本篇文章代码地址:gitee.com/laofublog/C…
原文博客地址:blog.laofu.online/2020/06/05/…
1. java的运行过程
在运行一段 java 代码的时候需要经过编译,验证,加载和运行,具体如下图:
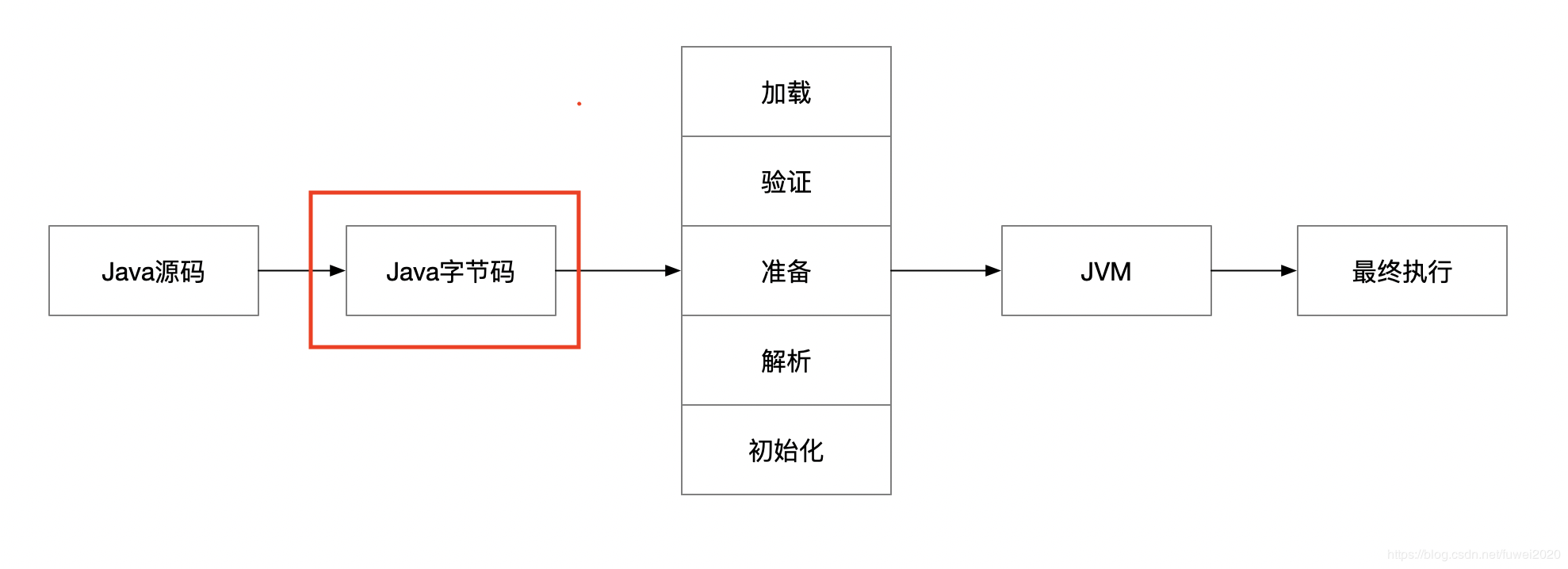
对于 Java 源码变成字节码的编译过程,我们暂且跳过不讨论。
想弄清楚 java 代码的运行原理,其实本质就是 java 字节码如何被 jvm 执行。
下面我们就从两个方面去认识字节码:
- 字节码是什么?
- 字节码如何被执行的?
我们先写一个简单的 java 程序:
public class AddMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=1;
int b=2;
int c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
}
}
对于上面的代码我们可以知道运行的结果是 3,这个结果是怎么被计算出来?
2 .class文件的构成
用java -d .命令把上面的代码编译成 class 文件,编译后得到 AddMain.class 文件,用文本工具打开后,结果如下图:
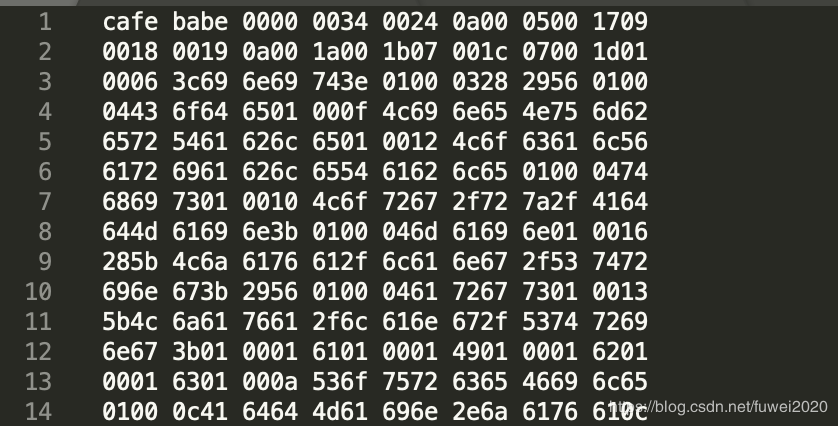
上面的数据是一个 16 进制的数据, 对 .class 文件暂且下一个定义,一个存储 16 进制的文件。具体这些 16 进制的内容到底是什么,需要查询具体的虚拟机规范。
3. class文件的基本结构
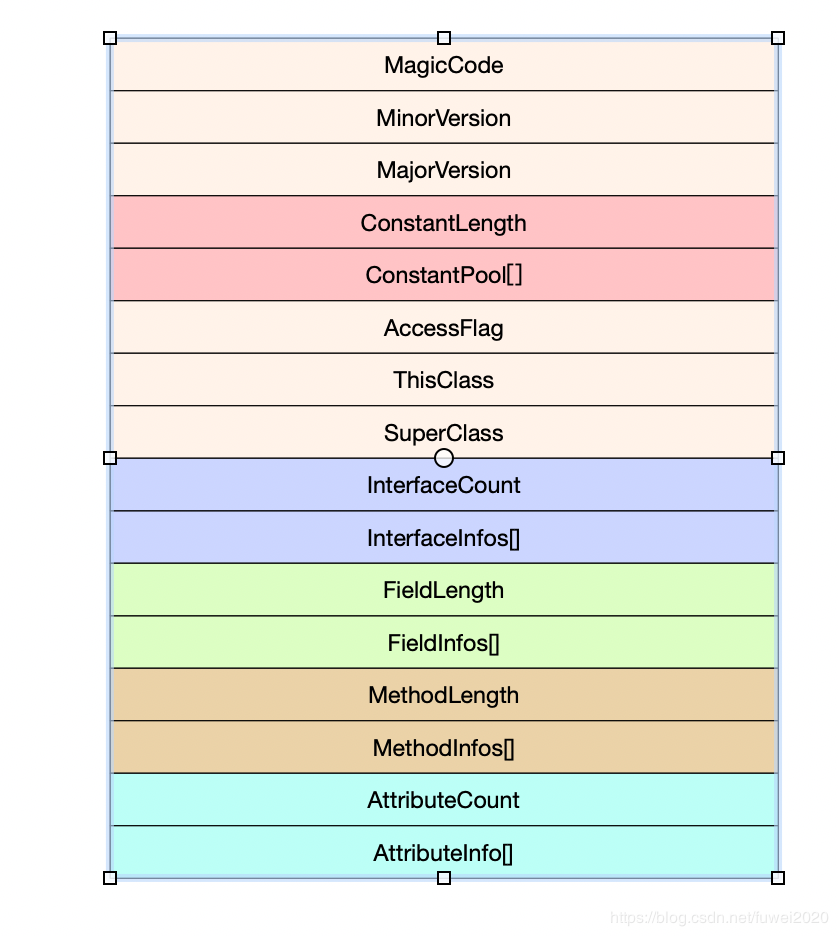
根据JVM的虚拟机规范(SE8)提供的资料,class文件 对应的结构体如下:
ClassFile {
u4 magic;
u2 minor_version;
u2 major_version;
u2 constant_pool_count;
cp_info constant_pool[constant_pool_count-1];
u2 access_flags;
u2 this_class;
u2 super_class;
u2 interfaces_count;
u2 interfaces[interfaces_count];
u2 fields_count;
field_info fields[fields_count];
u2 methods_count;
method_info methods[methods_count];
u2 attributes_count;
attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}
其中u2和u4分别代表占用的字节,u2代表占用两个字节,u4代表占用两个字节,cp_info constant_pool[constant_pool_count-1]代表是数组
对应的结构图如下:
4. 解析过程
对于类的解析过程,如果了解类的结构,则就是工作量的事情,如果对类的结构很熟悉的同学,可以跳过本节
4.1 文件的读取
对于解析文件过程,第一步首先是读取文件,我们以 DataInputStream 的流的形式把数据读入内存中,代码如下:
private DataInputStream dataInputStream;
public ClassReadCursor(String filePath) {
try {
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes).order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
this.dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(byteBuffer.array()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
在上面的操作中,我们把类的文件成功的转换成流文件 DataInputStream ,我们是类文件是按照顺序读取的,所以可以定义的游标的对象 cursor 来读取,对 cursor 可以封装几个读取的方法:
public void readFully(byte[] byteArr) throws IOException {
this.dataInputStream.readFully(byteArr);
}
public int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readUnsignedByte();
}
public int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readUnsignedShort();
}
public int readInt() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readInt();
}
public long readLong() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readLong();
}
public float readFloat() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readFloat();
}
public double readDouble() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readDouble();
}
public String readUTF() throws IOException {
return this.dataInputStream.readUTF();
}
}
4.2 获得魔数
Java中的魔数是一个固定的值cafe babe,一共占用 4 个字节,我们可以通过简单的方式把魔数取出来:
byte[] byteArr=new byte[4];
cursor.readFully(byteArr);
System.out.println(StringUtils.binaryToHexString(byteArr));
对应16进制转字符的方法:
public static String binaryToHexString(byte[] bytes) {
String hexStr = "0123456789ABCDEF";
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
String hex = "";
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
//字节高4位
hex = String.valueOf(hexStr.charAt((bytes[i] & 0xF0) >> 4));
//字节低4位
hex += String.valueOf(hexStr.charAt(bytes[i] & 0x0F));
result.append(hex);
}
return result.toString();
}
打印结果为:CAFE BABE
4.3 获得jdk版本
得到简单的魔数后,我们在向后面解析 4 个字节。
从开始的类结构图上可以看出,文件的内容是:0000 0034
Jdk 的 minor_version 和 major_version 版本号是分别占用两个字节,正好是一个 UnsignedShort 的长度,我们使用readUnsignedShort读取。
minor_version = cursor.readUnsignedShort();
major_version = cursor.readUnsignedShort();
得到的结果分别是:
minor_version=0, major_version=52
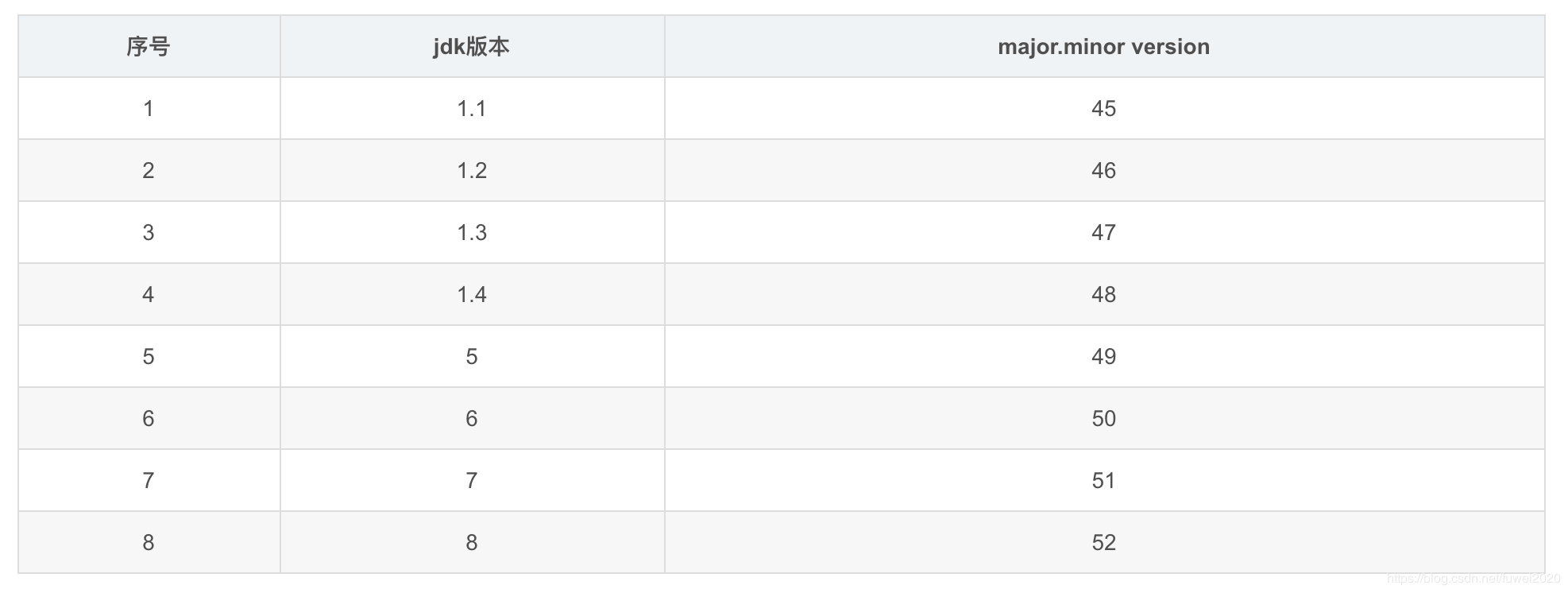
对比上面的版本号可以看出,笔者的jdk的版本是1.8
4.4 常量池
对于常量池来说,是一个数组结构的类型变量,首先我们需要读取数组的长度 constant_pool_count ,根据类的结构,可以得到对应的长度信息:
constant_pool_count= cursor.readUnsignedShort();
很明显是0x0024转成十进制的值为 36 。
在这里需要注意一点的是,此处的常量池的数组个数是 35,与正常的 java 的数组的使用习惯不同,此处的索引是从 1 开始。
在知道常量池的个数后,我们还需要知道常量池中的常量到底是什么?
在JVM中常量主要分为两类,一种是字面量,如文本字符串,声明为 final 类型的常量值。 另一种是属于符号引用,如:类和接口全限定名,字段的描述等等。
根据上面的大类,我们可以查阅 Jvm 的虚拟机规范,可以看到常量池单元在虚拟机中定义基本结构如下:
cp_info {
u1 tag;
u1 info[];
}
其中tag代表类型类型,后面 info[] 项的内容 tag 由的类型所决定。 tag 对应的类型如下:
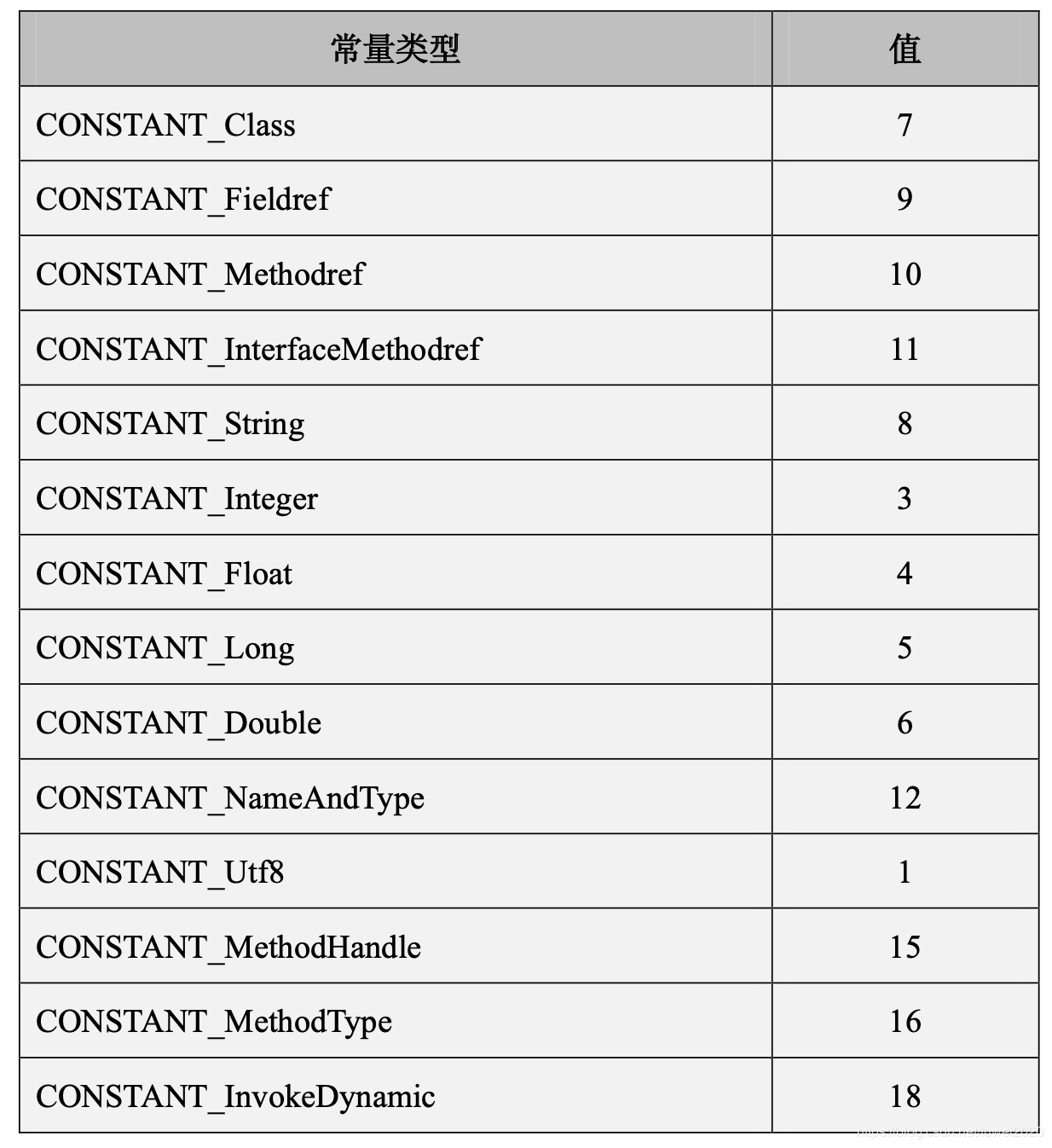
对于上面的常量的类型,我们依次看下:
4.4.1 解析常量池
在解析常量池之前我们可以通过javap -v命令来查看对应的常量池:
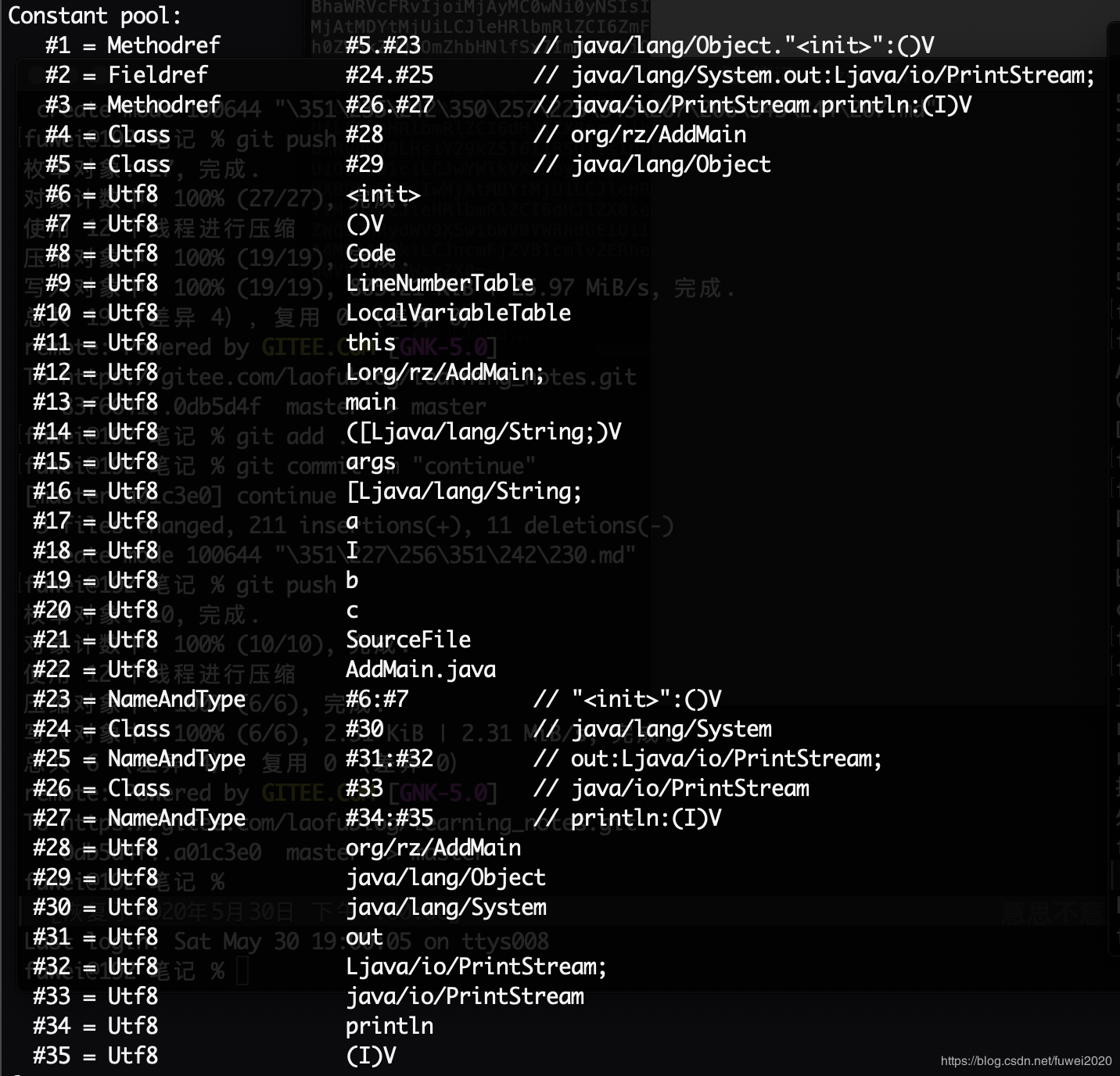
这个图片我们先保留,作为我们后面查询的依据。
对于常量池的解析,我们先来一个简单的设计,通过上面的魔数,版本号的获取,加上我们即将要解析的常量池,我们可以简单的定义一个类结构如下(ClassParseInfo,后续还会加字段):
public class ClassParseInfo {
public final String magic;
public final int minor_version;
public final int major_version;
public final int constantCount;
public final ConstantPool constant_pool;
}
其中ConstantPool是常量池,我们知道所有的常量的类型都满足cp_info结构,所以我们可以简单定义一个基类:
public class CPInfo {
private short tag;
public CPInfo(int tag) {
this.tag = (short)tag;
}
public short getTag() {
return tag;
}
}
而ConstantPool类的结构应该为:
public class ConstantPool {
private CPInfo[] cpInfos;
private final int count;
}
下面我们就先认识下各个常量池的类型:
CONSTANT_Class
CONSTANT_Class 结构用于表示类和接口,具体的格式如下:
CONSTANT_Class_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
}
- tag代表CONSTANT_Class的tag值7
- name_index 是常量池中的一个索引
对应的解析类的代码:
public class CONSTANT_Class_info extends CPInfo {
private int name_index;
public CONSTANT_Class_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException {
super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Class);
name_index=cursor.readUnsignedShort();
}
}
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info, CONSTANT_Methodref_info 和 CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info 结构
这三个的类型的结构基本一致:
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
CONSTANT_Methodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
-
tag 分别代表三个类型的标记值,CONSTANT_Fieldref(9),CONSTANT_Methodref(10)和CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref(11)
-
class_index
Class_index 代表是常量池的引用,从名字上面可以看出,常量池在此处的引用必须要是 类或者是接口的类型。
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info结构的 class_index 项的类型既可以是 类也可以是接口。CONSTANT_Methodref_info结构的 class_index 项的类型必须是类(不能是接口)。CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info` 结构的 class_index 项的类型必须是接口 (不能是类)。
-
name_and_type_index
这个代表是当前常量类型的name和type类型的索引,可以通过这个索引知道当前类的索引值。
-
解析类的代码
public class CONSTANT_Fieldref_info extends CPInfo {
private int class_index;
private int name_and_type_index;
public CONSTANT_Fieldref_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException {
super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Fieldref);
class_index=cursor.readUnsignedShort();
name_and_type_index=cursor.readUnsignedShort();
}
}
CONSTANT_String_info
CONSTANT_String_info代表java.lang.String类型的常量对象,格式如下:
CONSTANT_String_info {
u1 tag;
u2 string_index;
}
-
string_index
string_index 项的值必须是对常量池的有效索引,常量池在该索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info结构, 代表一个字符串
-
解析类的代码如下:
public class CONSTANT_String_info extends CPInfo {
private int string_index;
public CONSTANT_String_info(ClassReadCursor cusor) throws IOException {
super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_String);
this.string_index = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
}
}
CONSTANT_Integer_info 和 CONSTANT_Float_info 结构
CONSTANT_Integer_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Float_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
-
bytes CONSTANT_Integer_info 结构的 bytes 项表示 int 常量的值. CONSTANT_Float_info 表示 float 常量的值 对于 CONSTANT_Float_info 的表示方法比较特殊,此处不再深究,只需要记录二进制的数据。
-
解析代码
public class CONSTANT_Integer_info extends CPInfo {
private int value;
public CONSTANT_Integer_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException {
super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Integer);
value=cursor.readInt();
}
}
public class CONSTANT_Float_info extends CPInfo {
private float value;
public CONSTANT_Float_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException {
super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Float);
value=cursor.readFloat();
}
}
CONSTANT_Long_info 和 CONSTANT_Double_info 结构
CONSTANT_Long_info 和 CONSTANT_Double_info 结构表示 8 字节(long 和 double)的数值常量:
CONSTANT_Long_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Double_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
如果一个 CONSTANT_Long_info 或 CONSTANT_Double_info 结构的项在常量池中的索引为 n,则常量池中下一个有效的项的索引为 n+2,此时常量池中索引为 n+1 的项有效但必须被认为不可用 。
-
high_bytes 和 low_bytes
在CONSTANT_Long_info的结构中,无符号的highbyte和low_bytes共同来表示当前常量的值,具体算法为 high_bytes<<32+low_bytes
CONSTANT_Double_info的计算方法此处不做深究。
-
解析代码
public class CONSTANT_Long_info extends CPInfo { private long longValue; public CONSTANT_Long_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Long); longValue = cursor.readLong(); } } public class CONSTANT_Double_info extends CPInfo { private double douleValue; public CONSTANT_Double_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Double); this.douleValue = cursor.readDouble(); } }
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info 结构
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info 结构用于表示字段或方法.
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
-
Name_index
代表当前方法的名称,表示特殊的方法名或者表示一个有效的字段或方法的非限定名(Unqualified Name)。
-
Decriptor_index
当前方法或者字段描述的索引值。
public class CONSTANT_NameAndType_info extends CPInfo { private int name_inex; private int descriptor_index; public CONSTANT_NameAndType_info(ClassReadCursor cusor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_NameAndType); this.name_inex = cusor.readUnsignedShort(); this.descriptor_index = cusor.readUnsignedShort(); } }
CONSTANT_Utf8_info 结构
CONSTANT_Utf8_info 结构用于表示字符串常量的值:
CONSTANT_Utf8_info {
u1 tag;
u2 length;
u1 bytes[length];
}
-
length
length表示当前字符串的字节长度
-
bytes[] bytes[]是表示字符串值的 byte 数组,bytes[]数组中每个成员的 byte 值都不会是 0, 也不在 0xf0 至 0xff 范围内。
-
解析代码
public class CONSTANT_Utf8_info extends CPInfo { private int length; private String text; public CONSTANT_Utf8_info(ClassReadCursor cusor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_Utf8); text=cusor.readUTF(); } public String getText() { return text; } }
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info 结构
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info 结构用于表示方法句柄,结构如下:
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info {
u1 tag;
u1 reference_kind;
u2 reference_index;
}
-
reference_kind
reference_kind 项的值必须在 1 至 9 之间(包括 1 和 9),它决定了方法句柄的类型。
方法句柄类型的值表示方法句柄的字节码行为
-
reference_index
reference_index 项的值必须是对常量池的有效索引:
- 如果 reference_kind 项的值为 1(REF_getField)、2(REF_getStatic)、3
(REF_putField)或 4(REF_putStatic),那么常量池在 reference_index 索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_Fieldref_info(§4.4.2)结构,表示由一个字 段创建的方法句柄。
-
如果 reference_kind 项的值是 5(REF_invokeVirtual)、6 (REF_invokeStatic)、7(REF_invokeSpecial)或 8 (REF_newInvokeSpecial),那么常量池在 reference_index 索引处的项必须 是 CONSTANT_Methodref_info(§4.4.2)结构,表示由类的方法或构造函数 创建的方法句柄。
-
如果 reference_kind 项的值是 9(REF_invokeInterface),那么常量池在 reference_index 索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info (§4.4.2)结构,表示由接口方法创建的方法句柄。
-
如果 reference_kind 项的值是 5(REF_invokeVirtual)、6 (REF_invokeStatic)、7(REF_invokeSpecial)或 9 (REF_invokeInterface),那么方法句柄对应的方法不能为实例初始化() 方法或类初始化方法()。
-
如果 reference_kind 项的值是 8(REF_newInvokeSpecial),那么方法句柄对应的方法必须为实例初始化()方法。
-
解析代码
public class CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info extends CPInfo { private int reference_kind; private int reference_index; public CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_MethodHandle); reference_kind=cursor.readUnsignedByte(); reference_index=cursor.readUnsignedShort(); } }
CONSTANT_MethodType_info
CONSTANT_MethodType_info 表示方法类型,具体结构如下:
CONSTANT_MethodType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
-
descriptor_index descriptor_index 项的值必须是对常量池的有效索引,常量池在该索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info(§4.4.7)结构,表示方法的描述符
-
解析代码:
public class CONSTANT_MethodType_info extends CPInfo { private int descriptor_index; public CONSTANT_MethodType_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_MethodType); descriptor_index=cursor.readUnsignedShort(); } }
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info 结构
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info 用于表示 invokedynamic 指令所使用到的引导方法 (Bootstrap Method)、引导方法使用到动态调用名称(Dynamic Invocation Name)、参 数和请求返回类型、以及可以选择性的附加被称为静态参数(Static Arguments)的常量序列。
CONSTANT_MethodType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info {
u1 tag;
u2 bootstrap_method_attr_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
-
bootstrap_method_attr_index
bootstrap_method_attr_index 项的值必须是对当前 Class 文件中引导方法表的 bootstrap_methods[]数组的有效索引。
-
name_and_type_index
name_and_type_index项的值必须是对当前常量池的有效索引,常量池在该索引处的 项必须是 CONSTANT_NameAndType_info结构,表示方法名和方法描述符
-
解析代码:
public class CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info extends CPInfo { private int bootstrap_method_attr_index; private int name_and_type_index; public CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException { super(ConstantPoolType.CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic); bootstrap_method_attr_index = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); name_and_type_index = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); } }
经过上面的解读,我们可以写常量池解析的代码了
- 根据tag进入不同的构造函数
- 有一个公共的基类cp_info
我们可以使用最简单的switch-case的形式来写:
public class ConstantPool {
private CPInfo[] cpInfos;
private final int count;
public ConstantPool(ClassReadCursor cursor, int count) throws Exception {
this.count = count;
cpInfos = new CPInfo[count];
init(cursor);
}
public void init(ClassReadCursor cursor) throws Exception {
for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) {
int tag = cursor.readByte();
System.out.println("tag:" + tag);
switch (tag) {
case CONSTANT_Utf8: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Utf8_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Integer: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Integer_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Float: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Float_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Long: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Long_info(cursor);
i++;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Double: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Double_info(cursor);
i++;
break;
}
case CONSTANT_String: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_String_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Fieldref: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Fieldref_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Methodref: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Methodref_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_NameAndType: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_NameAndType_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_Class: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_Class_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_MethodHandle: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_MethodType: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_MethodType_info(cursor);
break;
}
case CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic: {
cpInfos[i] = new CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info(cursor);
break;
}
default: {
throw new Exception("未实现的类型i:" + i + ",tag:" + tag);
}
}
}
}
}
4.4.2 访问标记
在访问限定的修饰符中,有public,private等限定修饰词,标记和修饰符对应的关系如下:
public class AccessFlags {
public static final int ACC_PUBLIC = 0x0001; // class, inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_PRIVATE = 0x0002; // inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_PROTECTED = 0x0004; // inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_STATIC = 0x0008; // inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_FINAL = 0x0010; // class, inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_SUPER = 0x0020; // class
public static final int ACC_SYNCHRONIZED = 0x0020; // method
public static final int ACC_VOLATILE = 0x0040; // field
public static final int ACC_BRIDGE = 0x0040; // method
public static final int ACC_TRANSIENT = 0x0080; // field
public static final int ACC_VARARGS = 0x0080; // method
public static final int ACC_NATIVE = 0x0100; // method
public static final int ACC_INTERFACE = 0x0200; // class, inner
public static final int ACC_ABSTRACT = 0x0400; // class, inner, method
public static final int ACC_STRICT = 0x0800; // method
public static final int ACC_SYNTHETIC = 0x1000; // class, inner, field, method
public static final int ACC_ANNOTATION = 0x2000; // class, inner
public static final int ACC_ENUM = 0x4000; // class, inner, field
public static final int ACC_MANDATED = 0x8000; // method parameter
public static final int ACC_MODULE = 0x8000; // class
}
我们可以简单的使用读取无符号的整型来获取对应的访问标记,我们在类ClassParseInfo加一个access_flag字段:
private final int access_flag;
access_flag=cr.readUnsignedShort();
得到数值为0x00021。分别与上面的类型做&运算,得到访问的标记ACC_PUBLIC,ACC_SUPER`
4.4.3 类索引和父类索引
类索引是指当前类的在常量池中对应的位置,索引对应的位置一定是CONSTANT_Class_info
父类索引是当前类父类对应的位置,如果当前类有父类,则会显示当前的类在常量池的所以。如果没有父类,也会有一个基本的父类Object.
ClassParseInfo再加两个字段:
public final int this_class;
public final int super_class;
对应的解析代码:
this_class = cursor.readUnsignedShort();
super_class = cursor.readUnsignedShort();
得到的值是4和5。我们根据索引查到对应的值为两个CONSTANT_Class_info数据:
{
"tag":7,
"name_index":28
}
{
"tag":7,
"name_index":29
}
查看28,29对应的数据,分别为org/rz/AddMain和java/lang/Object:
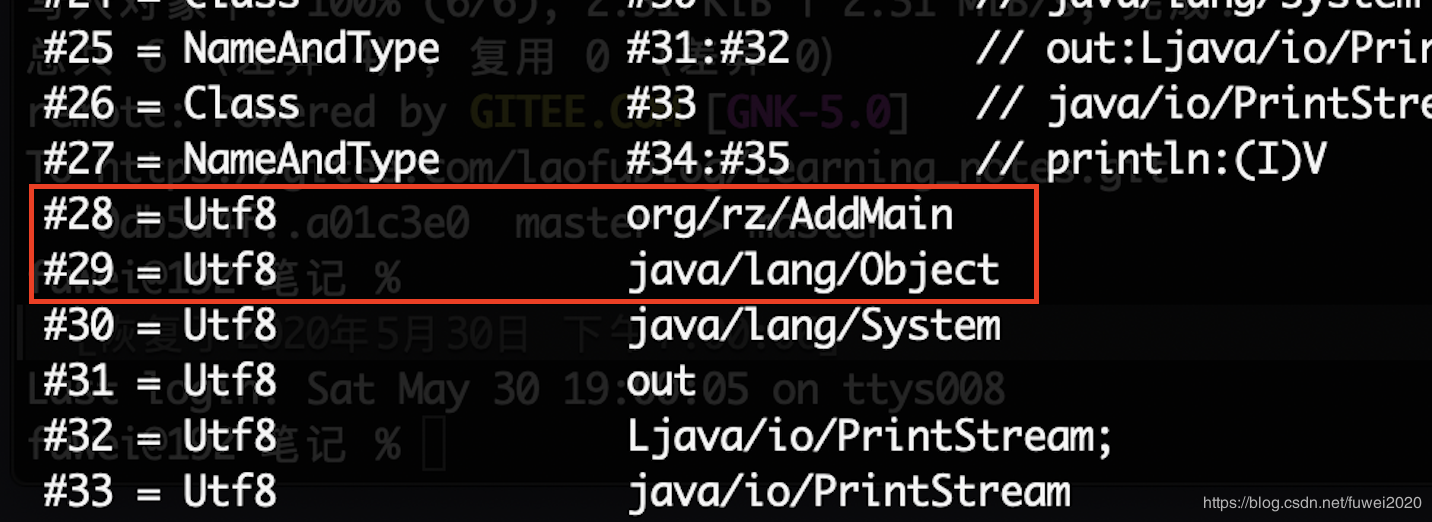
4.4.4 接口的数量和接口
demo中的接口的数量为0,所以我们不用获取interface.
4.4.5 字段
每个字段(Field)都由 field_info 结构所定义,在同一个 Class 文件中,不会有两个字 段同时具有相同的字段名和描述符。
field_info 结构格式如下:
field_info {
u2 access_flags;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
u2 attributes_count;
attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}
-
access_flags
access_flags 项的值是用于定义字段被访问权限和基础属性的掩码标志。
具体的类型如下:
标记名 值 说明 ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 public,表示字段可以从任何包访问。 ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 private,表示字段仅能该类自身调用。 ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 protected,表示字段可以被子类调用。 ACC_STATIC 0x0008 static,表示静态字段。 ACC_FINAL 0x0010 final,表示字段定义后值无法修改 ACC_VOLATILE 0x0040 volatile,表示字段是易变的。 ACC_TRANSIENT 0x0080 transient,表示字段不会被序列化。 ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 表示字段由编译器自动产生。 ACC_ENUM 0x4000 enum,表示字段为枚举类型。 -
name_index name_index 项的值必须是对常量池的一个有效索引。常量池在该索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info结构,表示一个有效的字段的非全限定名。
-
descriptor_index descriptor_index 项的值必须是对常量池的一个有效索引。常量池在该索引处的项必 须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info结构,表示一个有效的字段的描述符。
-
attributes_count attributes_count 的项的值表示当前字段的附加属性的数量。
-
attributes[] attributes 表的每一个成员的值必须是 attribute结构(后续会单独讨论)
4.4.6 方法
所有方法(Method),包括实例初始化方法和类初始化方法在内,都由 method_info 结构所定义。在一个 Class 文件中,不会有两个方法同时具有相同的方法名和描述符。
method_info 结构格式如下:
method_info {
u2 access_flags;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
u2 attributes_count;
attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}
-
access_flags
access_flags 项的值是用于定义当前方法的访问权限和基本属性的掩码标志.具体标记如下:
标记名 值 说明 ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 public,方法可以从包外访问 ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 private,方法只能本类中访问 ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 protected,方法在自身和子类可以访问 ACC_STATIC 0x0008 static,静态方法 ACC_FINAL 0x0010 final,方法不能被重写(覆盖) ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 0x0020 synchronized,方法由管程同步 ACC_BRIDGE 0x0040 bridge,方法由编译器产生 ACC_VARARGS 0x0080 表示方法带有变长参数 ACC_NATIVE 0x0100 native,方法引用非 java 语言的本地方法 ACC_ABSTRACT 0x0400 abstract,方法没有具体实现 ACC_STRICT 0x0800 strictfp,方法使用 FP-strict 浮点格式 ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 方法在源文件中不出现,由编译器产生 -
name_index name_index 项的值必须是对常量池的一个有效索引。常量池在该索引处的项必须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info结构,它要么表示初始化方法的名字(或 ),要么表示一个方法的有效的非全限定名
-
descriptor_index descriptor_index 项的值必须是对常量池的一个有效索引。常量池在该索引处的项必 须是 CONSTANT_Utf8_info结构,表示一个有效的方法的描述符
-
attributes_count 表示附加属性的数量
-
attributes[]
与字段附加属性一致。
4.4.7 属性
属性在 Class 文件格式中的 ClassFile结构、field_info结构,method_info结构和 Code_attribute结构都有使用,所有属性的通用格式如下:
attribute_info {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u1 info[attribute_length];
}
其中attribute_name_index代表当前属性在常量池中的索引,我们获得对应的名称后,可以匹配到对应类型的属性。属性的类型主要有:
public class AttributeType {
public static final String AnnotationDefault = "AnnotationDefault";
public static final String BootstrapMethods = "BootstrapMethods";
public static final String CharacterRangeTable = "CharacterRangeTable";
public static final String Code = "Code";
public static final String ConstantValue = "ConstantValue";
public static final String CompilationID = "CompilationID";
public static final String Deprecated = "Deprecated";
public static final String EnclosingMethod = "EnclosingMethod";
public static final String Exceptions = "Exceptions";
public static final String InnerClasses = "InnerClasses";
public static final String LineNumberTable = "LineNumberTable";
public static final String LocalVariableTable = "LocalVariableTable";
public static final String LocalVariableTypeTable = "LocalVariableTypeTable";
public static final String MethodParameters = "MethodParameters";
public static final String Module = "Module";
public static final String ModuleHashes = "ModuleHashes";
public static final String ModuleMainClass = "ModuleMainClass";
public static final String ModulePackages = "ModulePackages";
public static final String ModuleResolution = "ModuleResolution";
public static final String ModuleTarget = "ModuleTarget";
public static final String NestHost = "NestHost";
public static final String NestMembers = "NestMembers";
public static final String Record = "Record";
public static final String RuntimeVisibleAnnotations = "RuntimeVisibleAnnotations";
public static final String RuntimeInvisibleAnnotations = "RuntimeInvisibleAnnotations";
public static final String RuntimeVisibleParameterAnnotations = "RuntimeVisibleParameterAnnotations";
public static final String RuntimeInvisibleParameterAnnotations = "RuntimeInvisibleParameterAnnotations";
public static final String RuntimeVisibleTypeAnnotations = "RuntimeVisibleTypeAnnotations";
public static final String RuntimeInvisibleTypeAnnotations = "RuntimeInvisibleTypeAnnotations";
public static final String Signature = "Signature";
public static final String SourceDebugExtension = "SourceDebugExtension";
public static final String SourceFile = "SourceFile";
public static final String SourceID = "SourceID";
public static final String StackMap = "StackMap";
public static final String StackMapTable = "StackMapTable";
public static final String Synthetic = "Synthetic";
}
上面的这么多类型,我们只需要挑几个比较常用的重点说下,至于完整的可以参考JVM规范。
ConstantValue 属性
ConstantValue 属性表示一个常量字段的值。 具体的数据结构如下:
ConstantValue_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 constantvalue_index;
}
-
attribute_name_index
attribute_name_index 项的值,必须是一个对常量池的有效索引。
-
attribute_length ConstantValue_attribute 结构的 attribute_length 项的值固定为 2。
-
constantvalue_index constantvalue_index 项的值的索引。常量池在该索引处 的项给出该属性表示的常量值。constantvalue_index的类型一共分为下面几种:
| 字段类型 | 项类型 |
|---|---|
| long | CONSTANT_Long |
| float | CONSTANT_Float |
| double | CONSTANT_Double |
| int,short,char,byte,boolean | CONSTANT_Integer |
| String | CONSTANT_String |
-
对应的解析代码如下:
public class ConstantValue_attribute extends Attribute { private int constantvalue_index; private int constantvalue; public ConstantValue_attribute(ClassReadCursor cursor, int attribute_index) throws IOException { super(ConstantValue, attribute_index, cursor.readInt()); constantvalue_index = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); } }
Code属性
Code 属性是一个变长属性,位于 method_info结构的属性表,记录的方法的字节码指令及相关辅助信息。code的结构如下:
Code_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index; u4 attribute_length;
u2 max_stack;
u2 max_locals;
u4 code_length;
u1 code[code_length];
u2 exception_table_length;
{
u2 start_pc;
u2 end_pc;
u2 handler_pc;
u2 catch_type;
}
exception_table[exception_table_length];
u2 attributes_count;
attribute_info attributes[attributes_count];
}
code 中有几个需要注意的属性如下:
-
max_stack max_stack 项的值给出了当前方法的操作数栈在运行执行的任何时间点的最大深度
-
max_locals max_locals 项的值给出了分配在当前方法引用的局部变量表中的局部变量个数,包括 调用此方法时用于传递参数的局部变量。 long 和 double 型的局部变量的最大索引是 max_locals-2,其它类型的局部变量的 最大索引是 max_locals-1.
max_stack和max_locals在编译期就已经能够确定了。
-
attribute_info
attribute_info是code属性的属性。可以出现在 Code 属性的属性表中的成员只能是 LineNumberTable,LocalVariableTable,LocalVariableTypeTable和StackMapTable
-
解析代码:
public class Code_attribute extends Attribute { private int max_stack; private int max_locals; private int code_length; private int exception_table_length; private int attributes_count; private byte[] code; private byte[] paraCode; private Opcode[] opcodeArr; private ExceptionTable[] exceptionTables; private Attribute[] attributes; public Code_attribute(ClassReadCursor cursor, int attrTag) throws Exception { super(AttributeType.Code, attrTag, cursor.readInt()); max_stack = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); max_locals = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); code_length = cursor.readInt(); if (code_length > 0) { code = new byte[code_length]; cursor.readFully(code); opcodeArr = new Opcode[code_length]; paraCode=new byte[code_length]; } int index=0; int paraIndex=0; for (int i = 0; i < code_length; i++) { byte bCode = code[i]; Opcode opcode = Opcode.valueOf(Byte.toUnsignedInt(bCode)); opcodeArr[index++] = opcode; if(opcode.operandCount>0){ for (int j = 0; j < opcode.operandCount; j++) { paraCode[paraIndex++]=code[i+j+1]; } } i += opcode.operandCount; } exception_table_length = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); if (exception_table_length > 0) { exceptionTables = new ExceptionTable[exception_table_length]; for (int i = 0; i < exception_table_length; i++) { int start_pc = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); int end_pc = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); int handler_pc = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); int catch_type = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); this.exceptionTables[i] = new ExceptionTable(start_pc, end_pc, handler_pc, catch_type); } } attributes_count = cursor.readUnsignedShort(); if (attributes_count > 0) { attributes = new Attribute[attributes_count]; for (int i = 0; i < attributes_count; i++) { Attribute attribute = AttributeFactory.create(cursor); attributes[i] = attribute; } } } } -
code属性解析完成后是一个16进制的数字,这时候就需要对应的指令来映射出对应的代码。 例如:
0x03-->iconst_0,很多指令后面还会跟上几位参数,如if_icmpeq,后面的两位都是参数。
StackMapTable
StackMapTable属性主要用于字节码的验证,是类型检测器(Type Checker)会检查和处理目标方法的局部变量和操作数栈所需要的类型。 对于我们运行字节码作用不大,我们知道能正常解析出属性即可,对应的数据结构如下:
StackMapTable_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 number_of_entries;
stack_map_frame entries[number_of_entries];
}
其中比较复杂的stack_map_frame这个还有很多数据接口,此处不一一列举,后面直接贴出解析代码:
public class StackMapTable_attribute extends Attribute
{
private int attribute_name_index;
private int attribute_length;
private int number_of_entries;
private StackMapFrame[] stackMapFrames;
public StackMapTable_attribute(ClassReadCursor cursor,int attrTag) throws IOException {
super(StackMapTable, attrTag, cursor.readInt());
number_of_entries = cursor.readUnsignedShort();
//todo:此处还不知道到怎么转换
// String intNext = cusor.getHexNext(attribute_length-2);
if (number_of_entries > 0) {
stackMapFrames = new StackMapFrame[number_of_entries];
for (int i = 0; i < number_of_entries; i++) {
short frameType =(short) cursor.readUnsignedByte();
StackMapFrame stack_map_frame = FrameFactory.create(frameType,cursor);
stackMapFrames[i]=stack_map_frame;
}
}
}
}
public class FrameFactory {
public static StackMapFrame create(short frameType, ClassReadCursor cursor) throws IOException {
if (frameType <= 63) {
return new SameFrame(frameType);
}
if (frameType <= 127) {
return new SameLocals1StackItemFrame(frameType, cursor);
}
if (frameType == 247) {
return new SameLocals1StackItemFrameExtend(frameType, cursor);
}
if (frameType >= 248 && frameType <= 250) {
return new ChopFrame(frameType, cursor);
}
if(frameType==251){
return new SameFrameExtended(frameType,cursor);
}
if (frameType >=252 && frameType <= 254) {
return new AppendFrame(frameType, cursor);
}
return new UndefineFrame(frameType);
}
}
Exceptions 属性
Exceptions 属性指出了一个方法需要检查的可能抛出的异常。一个 method_info 结构中最多只能有一个 Exceptions 属性。
Exceptions 属性格式如下:
Exceptions_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 number_of_exceptions;
u2 exception_index_table[number_of_exceptions];
}
- attribute_length
attribute_length 项的值给出了当前属性的长度,不包括开始的 6 个字节。
-
number_of_exceptions
number_of_exceptions 项的值给出了 exception_index_table[]数组中成员的数量。
-
exception_index_table[]
exception_index_table[]数组的每个成员的值都必须是对常量池的有效索引。常量 池在这些索引处的成员必须都是 CONSTANT_Class_info结构,表示这个 方法声明要抛出的异常的类的类型。
一个方法如果要抛出异常,必须至少满足下列三个条件中的一个:
- 要抛出的是 RuntimeException 或其子类的实例。
- 要抛出的是 Error 或其子类的实例。
- 要抛出的是在 exception_index_table[]数组中申明的异常类或其子类的实例。 这些要求没有在 Java 虚拟机中进行强制检查,它们只在编译时进行强制检查
SourceFile属性
SourceFile属性表示当前类的源码路径,具体结构如下:
SourceFile_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 sourcefile_index;
}
在上面的Javap命令中有体现:SourceFile: "AddMain.java",此处不再赘述。具体解析的代码如下:
public class SourceFile_attribute extends Attribute {
public SourceFile_attribute(ClassReadCursor cursor, int attrTag) throws IOException {
super(SourceFile, attrTag, cursor.readUnsignedShort());
}
}
LineNumberTable属性
LineNumberTable 属性是可选变长属性,位于 Code结构的属性表。它被调试器用于确定源文件中行号表示的内容在 Java 虚拟机的 code[]数组中对应的部分。
在 Code 属性 的属性表中,LineNumberTable 属性可以按照任意顺序出现,此外,多个 LineNumberTable 属性可以共同表示一个行号在源文件中表示的内容,即 LineNumberTable 属性不需要与源文件 的行一一对应。
LineNumberTable_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 line_number_table_length;
{
u2 start_pc;
u2 line_number;
}
line_number_table[line_number_table_length];
}
-
line_number_table[]
line_number_table[]数组的每个成员都表明源文件中行号的变化在 code[]数组中 都会有对应的标记点。line_number_table 的每个成员都具有如下两项:
- start_pc
start_pc 项的值必须是 code[]数组的一个索引,code[]数组在该索引处的字符 表示源文件中新的行的起点。start_pc 项的值必须小于当前 LineNumberTable 属性所在的 Code 属性的 code_length 项的值。
- line_number line_number 项的值必须与源文件的行数相匹配。
LocalVariableTable属性
被调试器用于确定方法在执行过程中局部变量的信息。具体的结构如下:
LocalVariableTable_attribute {
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 local_variable_table_length;
{
u2 start_pc;
u2 length;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
u2 index;
}
local_variable_table[local_variable_table_length];
}
local_variable_type_table[]数组的每一个成员表示一个局部变量的值在 code[] 数组中的偏移量范围
-
local_variable_type_table[]
local_variable_table[]数组的每一个成员表示一个局部变量的值在 code[] 数组中的偏移量范围。它同时也是用于从当前帧的局部变量表找出所需的局部变量的索引
具体的解析代码如下:
public class LocalVariableTable_attribute extends Attribute {
private int attribute_length;
private int local_variable_table_length;
private List<local_variable_table> local_variable_tables;
public LocalVariableTable_attribute(ClassReadCursor cusor, int attrTag) throws IOException {
super(LocalVariableTable, attrTag, cusor.readInt());
local_variable_table_length = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
if (local_variable_table_length > 0) {
local_variable_tables = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < local_variable_table_length; i++) {
int start_pc = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
int length = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
int name_index = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
int descriptor_index = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
int index = cusor.readUnsignedShort();
local_variable_tables.add(new local_variable_table(start_pc, length, name_index, descriptor_index, index));
}
}
}
}
class local_variable_table {
private int start_pc;
private int length;
private int name_index;
private int descriptor_index;
private int index;
public local_variable_table(int start_pc, int length, int name_index, int descriptor_index, int index) {
this.start_pc = start_pc;
this.length = length;
this.name_index = name_index;
this.descriptor_index = descriptor_index;
this.index = index;
}
}
对于上面的字段,方法和属性的解析,我们对ClassParseInfo再增加几个字段,变成:
public final String magic;
public final int minor_version;
public final int major_version;
public final int constantCount;
public final ConstantPool constant_pool;
public final AccessFlags access_flags;
public final int this_class;
public final int super_class;
public final int[] interfaces;
public final Field[] fields;
public final Method[] methods;
public final int attributeCount;
public final Attribute[] attributes;
5 JVM的运行
Java字节码的文件我们已经解析完了,首先看下我们解析出来方法的指令:
0 "iconst_1"
1 "istore_1"
2 "iconst_2"
3 "istore_2"
4 "iload_1"
5 "iload_2"
6 "iadd"
7 "istore_3"
8 "getstatic"
9 "iload_3"
10 "invokevirtual"
11 "_return"
对比下javap指令生成的数据:
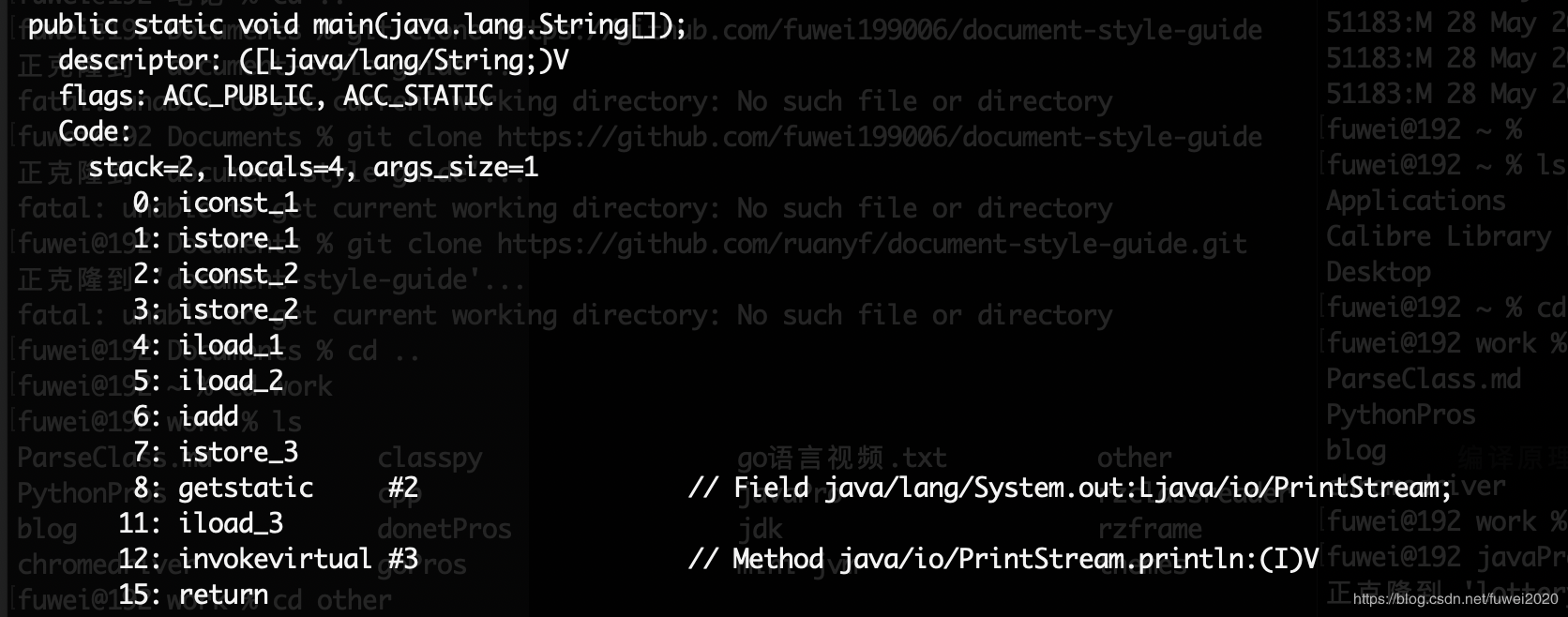
通过上面的操作,我们实现了对class文件的解析,并得到了常量池和JVM的相关指令。
5.1 模拟JVM指令的运行
模拟JVM的运行,需要有两个个方面的知识准备
- JVM的结构
- 字节码的含义
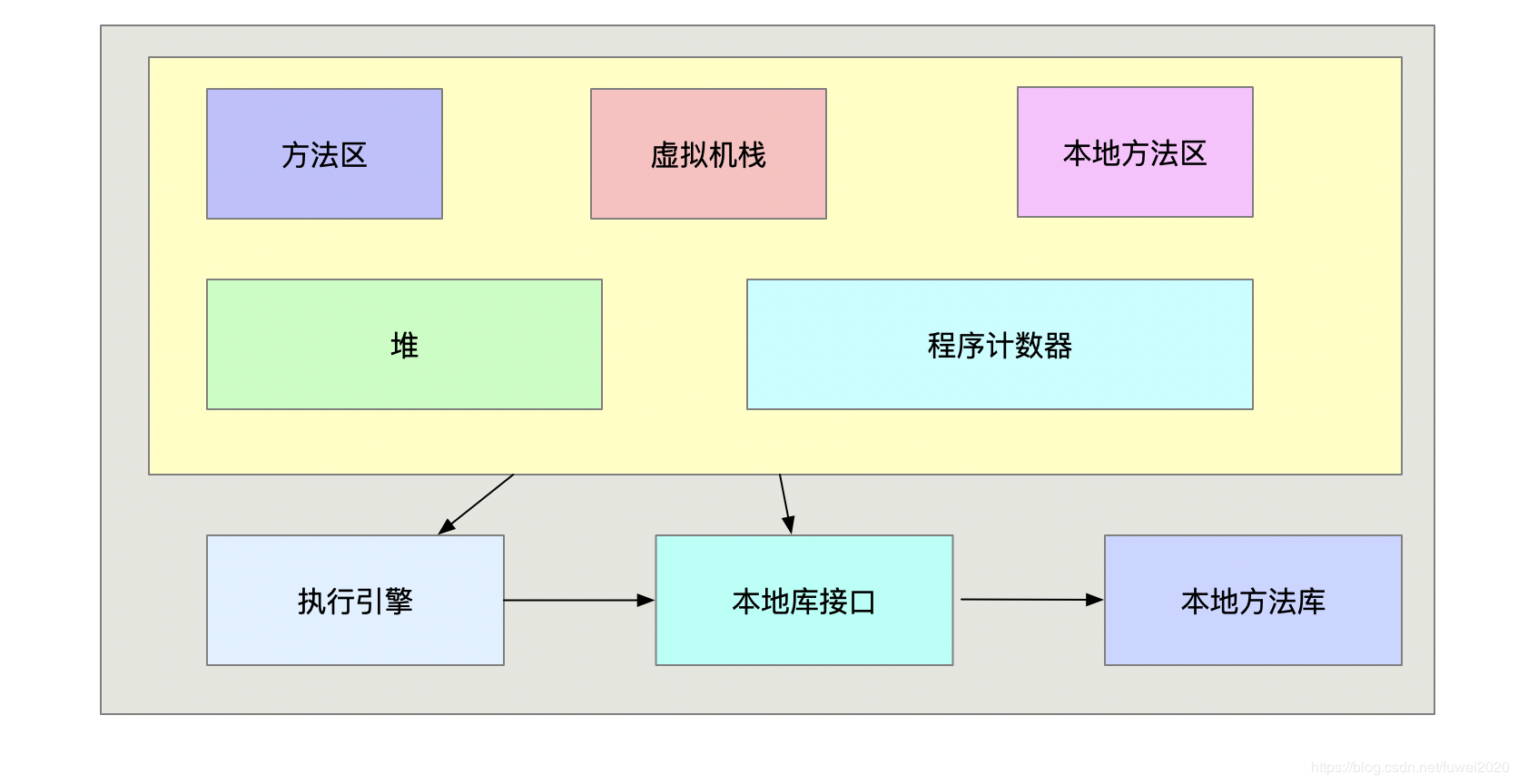
5.1.1 JVM的结构
对于JVM的结构,在很多地方都有描述,此处不再赘述,具体结构如下:
5.1.2 方法区
重点说下方法区,方法区有两个实现
- 永久代(1.7以前),永久代分配到堆上
- 元空间(1.8),元空间在直接内存上面(分配的快,回收的慢,元空间加载后不会被回收)
我们上面说的class加载后的内存都在当前这个内存中。
5.1.3 虚拟机栈
虚拟机栈是栈帧的集合的统称,栈帧是虚拟机执行时方法调用和方法执行时的数据结构,它是虚拟栈数据区的组成元素,每一个方法对应了一个栈帧。
栈帧的组成分为4个部分: 局部变量表,操作数栈,动态链接和返回地址。
- 局部变量表 方法内部的变量列表,第一个是当前类的指针
- 操作数栈 是变量操作的临时存储空间,通过入栈和出栈来操作数据
- 动态链接 java的运行过程不存在link的过程,所以在一个类中调用另外一个类的方法时候,需要动态寻找的类的地址。
- 返回地址 当前方法返回的地址。
5.1.4 堆
堆是是存放引用变量真实内存的地方,可以理解成JVM的后方"仓库",负责存储和获取真实内存的地方。
5.2. 类的转换过程
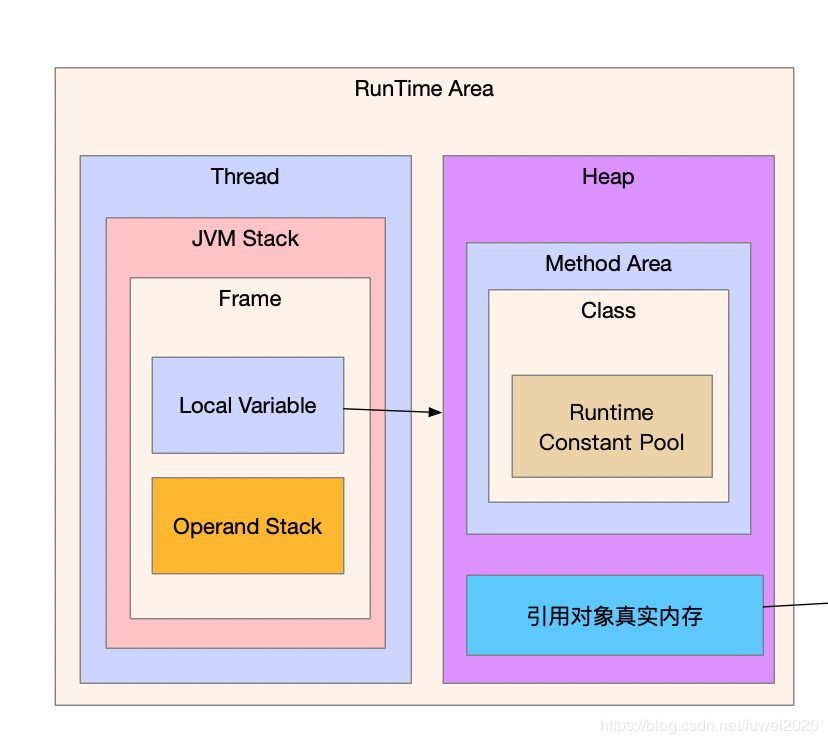
从上面的分析可以得到一个变量的转换过程:
Java class文件 --> 类解析产生常量池 --> JVM指令转为局部变量表和操作数栈。
通过上面的分析,可以简单的把运行时数据去归纳成如下方式:
5.2.1 字节码含义
JVM的指令对应的操作,可以查看JVM的指令表,或者查看笔者的这篇文章:JVM指令的速记
这里我仅列出当前所使用的的指令的含义:
| 指令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| iconst_1 | 将int型1推送至栈顶 |
| istore_1 | 将栈顶int型数值存入第二个本地变量 |
| iconst_2 | 将int型2推送至栈顶 |
| istore_2 | 将栈顶int型数值存入第三个本地变量 |
| iload_1 | 将第二个int型本地变量推送至栈顶 |
| iload_2 | 将第三个int型本地变量推送至栈顶 |
| iadd | 将栈顶两int型数值相加并将结果压入栈顶 |
| istore_3 | 将栈顶int型数值存入第四个本地变量 |
| getstatic | 获取指定类的静态域, 并将其压入栈顶 |
| iload_3 | 将第四个int型本地变量推送至栈顶 |
| invokevirtual | 调用实例方法 |
| return | 从当前方法返回void |
5.3 运行过程分析实战
根据我们上面的分析,我们尝试手工模拟下指令对于运行区数据的影响。
从上面的分析中,每一个方法都会创建一个栈帧。在栈帧中,定义一个长度为4的数组来表示局部变量表,用一个长度为2的栈表示操作数栈。
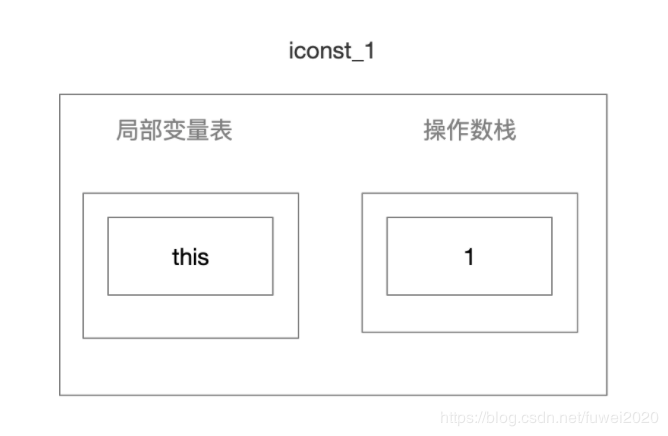
下面尝试分析下方法的执行步骤:
- iconst _1 将int型1推送至栈顶
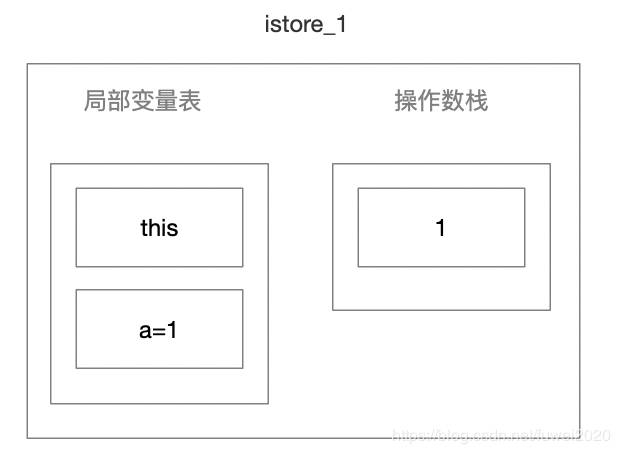
- istore_1 把栈顶的值赋给第二变量
- iconst_2 同
iconst_1
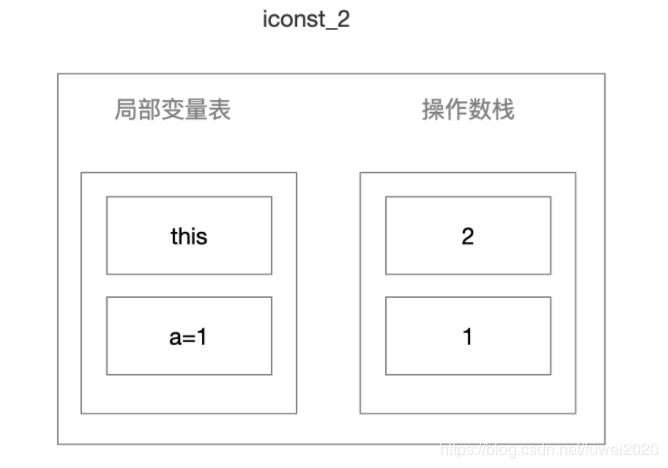
-
istore_2
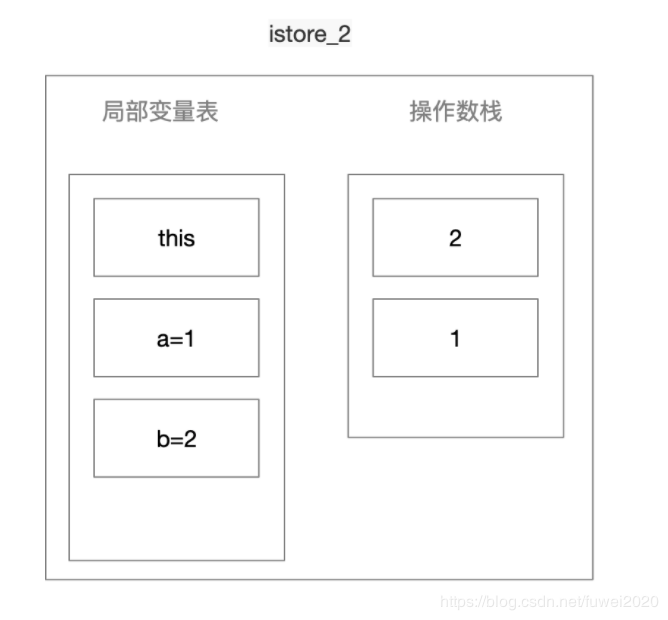
-
iload_1
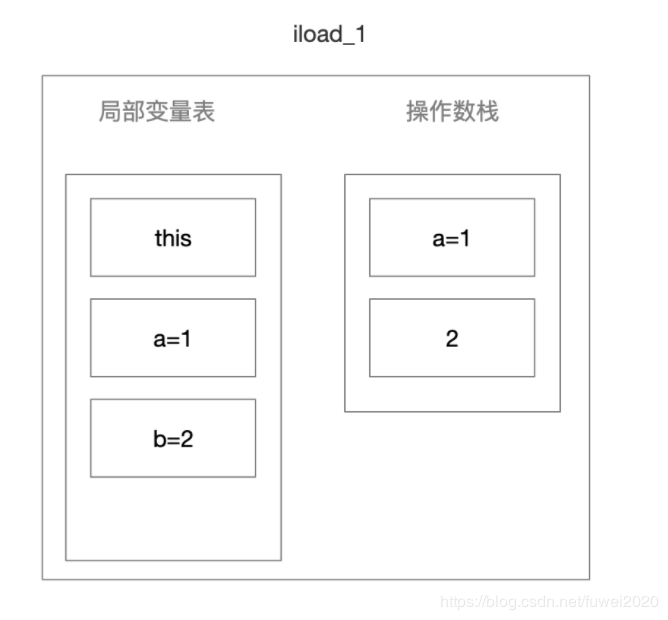
-
Iload_2
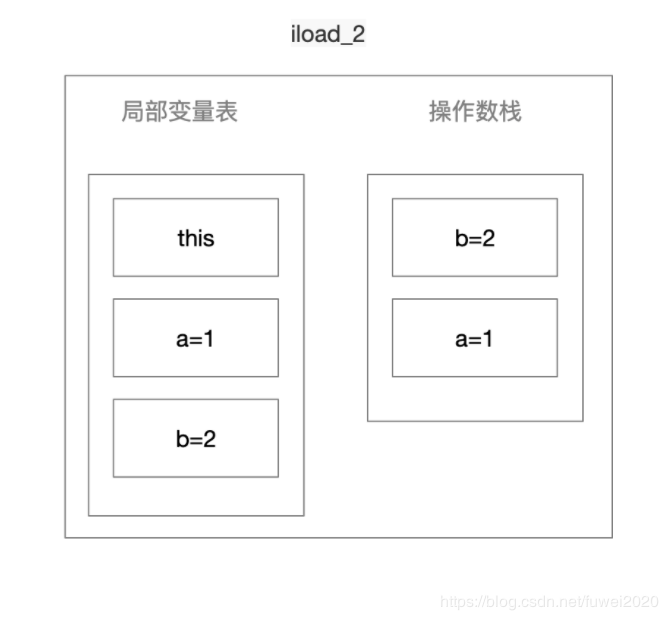
-
iadd 将栈顶两int型数值相加并将结果压入栈顶
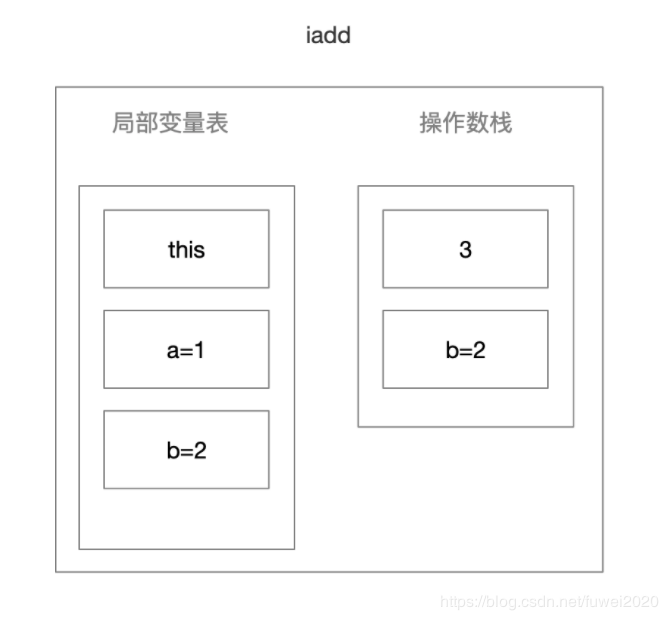
-
istore_3 将栈顶int型数值存入第四个本地变量
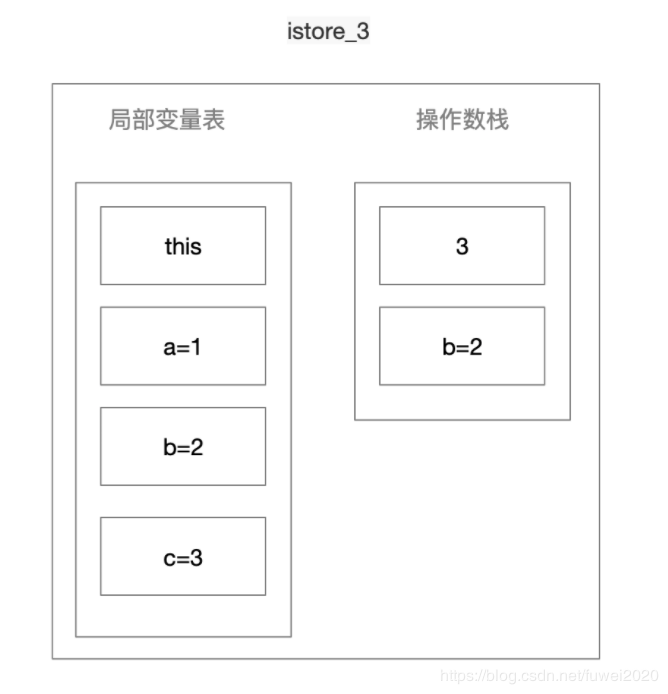
-
getstatic 获取指定类的静态域, 并将其压入栈顶
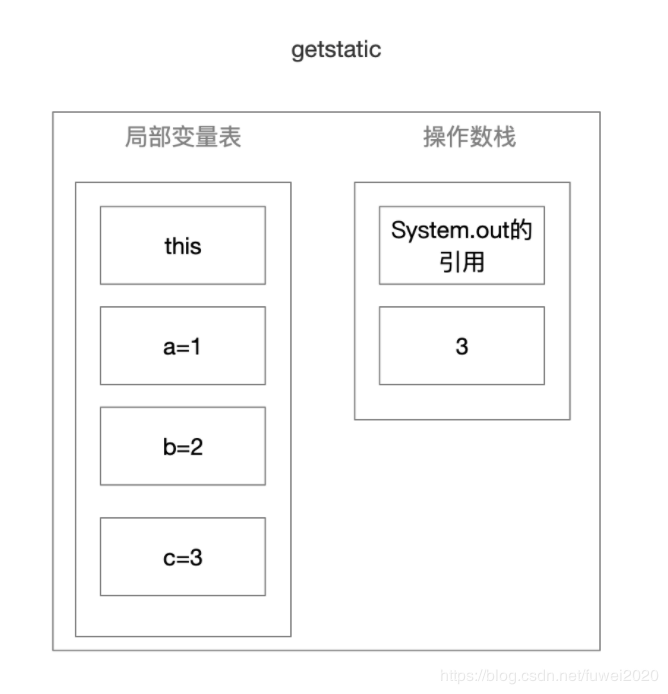
-
Iload_3
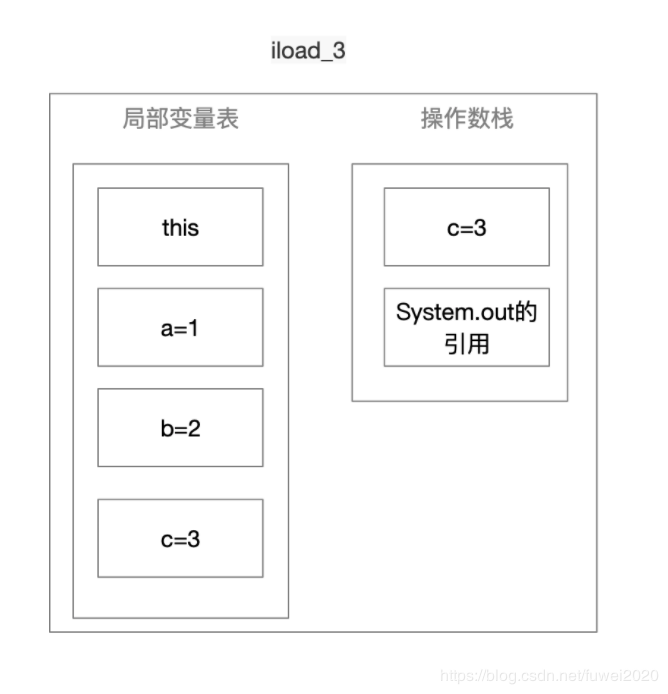
-
invokevirtual 调用实例方法
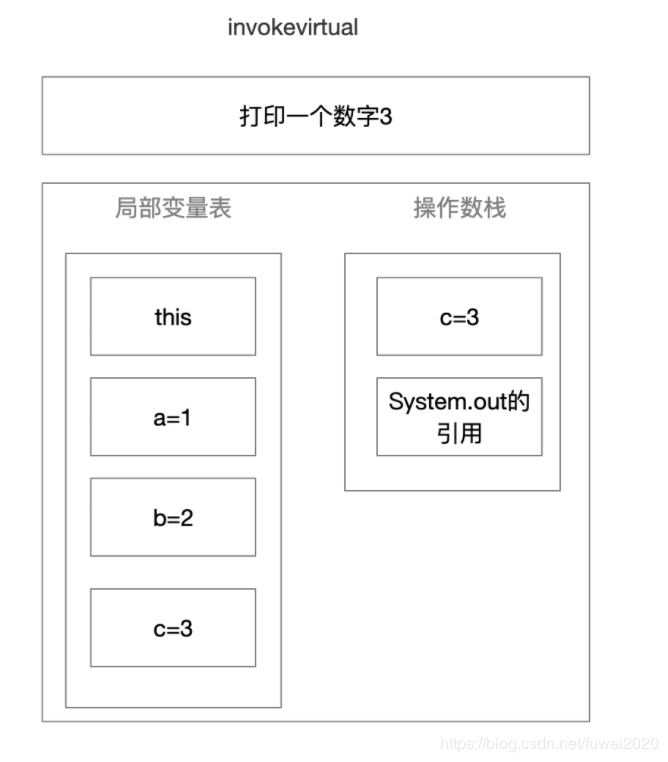
5.4 代码实现
-
找到main方法
static Method getMainMethod(ClassParseInfo classParseInfo){ Method[] methods = classParseInfo.methods; for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) { int name_index = methods[i].getName_index(); CONSTANT_Utf8_info utf8Constant = classParseInfo.constant_pool.getUtf8Constant(name_index); if(utf8Constant.getText().equalsIgnoreCase("main")){ return methods[i]; } } return null; } -
创建Frame
Frame 是代表栈帧,在创建方法的时候都需要创建一个栈帧。在Frame中,使用List表示本地变量表,Stack代表操作数栈。
public class Frame { private List<Slot> localVars; private Stack<Slot> operateStack; private int maxLocalVars; private int maxStack; public Frame(int maxLocalVars, int maxStack) { this.maxLocalVars = maxLocalVars; this.maxStack = maxStack; localVars = new ArrayList<>(maxLocalVars); operateStack = new Stack<>(); } public void setVars(int index,Slot slot) { this.localVars.add(slot); } public Slot getVar(int index) { return localVars.get(index - 1); } public void pushVar(Slot slot) { operateStack.push(slot); } public Slot pop() { if (this.operateStack.isEmpty()) return null; return this.operateStack.pop(); } } -
创建指令Instruction接口
在上面的分析过程中,每一个指令都会对
Frame进行操作,我们定义一个接口Instruction.public interface Instruction { void execute(Frame frame); } -
指令的实现
- Const指令的实现:
public class IConst implements Instruction { private int value; public IConst(int value) { this.value = value; } @Override public void execute(Frame frame) { pushValue(frame,value); } public void pushValue(Frame frame, int value) { frame.pushVar(new Slot(value)); } }
ILoad的实现
public class Load implements Instruction {
public Load(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
private final int index;
@Override
public void execute(Frame frame) {
Slot var = frame.getVar(index);
frame.pushVar(var);
}
}
Store指令实现:
public class Store implements Instruction {
final int index;
public Store(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
@Override
public void execute(Frame frame) {
setVar(frame,this.index);
}
public void setVar(Frame frame, int index) {
Slot pop = frame.pop();
frame.setVars(index, pop);
}
}
GetStatic和InvokeVirtual的mock:
为了降低代码的复杂度,我们对GetStatic和InvokVirtual方法进行Mock。
在GetStatic是获得一个静态变量入栈。在当前的代码中,静态变量就是`System.out。在GetStatic实现的时候,我们直接采用System.out的静态变量入栈。
public class GetStatic implements Instruction {
@Override
public void execute(Frame frame) {
frame.pushVar(new Slot(System.out));
}
}
在InvokeVirtual的方法中,直接转换成对应的方法调用:
public class InvokeVirtual implements Instruction {
//mock
@Override
public void execute(Frame frame) {
Slot pop = frame.pop();
Slot out = frame.pop();
PrintStream sysOut = (PrintStream) out.getRef();
sysOut.println(pop.getValue());
}
}
- InstructionFactory 工厂实现
public class InstructionFactory {
public static Instruction getInstruction(Opcode opcode, Object... obj) {
switch (opcode) {
case iconst_1:
return new IConst(1);
case iconst_2:
return new IConst(2);
case iload_1:
return new Load(1);
case iload_2:
return new Load(2);
case iload_3:
return new Load(3);
case istore_1:
return new Store(1);
case istore_2:
return new Store(2);
case istore_3:
return new Store(3);
case iadd:
return new Add();
case _return:
return new Return();
case getstatic:
return new GetStatic();
case invokevirtual:
return new InvokeVirtual();
default: {
System.out.println(opcode + "未实现");
return null;
}
}
}
}
-
主方法实现:
Code_attribute code = (Code_attribute) Arrays.stream(mainMethod.getAttributes()).filter(x -> x.tagName.equalsIgnoreCase("code")).findFirst().orElse(null); Frame frame = new Frame(code.getMax_locals(), code.getMax_stack()); byte[] paraCodeArr = code.getParaCode(); for (Opcode op : code.getOpcodeArr()) { if (op == null) continue; byte[] bytes = new byte[0]; if (op.operandCount > 0) { bytes = Arrays.copyOf(paraCodeArr, op.operandCount); paraCodeArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(paraCodeArr, op.operandCount - 1, paraCodeArr.length - 1); } Instruction instruction = InstructionFactory.getInstruction(op); instruction.execute(frame); }
最终执行结果:3