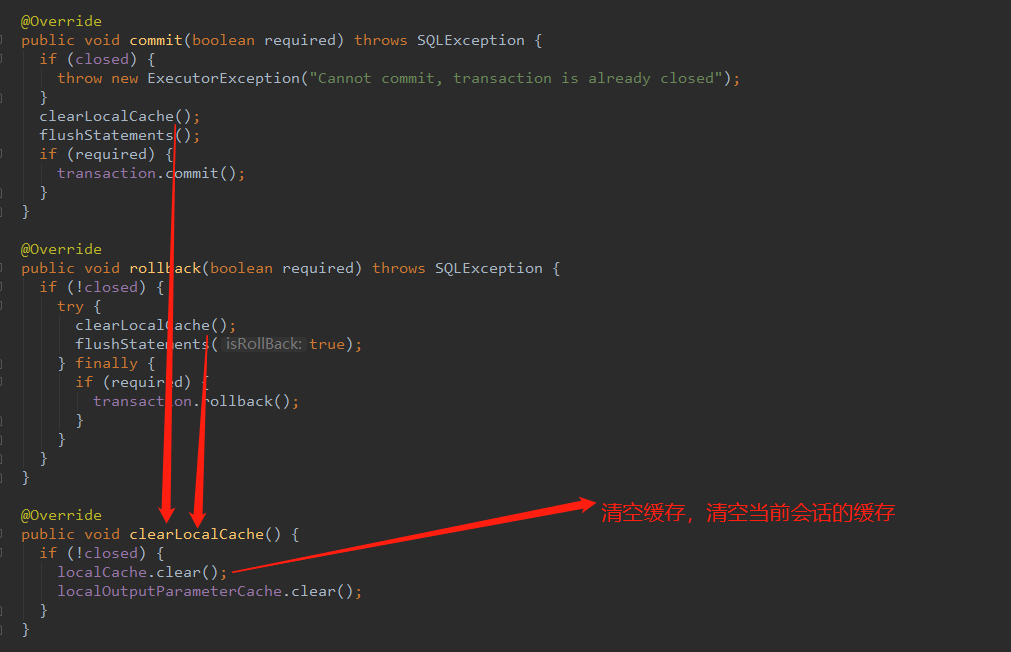
总结
MyBatis一级缓存是会话SqlSession级别的缓存,MyBatis一级缓存底层使用HashMap进行储存,是线程不安全的MyBatis一级缓存范围有SESSION,STATEMENT